 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


Businesses and individuals are increasingly depending on strong computer resources to carry out complicated tasks in today's technologically advanced environment. Due to their capacity for handling severe parallel processing, graphics processing units (GPUs) have greatly increased in popularity. This makes them indispensable for a variety of applications, from deep learning to scientific simulations. On the other side, cloud computing offers scalable and adaptable computer resources online. When GPUs are integrated into cloud servers, it gives rise to GPU cloud servers. This guide aims to delve into the working mechanism of GPU cloud servers, detailing their components, benefits, and applications.
1. Understanding GPU Cloud Hosting
Understanding GPU Cloud Server requires an understanding of how cloud computing and graphics processing units (GPUs) work together. A GPU cloud server combines the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs with the scalability and flexibility of cloud services at its heart. Physically, it upgrades processing capability by integrating specialist GPU hardware into the cloud infrastructure. The virtualization layer enables effective GPU resource allocation, guaranteeing that numerous users may utilize a single GPU concurrently. The hypervisor and APIs are important elements that enable smooth task execution and interaction. In the end, GPU cloud servers enable a variety of applications, from machine learning to scientific simulations, by offering quick, affordable, and scalable access to significant GPU processing capacity.
2. Components of a GPU Cloud Server
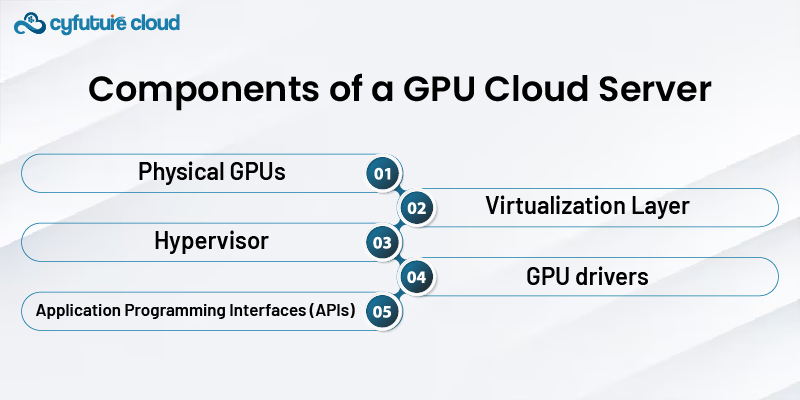
2.1. Physical GPUs:
The actual GPU hardware serves as the basis of a GPU cloud server. Modern GPUs are built with highly specialized cores that can effectively complete tasks in parallel. The actual GPUs placed in the cloud server hosting hardware offer the processing power required for a variety of applications.
2.2. Virtualization Layer
The virtualization layer lies above the actual GPUs and allows the GPU's resources to be split up into several virtualized instances. With the help of virtualization, several users may access and use the same physical GPU at the same time without interfering with one another's operations.
2.3. Hypervisor
A crucial element in charge of administering and regulating the virtualization layer is the hypervisor. It distributes GPU resources to several virtual instances in order to ensure equitable utilization and avoid resource conflicts. VMware, Xen, and Microsoft Hyper-V are a few of the well-known hypervisors.
2.4. GPU drivers
GPU drivers are software elements that allow the operating system and the GPU hardware to communicate. They are essential in making sure that the virtualized GPUs get the right instructions to effectively use the actual GPU.
2.5. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs serve as a bridge between software programs and GPU hardware. For NVIDIA GPUs and AMD GPUs, respectively, CUDA and ROCm are popular APIs used in GPU cloud servers. These APIs are used by programmers to take use of the GPU's processing capabilities for their unique applications.
3. How GPU Cloud Hosting Work
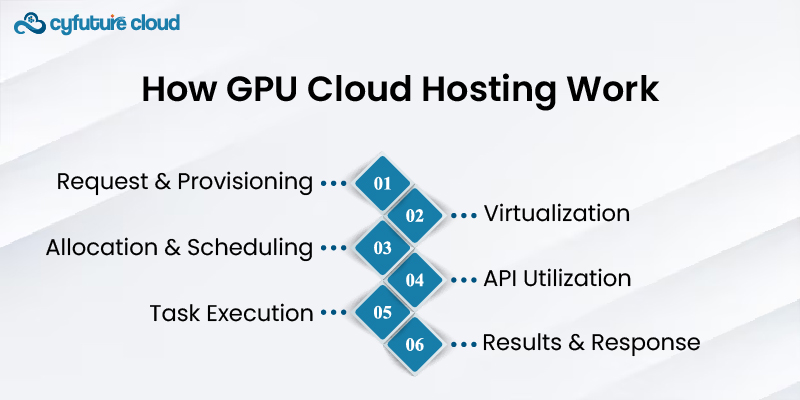
3.1. Request and Provisioning
Through the cloud service provider, users submit a request to obtain GPU resources. Following that, the supplier assigns the necessary GPU resources depending on the user's specs and needs, providing the best possible hardware compatibility.
3.2. Virtualization
After accepting the request, the hypervisor configures the virtualization layer. The physical GPU is used to produce virtual GPU instances, with each virtual instance receiving a share of the physical GPU's resources. Multiple people can utilize the same physical GPU at once thanks to this procedure.
3.3. Allocation and Scheduling
Based on specified policies or resource availability, the hypervisor distributes virtual GPUs to various users or applications. Additionally, it controls scheduling to guarantee equitable use of the GPU as a Service resources.
3.4. API Utilization
Users interact with the virtual GPUs by sending instructions and tasks to the virtualized GPU using APIs like CUDA or ROCm. These orders are converted by the APIs into instructions that the actual GPU hardware can carry out.
3.5. Task Execution
The GPU effectively handles the burden by running tasks concurrently across its specialized cores. To avoid conflicts and guarantee maximum performance, the virtualization layer controls and keeps track of these operations.
3.6. Results and Response
The GPU produces the results after completing the tasks given to it, which are then transmitted to the user or application via the virtualization layer. Users can obtain these results and, depending on their needs, further analyze or use them.
4. Applications of GPU Cloud Hosting

4.1. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are two of the most popular fields in which GPU cloud servers are used. GPUs are excellent at parallel computing, which makes them perfect for deep learning model training. Natural language processing, image and audio recognition, and recommendation systems all significantly rely on the enormous computing capacity that GPUs provide. Cloud-based GPU resources speed up model training, facilitating faster AI solution deployment and testing.
4.2. Scientific Research and Simulations
GPU cloud servers are now essential for conducting complex simulations and computations in the field of science. For simulations, molecular modeling, climate forecasts, and other tasks, fields including physics, chemistry, biology, and astronomy use graphics processing units (GPUs). Researchers can handle enormous volumes of data and conduct simulations more quickly because of the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs, which has helped them make strides in a variety of scientific fields.
4.3. Data analytics and big data processing
In the age of big data, it is essential to analyze and process massive datasets. Data analytics are considerably accelerated by GPU cloud servers by parallelizing data processing operations. Data mining, pattern recognition, and real-time analytics algorithms can quickly analyze and extract insights from enormous volumes of data. This is especially important for sectors that depend heavily on data-driven decisions, like banking, healthcare, ecommerce, and marketing.
4.4. 3D Rendering and Animation
Industries related to entertainment, design, and architecture heavily rely on GPU cloud hosting for 3D rendering and animation. GPUs can rapidly process and render complex 3D scenes, enhancing the efficiency and speed of creating high-quality animations, special effects, and virtual reality experiences. The gaming industry, film production, advertising, and architectural design all leverage GPU cloud servers for rendering and visualization.
5. Advantages of GPU Cloud Hosting
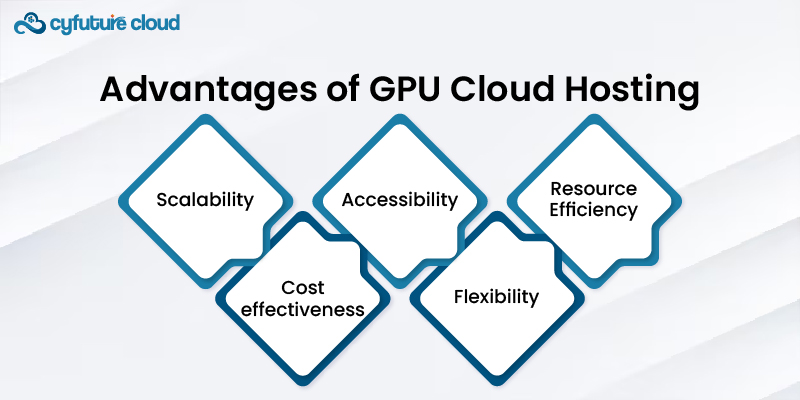
5.1. Scalability
GPU cloud servers offer scalability, allowing users to easily scale up or down based on their requirements without significant hardware investments.
5.2. Cost-effectiveness
By utilizing cloud-based GPU resources, businesses can avoid the high upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining dedicated GPU hardware.
5.3. Accessibility
GPU cloud hosting provides remote access to powerful computing resources, enabling users to perform GPU-intensive tasks from anywhere with an internet connection.
5.4. Flexibility
Users can choose from various GPU configurations and specifications based on their specific needs, ensuring optimal application performance.
5.5. Resource Efficiency
Virtualization technology maximizes GPU utilization by efficiently allocating resources among multiple users, reducing waste and improving overall resource efficiency.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, GPU cloud servers are a significant development in the field of computing because they combine the flexibility and accessibility of cloud computing with the processing power of a100 GPU. Because they enable quicker and more effective processing across a variety of applications, these servers have a significant impact on many sectors. For businesses and people wishing to take advantage of the enormous potential of cloud hosting, understanding their components, functioning, advantages, and applications is essential. It is impossible to overestimate their contribution to the advancement of machine learning, research, data analytics, and several other applications. The use of GPU cloud servers is anticipated to grow as technology progresses, spurring innovation and altering how we tackle difficult computing problems in a variety of fields

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


