 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


Effective internet navigation is crucial in today’s fast-paced digital world. At the core of this efficiency lies DNS (Domain Name System) caching, which plays a major role in how quickly and reliably we can access websites and applications. But is DNS caching always beneficial? Let’s explore its features, benefits, drawbacks, and best practices for managing it.
DNS caching refers to the temporary storage of DNS query results, which helps websites load faster and reduces unnecessary network requests. When you type a website URL into your browser, your computer must translate that domain into its corresponding IP address—the unique identifier of the web server. Normally, DNS servers handle this translation, but once a lookup is completed, the result is cached either on your device, at your ISP’s resolver, or at other points in the DNS chain. This cached information prevents repetitive queries and ensures quicker access the next time you visit the same site.
For users who want to view or manage their DNS cache manually, Chrome provides built-in tools. By entering chrome://net-internals/#dns into the address bar, you can see cached entries and clear them if needed. Similarly, navigating to chrome://net-internals gives access to Chrome’s broader network troubleshooting tools, making it easier to resolve browsing issues caused by stale or outdated DNS records.
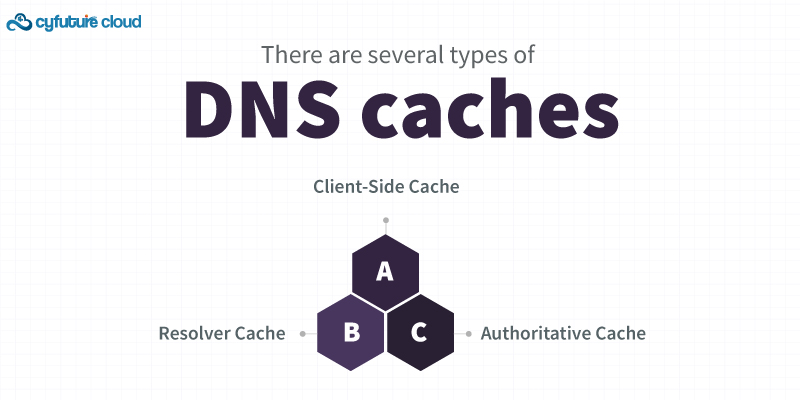
Client-Side Cache: This is kept on your local computer. Once the URL has been translated into an IP address, this information is cached locally on your device to speed up future requests to the same URL.
Resolver Cache: This is managed at the DNS resolver server level and contains records of recently queried domain names. It reduces the need for repeated lookups to the root or authoritative DNS servers.
Authoritative Cache: This cache is maintained by authoritative DNS servers that have direct knowledge of the domain names they serve. It contains records that are directly managed and updated by the domain’s owner.
If you ever want to view or clear your local DNS cache while troubleshooting, browsers like Chrome provide built-in tools. Using chrome://net-internals, users can view cached records and flush them when needed. Some also try chrome://net-internals, which offers broader debugging utilities within Chrome.
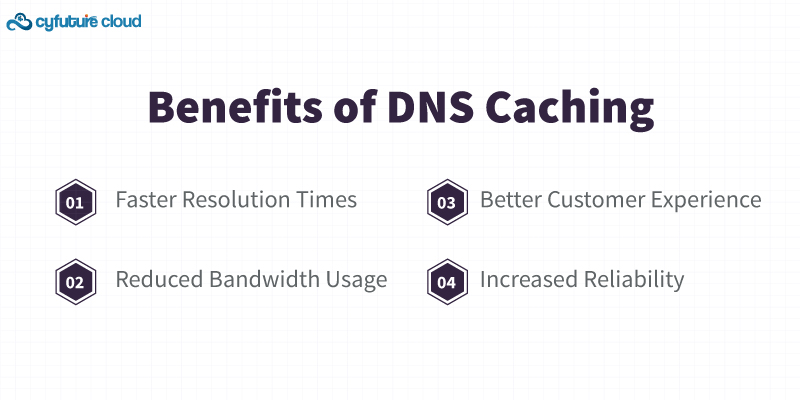
One of the most significant advantages of DNS caching is faster website access. When a URL is requested, if the IP address is already cached, the time to resolve the URL is reduced because the system doesn’t need to perform a full DNS lookup. This speed enhancement can be particularly noticeable with frequently visited sites. For instance, if you access a popular site like your favorite news portal, caching helps load the page almost instantly on subsequent visits.
DNS caching minimizes the number of queries sent to DNS servers. By storing DNS results locally or on intermediate servers, caching reduces the need to constantly query upstream DNS servers. This reduction in queries decreases bandwidth consumption and can lead to cost savings for both network operators and users. It also manages internet traffic and helps in managing internet traffic toward providing a smoother browsing experience.
Faster website access directly translates to a better user experience. When DNS queries are resolved quickly, websites load faster, which can improve user satisfaction and retention. This would translate into happier customers and possibly better engagement on the part of customers with the business online services. A resilient DNS system ensures that users experience delays at least to the smallest extent, which is very important to the continued competitive advantage in customer loyalty.
DNS caching can also enhance reliability. During periods of high traffic or server outages, cached DNS records can still provide access to websites. If a DNS server is down, the cached records on local devices or intermediate servers can prevent interruptions in service. This capability is especially valuable during unexpected network issues, ensuring that users can still access essential online services.

One downside of DNS caching is the potential for stale data.If the IP address of a website has changed but the caching does not refresh the cache in time, it may return errors such as 404 pages not found or show irrelevant content on the site. That is when TTL comes in, as this is what dictates how long the DNS record is refreshed to recalculate before returning the information. Good TTL settings will be able to keep balancing performance and cache freshness so that users will be getting their information fresh without impact on speed.
DNS caching can also pose security risks. One notable threat is DNS cache poisoning, where attackers insert malicious data into the cache. This could send users off to phishing sites or even steal sensitive information. Implementing security in the form of DNSSEC ensures that protection against such vulnerabilities, since data in DNS needs integrity and authenticity. However, the monitoring and updating of security protocols are always essential to protect from these risks.

DNS caching management helps to obtain the best advantages and reduce some of the disadvantages. Here are some best practices to consider:
Cache Regularly: Clear DNS caches periodically so that the stale data problem is avoided, and users will be accessing the latest information of the website.
Set Appropriate TTL Values: Configure TTL settings based on the type of record and its likelihood of change. Shorter TTLs for frequently changing records can help maintain cache accuracy.
Monitor and Update Security Protocols: Stay vigilant with security measures to protect against threats like cache poisoning. Regular updates and security checks can fortify your DNS infrastructure.
DNS caching is essential for delivering fast, reliable, and efficient access to websites. It reduces bandwidth usage, minimizes page load times, and builds resilience into web browsing. However, issues like stale data and security risks must be actively managed. By setting smart TTL values, monitoring cache freshness, and making use of tools like chorme //net-internals/#dns to flush or debug your DNS cache, you can maximize its benefits while reducing risks.
For expert guidance and customized solutions in DNS caching management, Cyfuture’s specialists can help you optimize your strategy for peak performance and security.
1. What is DNS caching and why is it important?
DNS caching is the temporary storage of DNS query results, allowing faster website loading and reduced network traffic. It prevents your computer from repeatedly querying DNS servers for the same domain.
2. How can I check my DNS cache in Chrome?
You can view or clear your DNS cache in Chrome by typing chrome://net-internals/#dns in the address bar. This shows cached entries and provides an option to flush them.
3. What is the difference between chrome://net-internals and chrome://net-internals/#dns?
chrome://net-internals/#dns specifically focuses on DNS cache information and flushing, while chrome://net-internals gives access to Chrome’s broader network diagnostic tools.
4. How often does DNS cache refresh?
The refresh rate depends on the TTL (Time-to-Live) settings of the DNS record. Shorter TTLs mean more frequent updates, while longer TTLs keep records cached for a longer duration.
5. Can DNS caching cause problems?
Yes. If cached entries become outdated (stale data), you may face errors like old IP addresses, misdirected URLs, or website loading failures.
6. How do I flush DNS cache on Chrome?
Go to chrome://net-internals/#dns and click “Clear host cache.” This resets stored records and can fix access issues caused by outdated entries.
7. Is DNS caching safe?
DNS caching is generally safe, but it can be vulnerable to attacks such as DNS cache poisoning. Using DNSSEC and clearing caches periodically helps mitigate risks.
8. Will clearing my DNS cache affect browsing speed?
Clearing the DNS cache may temporarily slow down website resolution for the first visit since the system needs to fetch fresh records. However, it improves accuracy by removing outdated entries.
9. Is DNS caching handled only by browsers like Chrome?
No. DNS caching works at multiple levels—your device (client-side cache), DNS resolver servers, and authoritative DNS servers. Browsers like Chrome just give you a way to view and manage local caches.
10. Do I need to clear DNS cache regularly?
It’s not always necessary, but clearing the cache helps if you’re facing issues like websites not loading properly, redirected links, or outdated content. Tools like chrome://net-internals/#dns make this process simple.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


