
If you’ve ever experienced issues with web pages not loading properly, slow connections, or strange DNS-related errors in Chrome, you might have come across references to chrome //net-internals/#dns. This powerful internal tool helps diagnose and fix Domain Name System (DNS) issues that affect how Chrome connects to websites. In this article, we'll explain what this page is, how it works, and why it’s useful for troubleshooting and improving your browser's performance.
What is chrome.//net-internals/dns?
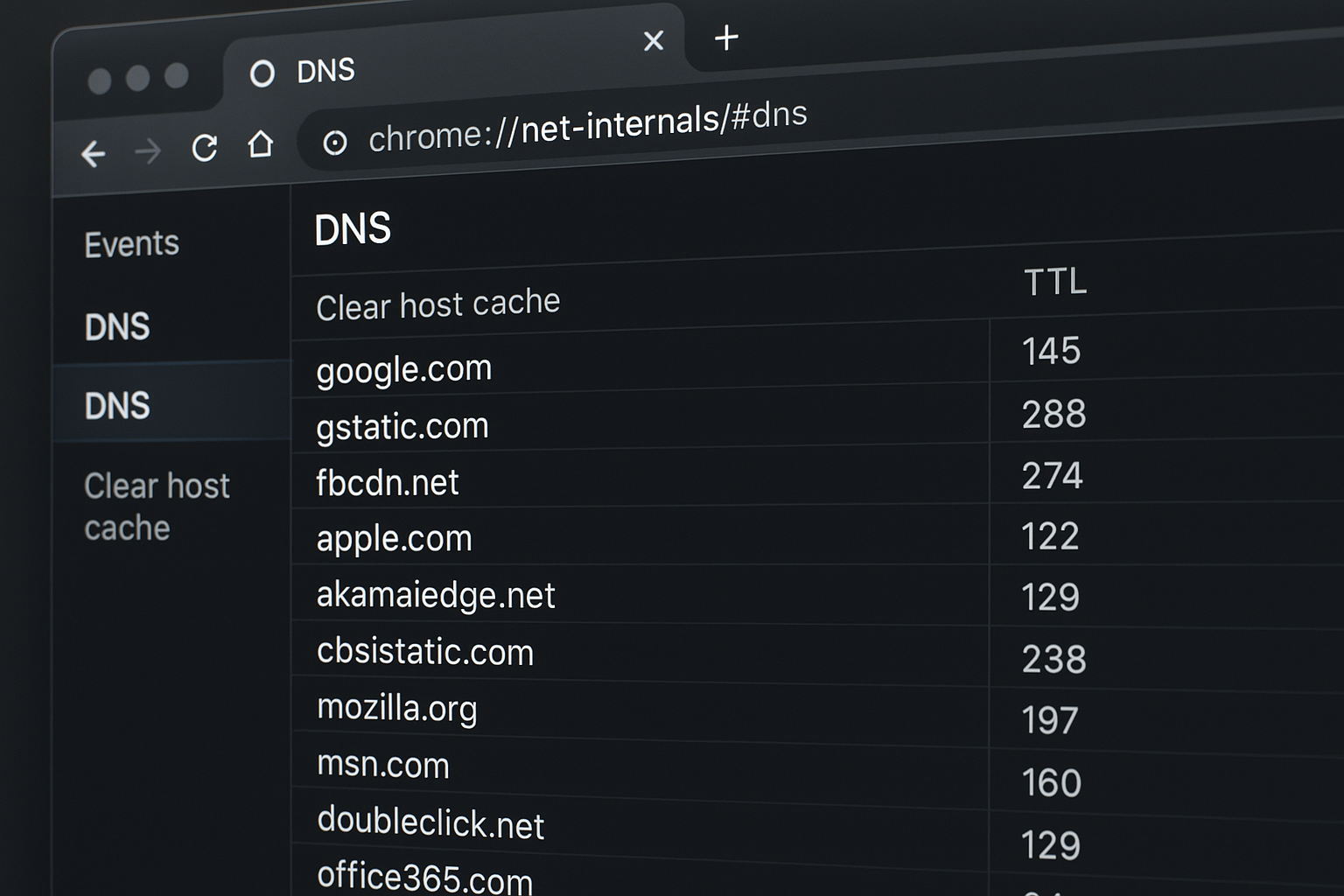
chrome //net-internals/#dns is a built-in diagnostic page in Google Chrome that provides detailed information about Chrome’s DNS behavior. It is primarily used to view, clear, and troubleshoot Chrome’s DNS cache, which stores information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses to speed up future access.
While most users are unaware of it, this page is a powerful tool for developers, network administrators, and advanced users who want to manage how Chrome handles DNS resolutions.
It allows you to:
◾ View Chrome’s DNS cache
◾ Clear outdated DNS entries
◾ Diagnose hostname resolution issues
Fix DNS errors instantly
Follow the steps below:
Open a new window or tab in Chrome.
Enter the following URL exactly:
chrome://net-internals/#dns
⚠️ Incorrect version users often type: chrome.//net-internals
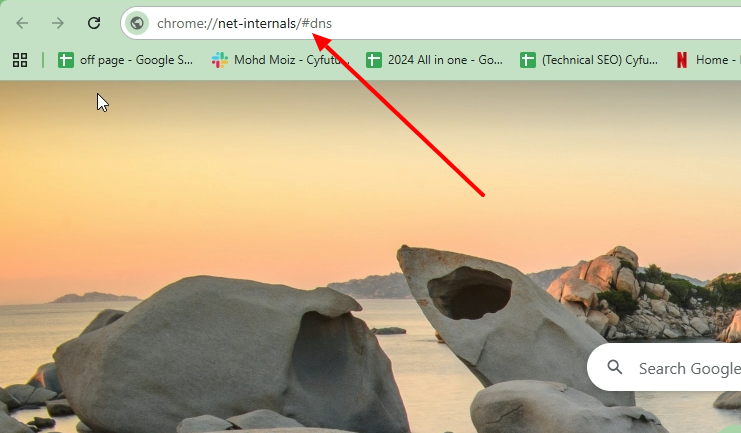
You should now see Chrome’s DNS dashboard.
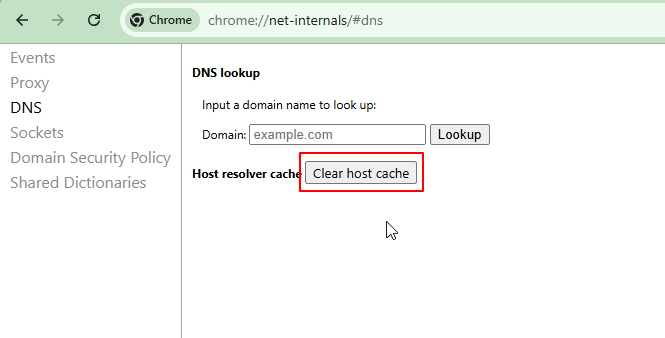
On the DNS page, locate the Clear host cache button.
Click the button once to flush Chrome’s DNS cache.
To apply the changes:
1. Close all Chrome windows
2. Reopen Chrome
3. Visit the website again
This page displays:
◾ Total DNS entries
◾ Secure vs. insecure DNS lookups
◾ Expiration times
◾ Hostnames and IP mapping
◾ Lookup failures
Clearing DNS cache resolves:
◾ DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN
◾ ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED
◾ DNS_PROBE_STARTED
◾ DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NO_INTERNET
◾ “Website not found” errors
◾ Chrome-only DNS failures
If clearing Chrome’s DNS cache isn’t enough, try the following:
Run:
ipconfig /flushdns
Use these public DNS services:
8.8.8.8
8.8.4.4
1.1.1.1
1.0.0.1
Network-level DNS issues are also common.
Go to:
Settings → Reset and Clean Up → Restore Settings
The chrome://net-internals/#dns tool is one of Chrome’s most effective troubleshooting utilities for fixing DNS errors. Clearing the DNS cache refreshes domain mappings and instantly resolves many connection issues.
This step-by-step guide—with screenshot placeholders—helps users visually understand the process and fix DNS issues confidently.
The chrome://net-internals/#dns tool is a powerful feature that allows you to clear the DNS cache on your mobile device, whether you're using Chrome on Android, iPhone, or iPad.
Now, you might be wondering: how can you clear the host cache in Chrome's net-internals DNS on mobile? The solution is simple and straightforward.
To clear the host cache on Chrome's net-internals DNS page, simply follow the same steps as mentioned earlier. Open the Chrome browser on any mobile device—be it Android, iPhone, or iPad—and navigate to chrome://net-internals/#dns to clear the host cache.
chrome://net-internals/#dns Mobile
chrome://net-internals/#sockets
If that doesn't work, try the following simple steps:
1) Open the Chrome app on your Android/iOS phone or tablet.
2) Tap the “More” button located at the top-right corner of the screen.
3) Select “History” from the list of options.
4)Choose a time range by tapping on the drop-down menu located at the top of the screen. To clear all browsing data, select “All time.”
5) Check the boxes next to “Cookies and site data” and “Cached images and files.”
6)Tap the “Clear data” button located at the bottom of the screen.
The chrome://net-internals/#dns tool may not always work or resolve DNS issues. If you encounter any problems, consider using the alternative DNS flushing methods outlined below.
1) Purge DNS cache using Command Prompt
2) By Restarting DNS Client Service
3) By Resetting Chrome Flags
If you're using Windows, macOS, or Chrome, you can quickly clear your DNS cache by following these easy steps.
Step 1: Go to your Start menu > Search “Command Prompt” > Right-click on it and select “Run as Administrator“.
Step 2: When the Command prompt window appears, type the given command below and press Enter.
Step 1: In your Mac open the Terminal application.
Step 2: Now type the given command below and hit the Return Key.
Step 3: Now enter your password and hit the Return Key.
Step 4: Now open your browser and attempt to access the website again. This will allow you to check whether or not the error has been resolved.
Option 1: Open up the Command Prompt window using key combinations of Windows Key+R
Once the terminal opens, type services.msc and press Enter to access the Local Services page. Locate the DNS Client service, right-click on it, and select Restart. This action refreshes the DNS cache, potentially resolving any errors.
Option 2: Alternatively, depending on your Windows OS version, you can use the Command Prompt to resolve the issue. Simply search for cmd in the Run dialog to open the Command Prompt. Then, enter the following commands to refresh the DNS cache:
Chrome Flags are experimental features in Google Chrome that are disabled by default but can be manually enabled for testing. However, activating certain Chrome Flags may sometimes trigger the DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN error.
To reset Chrome Flags to their default settings, follow these steps:
1) Open the Chrome browser on your device.
2) In the address bar, type chrome://flags and press Enter.
3) Locate the “Reset all to default” button at the top of the page and click on it.
4) A prompt will appear asking you to confirm the reset. Click on “Reset all” to confirm.
5) Once the reset is complete, you will be prompted to relaunch Chrome to apply the changes.
1. Enter “Terminal” into Spotlight
2. Go to the Terminal window and enter the following command:
Flushing the DNS cache on Linux can be done through the terminal using the “systemd-resolve” command. Here are the steps to follow:
1. Open a terminal on your Linux system.
2. Type the following command and press Enter
3. This command will flush both the negative and positive DNS cache entries.
4. To verify that the DNS cache has been cleared, type the following command and press Enter:
This command will display statistics of the resolved DNS queries. If the cache has been cleared, the count of “CacheHit” should be zero.
Here are some pros and cons of using the //net-internals/#dns feature in Chrome:
Pros:
- Clears the DNS cache in Chrome, helping resolve website loading and connectivity issues.
- Simple and quick process that can be done in just a few steps.
- Built directly into Chrome, eliminating the need for additional software.
Cons:
- Deleting the DNS cache removes stored domain name and IP address associations, temporarily slowing website loading times as the cache rebuilds.
- Designed for advanced users, it may be confusing for those unfamiliar with browser settings.
- Incorrect or improper use can lead to unintended issues or potential data loss.
If you're facing connectivity issues caused by outdated DNS records, clearing the host cache can help. For instance, if a website updates its IP address but your device retains the old one, it may lead to connection problems.
Clearing the host cache prompts your device to perform a fresh DNS lookup, ensuring it retrieves the updated IP address and establishes a successful connection to the website.
Entering chrome://net-internals/#dns in Chrome’s address bar takes you to a page where you can click "Clear host cache" to flush the DNS cache. The interface includes multiple tabs, offering various insights into DNS resolution data.
The DNS section of Chrome Net Internals provides critical insights into how DNS resolutions are handled within the browser. Key features include:
DNS Cache Overview: This feature displays the current state of the DNS cache, including resolved domains, associated IP addresses, and their respective TTL (Time to Live) values. By examining this cache, users can determine whether a domain is being resolved from stored data or if a fresh query is necessary.
DNS Resolution Statistics: This component offers valuable metrics regarding DNS lookup times, the success rate of resolutions, and the frequency of failures. By monitoring these statistics, users can identify patterns that may indicate performance issues with DNS queries.
Live Query Logging: chrome.//net-internals/dns allows for real-time logging of DNS queries, making it easier to trace specific requests and analyze resolution behavior. This feature is especially beneficial for troubleshooting connectivity issues related to particular domains.
While utilizing chrome.//net-internals/dns, users may encounter various DNS-related challenges, including:
Lookup Failures: Instances where Chrome is unable to resolve a domain name can lead to accessibility issues. By reviewing the DNS cache, users can ascertain if a domain is cached with incorrect information, necessitating a cache refresh.
Slow DNS Resolution: Prolonged DNS lookup times can hinder webpage loading speeds. Users can consult resolution statistics in chrome.//net-internals/dns to determine if certain DNS servers are causing delays.
Stale Cache Entries: Over time, cached DNS entries may become outdated, resulting in incorrect resolutions. Flushing the DNS cache can remedy these issues and prompt new queries.
To effectively troubleshoot DNS issues using chrome.//net-internals/dns, consider the following steps:
Examine the DNS Cache: Navigate to the DNS section and inspect the current cache entries. If you notice incorrect mappings, flushing the cache may be necessary.
Flush the DNS Cache: To clear outdated entries, select the option to "Flush DNS Cache" within the DNS section. This action forces Chrome to discard existing data and perform new lookups.
Monitor Live Queries: Utilize the query logging feature to track DNS lookups in real-time. Observing these queries can help identify recurring issues or specific domains that are problematic.
Analyze Performance Metrics: Review DNS resolution statistics to identify any slow or failed queries. This information can be instrumental in selecting a more reliable DNS provider or optimizing network configurations.
To optimize your DNS management within Chrome, consider implementing the following best practices:
Use Reliable DNS Providers: Choose reputable and secure DNS service providers with high uptime and DDoS protection.
Enable Redundancy and Failover: Configure secondary DNS servers to ensure availability in case the primary server fails.
Implement DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions): Protect against DNS spoofing and cache poisoning by signing DNS data.
Regularly Update and Patch DNS Software: Keep DNS servers updated to prevent vulnerabilities and security breaches.
Use Access Controls and Authentication: Limit administrative access to authorized personnel and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Monitor DNS Traffic: Detect anomalies, potential attacks, or misconfigurations by analyzing DNS query logs.
Configure TTL (Time to Live) Settings Wisely: Balance between performance and flexibility by setting appropriate TTL values for different records.
Implement Split DNS Configuration: Separate internal and external DNS zones to enhance security and restrict sensitive data exposure.
Backup DNS Records Regularly: Ensure quick recovery from accidental deletions or server failures.
Conduct Regular Audits and Testing: Review DNS records for accuracy, remove obsolete entries, and test for potential vulnerabilities.
Google Chrome provides several hidden tools for network diagnostics and troubleshooting — one of the most useful being chrome://net-internals/#dns, also known as Chrome Net Internals. This internal settings page helps users view, analyze, and clear DNS cache data directly from the browser.
When you open chrome.//net-internals/dns or chrome //net-internals/#dns, you can view detailed DNS resolution information, check cache status, and fix issues like slow loading or DNS lookup failures. If you want to perform a full refresh, simply click the “Clear host cache” button on the chrome //net-internals/#dns clear page.
For those who frequently troubleshoot network performance, exploring chrome://net-internals/ or chrome.//net-internals/ can reveal additional tools beyond DNS, including socket pools and proxy configuration options. You can even review chrome.//net-internals/dns history or chrome net internals guide dns history to understand how Chrome has handled previous DNS requests.
If you encounter issues accessing the tool, try entering variations like crome //net-internals/#dns, chorme //net-internals/#dns, or //net-internals/#dns — all redirect to the same internal diagnostic environment. Likewise, you can access it using www.chrome //net-internals/dns or open chrome net internals/#dns to jump straight into the DNS cache section.
Whether you’re on desktop or mobile using chrome.//net-internals/dns mobile, the net internals dashboard helps you monitor DNS activities and resolve connection problems efficiently. Advanced users can also access chrome net internals /# dns or simply chrome net internals to manage Chrome’s DNS system and network-level configurations with precision.
Overall, chrome://net-internals and net-internals/#dns remain invaluable tools for diagnosing, clearing, and monitoring Chrome’s DNS cache — ensuring faster, error-free browsing every time you visit your favorite sites.
Mastering chrome.//net-internals/dns is essential for developers and network professionals who wish to diagnose and resolve web connectivity issues efficiently. By leveraging the insights provided by this tool, users can gain a comprehensive understanding of DNS behavior within Chrome, allowing them to optimize their network performance effectively.
1. What is chrome net internals?
Chrome net internals is a built-in diagnostic tool in Google Chrome used to view and troubleshoot network activity, including DNS resolution, sockets, proxy settings, and more. You can access it by typing chrome://net-internals in the address bar.
The chrome net internals DNS page (chrome://net-internals/#dns) displays information about the browser’s internal DNS cache, including active hostnames and their resolved IP addresses. It also provides options to clear the DNS cache.
1. Open Chrome and type chrome://net-internals/#dns in the address bar.
2. Click the "Clear host cache" button.
This flushes the internal DNS cache stored by Chrome.
4. Why would I use chrome net internals DNS to clear the DNS cache?
Clearing the DNS cache using chrome net internals DNS helps resolve issues like site loading problems, outdated DNS records, or network configuration changes. It forces Chrome to re-fetch DNS data from the server.
No. Chrome net internals DNS only clears the browser-level DNS cache. To fully flush DNS, you may also need to clear the operating system’s DNS cache separately (e.g., using ipconfig /flushdns on Windows).
If websites are not loading correctly or showing old information on your phone, clearing the DNS cache in Chrome mobile can help. The DNS cache stores website data to make browsing faster, but sometimes it needs to be refreshed.
To clear DNS cache in Chrome mobile, follow these steps:
1. Open the Chrome app on your Android or iPhone.
2. In the address bar, type chrome://net-internals/#dns and press enter.
3. You will see a page with DNS information.
4. Tap on the option “Clear Host Cache” to delete the stored DNS records.
That’s it! Now your browser will fetch fresh DNS information, which can fix loading problems and improve browsing speed.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!