 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


Have you ever faced a situation where a website refuses to load on Google Chrome, even though it works fine on other browsers? This frustrating issue can stem from DNS (Domain Name System) problems, cached network data, or server-side issues. When such problems occur, it can disrupt work, online transactions, or access to cloud-based services.
Fortunately, Chrome provides a built-in tool called chrome.//net-internals/dns that helps diagnose and resolve these issues. This tool allows users to inspect DNS queries, clear cached records, and troubleshoot connectivity problems. Whether you're managing a hosting environment, running a cloud-based application, or simply browsing, understanding how to use chrome.//net-internals/dns can help restore website accessibility.
This guide will walk you through common website loading issues, how Chrome’s DNS tools work, and the necessary steps to fix them. Follow along to get your browsing back on track efficiently.
Google Chrome offers a hidden diagnostic tool called chrome.//net-internals/dns, which provides insights into network activity, including DNS resolutions. The DNS (Domain Name System) translates website URLs into IP addresses, allowing browsers to connect to the correct servers. However, cached DNS records or outdated entries can sometimes cause website loading issues.
By accessing Chrome Net Internals, users can:
View detailed DNS resolutions
Identify failed DNS queries
Clear DNS cache to resolve loading issues
Analyze network-related problems affecting website access
Understanding how to use this tool can significantly help troubleshoot browsing problems, especially for those managing cloud services, hosting solutions, or online applications.
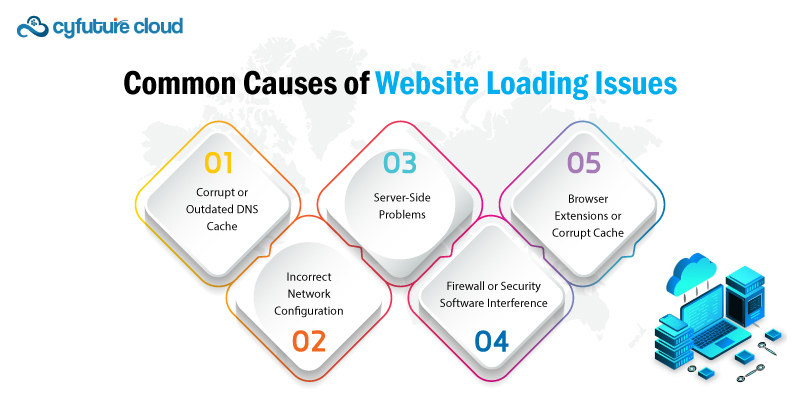
Before diving into the solutions, it's important to understand the common reasons websites fail to load in Chrome:
Corrupt or Outdated DNS Cache – When Chrome stores outdated DNS entries, it may prevent access to updated server locations.
Incorrect Network Configuration – Issues with local network settings or the ISP's DNS servers can impact browsing.
Server-Side Problems – The website's hosting server may be down or experiencing connectivity issues.
Firewall or Security Software Interference – Overprotective security software can block access to certain websites.
Browser Extensions or Corrupt Cache – Some extensions or cached files can interfere with website loading.
Now, let’s explore how chrome.//net-internals/dns can help resolve these issues.

To begin diagnosing DNS-related issues in Chrome, follow these steps:
Open Google Chrome.
In the address bar, type chrome://net-internals/#dns and press Enter.
This will take you to Chrome’s DNS debugging page.
Here, you will see a list of cached DNS entries along with timestamps and resolutions. If a website is failing to load, an incorrect or outdated DNS entry might be the cause.
A quick way to resolve website loading issues is by clearing the DNS cache.
On the chrome.//net-internals/dns page, locate the "Clear host cache" button.
Click on it to remove all stored DNS entries.
Close and reopen Chrome, then try accessing the website again.
Clearing the DNS cache forces Chrome to retrieve fresh DNS records, which can resolve issues caused by outdated or incorrect entries.
In addition to clearing the DNS cache, flushing socket pools can help reset network connections.
Go to chrome://net-internals/#sockets
Click "Flush socket pools"
Restart Chrome and check if the website loads correctly.
This step ensures that any lingering connections causing website loading issues are terminated and refreshed.
If the issue persists, consider changing your DNS settings to a more reliable server, such as Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1).
Open Control Panel → Network and Internet → Network and Sharing Center.
Click on Change adapter settings (left sidebar).
Right-click your active internet connection and select Properties.
Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Choose Use the following DNS server addresses and enter:
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8
Alternate DNS server: 8.8.4.4
Click OK and restart your internet connection.
After making these changes, try accessing the problematic website again.
If you're managing a website hosted on a cloud platform, ensure that your server is operational. Many hosting providers offer server status dashboards where you can check for outages or maintenance updates.
If the site is down globally, you may need to restart the hosting server or troubleshoot configurations.
Ensure your SSL certificate is valid, as expired certificates can prevent Chrome from loading sites.
If using a CDN (Content Delivery Network) like Cloudflare, check for DNS propagation delays.
Website loading issues in Chrome can be frustrating, but chrome.//net-internals/dns provides a powerful tool to diagnose and resolve them. By clearing the DNS cache, flushing socket pools, changing DNS settings, and checking hosting servers, you can effectively troubleshoot most browsing problems.
For those managing cloud-hosted websites, ensuring proper server configurations and DNS settings is crucial for seamless access. If issues persist despite these fixes, consider reaching out to your hosting provider or IT support team.
By leveraging Chrome's built-in DNS tools, you can maintain smooth and uninterrupted browsing, ensuring a better user experience whether you're a casual user or managing a cloud infrastructure.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


