 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

In today's digital age, businesses of all sizes depend on a strong IT infrastructure to sustain their daily operations. Managing and maintaining this infrastructure can be daunting. This is where server colocation becomes crucial. But what is server colocation exactly, and how can it boost your business operations? This blog will explore server colocation services, highlight their benefits, and help you evaluate whether they fit your IT needs. We'll also discuss tools like a colocation pricing calculator to assist in making informed decisions.
At its core, server colocation is a service provided by data centers or hosting companies, where you can rent physical space to house your servers and IT equipment. Instead of hosting your equipment on-site, you place it in a professional data center. Your servers share a common physical space with those of other businesses, but each client's equipment remains distinctly segregated. Here's a closer look at the key aspects of server colocation:

1. Physical Space Rental: Server colocation involves renting rack space within a data center. Depending on your requirements, this space can vary from a single rack unit to an entire private suite.
2. Robust Security: Data centres have cutting-edge security systems in place, such as biometric access control, surveillance cameras, and on-site security officers. This safeguards your equipment from unauthorised access and physical threats.
3. High-Speed Connectivity: Colocation facilities offer high-speed, redundant internet connectivity through multiple internet service providers (ISPs). This connectivity is vital for maintaining uptime and fast data transfer.
4. Power and Cooling: Data centers have backup power generators and cooling systems to prevent service disruptions. These facilities are designed to ensure uninterrupted server operation, even during power outages.
5. Redundancy: Redundancy is a fundamental design principle in data centers. This includes backup power, internet connectivity, and cooling systems. Redundancy minimizes the risk of downtime due to technical issues.
6. Cost-Effective: Server colocation can be a cost-effective alternative to building and maintaining an in-house data center. Rather than investing in data center infrastructure, organizations pay only for the space, power, and cooling they use.
7. Remote Management: Organizations can remotely manage their colocated servers securely. This eliminates the need for on-site maintenance and allows for easy scalability.
8. Compliance and Standards: Many colocation facilities provide environments that adhere to various industry compliance standards, simplifying regulatory compliance for businesses.
9. Disaster Recovery: Colocation can be a crucial component of a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy. In the event of a disaster at the primary location, data and services can be quickly restored from backup systems in the colocation facility.
10. Technical Support: Some colocation providers offer technical support and services, including hardware replacement and troubleshooting assistance.
11. Predictable Costs: Colocation services often come with fixed monthly costs, providing cost predictability for businesses.
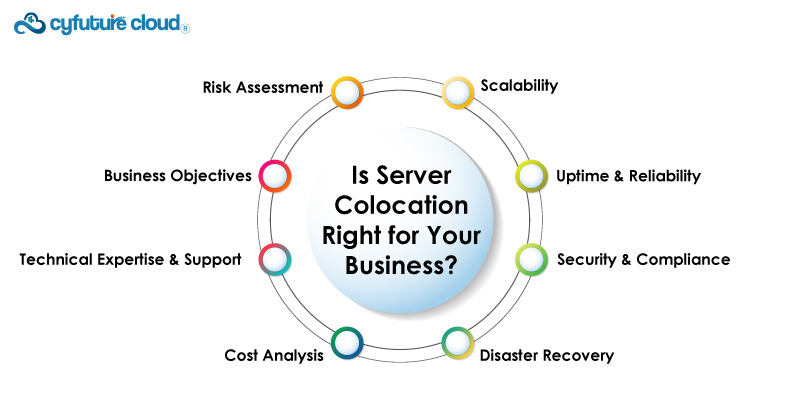
Determining whether server colocation is right for your business is a crucial decision that involves considering various factors. Below, we'll explore in detail the key considerations to help you evaluate if server colocation aligns with your business needs and objectives.
Server colocation is an excellent option for businesses that require scalability and flexibility. If your IT infrastructure needs are expected to grow or fluctuate over time, colocation provides a solution that allows you to easily add or remove servers as necessary. This scalability is particularly valuable for businesses that experience periodic surges in data and processing requirements.
Colocation facilities are designed with a focus on reliability and uptime. They offer redundant power sources, backup generators, multiple internet connections, and advanced cooling systems. These measures reduce the possibility of downtime due to power failures, technical difficulties, or network disruptions. If your company depends on continuous access to data and applications, particularly mission-critical systems, server colocation can provide a high level of reliability.
Many businesses operate in industries with stringent security and compliance regulations, such as healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), or government (FISMA). Colocation facilities often provide environments that adhere to these standards, with robust security measures, controlled access, and stringent data protection protocols. If your industry requires adherence to specific compliance standards, server colocation can simplify the process of maintaining regulatory compliance.
A well-planned disaster recovery strategy is vital for business continuity. Server colocation can be an essential part of this strategy. By colocating your servers in a separate geographic location from your primary site, you create a backup that can quickly be activated in the event of a disaster at your main location. This ensures the continuity of your data and services.
The decision to opt for server colocation should be based on a thorough cost analysis. Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for in-house infrastructure, including server hardware, cooling systems, power supply, staffing, and facility maintenance. Then, compare this to the costs associated with server colocation. While colocation comes with a monthly fee, it typically eliminates significant upfront capital expenses and reduces ongoing operational costs. Consider the long-term financial benefits and predictability of colocation services.
Evaluate your in-house technical expertise and the level of support you require. While colocation facilities offer robust security and infrastructure, you are still responsible for managing and maintaining your servers. Some colocation providers offer technical support and services, including hardware replacement and troubleshooting assistance. If your team lacks the necessary technical skills, these services can be invaluable.
Consider your business's long-term objectives and how server colocation aligns with these goals. If growth, reliability, and data security are central to your strategic plan, colocation may be the ideal solution. It allows you to focus on your core business operations while entrusting your IT infrastructure to experts dedicated to its seamless operation.
Conduct a risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities and potential disruptions to your in-house IT infrastructure. Consider factors like natural disasters, power outages, and equipment failures. Server colocation minimizes many of these risks by placing your servers in professionally managed, resilient facilities.
What is server colocation? In essence, it offers a range of advantages, including enhanced security, redundancy, connectivity, and cost efficiency. To determine if it suits your business, evaluate your specific IT requirements, budget, and long-term objectives. By opting for server colocation services, companies can concentrate on their main operations, entrusting their IT infrastructure to experts who ensure seamless performance. For a detailed financial assessment, consider using a colocation pricing calculator to compare costs and make an informed decision.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


