 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

It is crucial for anyone looking to use cloud computing to understand the services. Within the numerous cloud models offered, Managed Cloud and Public Cloud are two distinct services. Although the two are somewhat similar in their nature, they are also quite different in terms of performance, cost, and handling.
Public Cloud is a type of cloud computing model where services and resources are made available to buyers through cloud services from third-party sellers over the Internet. Storage, applications, and virtual machines are examples of services that are shared with other users, or “tenants.” For instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Cyfuture Cloud, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are known as public cloud providers.
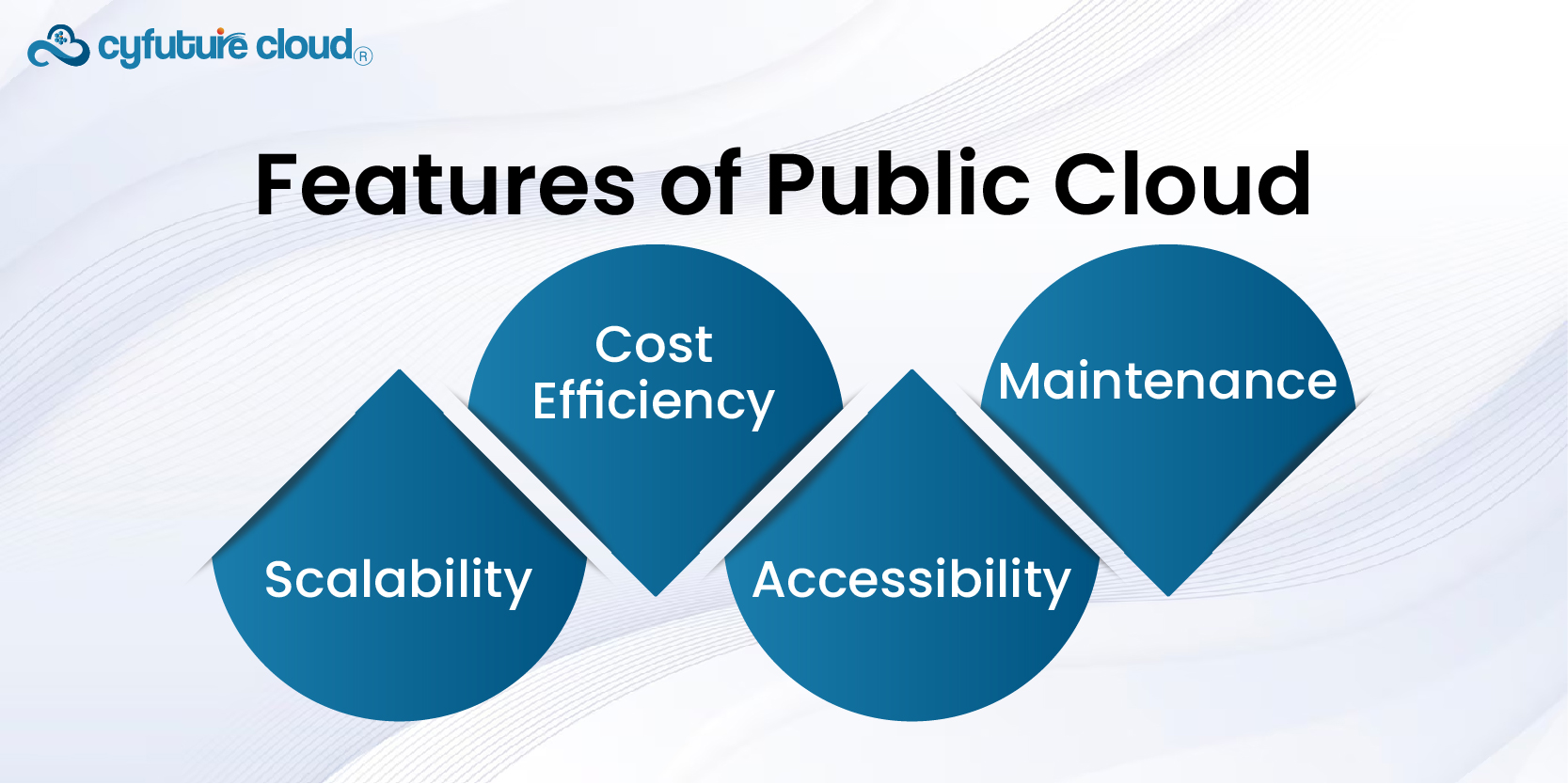
- Scalability: Public cloud versions are almost infinitely elastic in terms of provision. This means you can scale up or scale down depending on the level of your workload and this is very important for many businesses.
- Cost Efficiency: This is because resources such as the computing infrastructure are used to support multiple tenants, and as such, the cost of ownership is divided. The Public Cloud’s consumption model is based on a utility computing model or service-based model, which implies that a user pays for the services used.
- Accessibility: Also, since services can be delivered online, employees are less encumbered by a traditional organizational structure, making it easier for them to work remotely.
- Maintenance: Users also do not have to worry about how the infrastructure is being maintained, who is doing updates, and security, as this is handled by providers of public clouds.
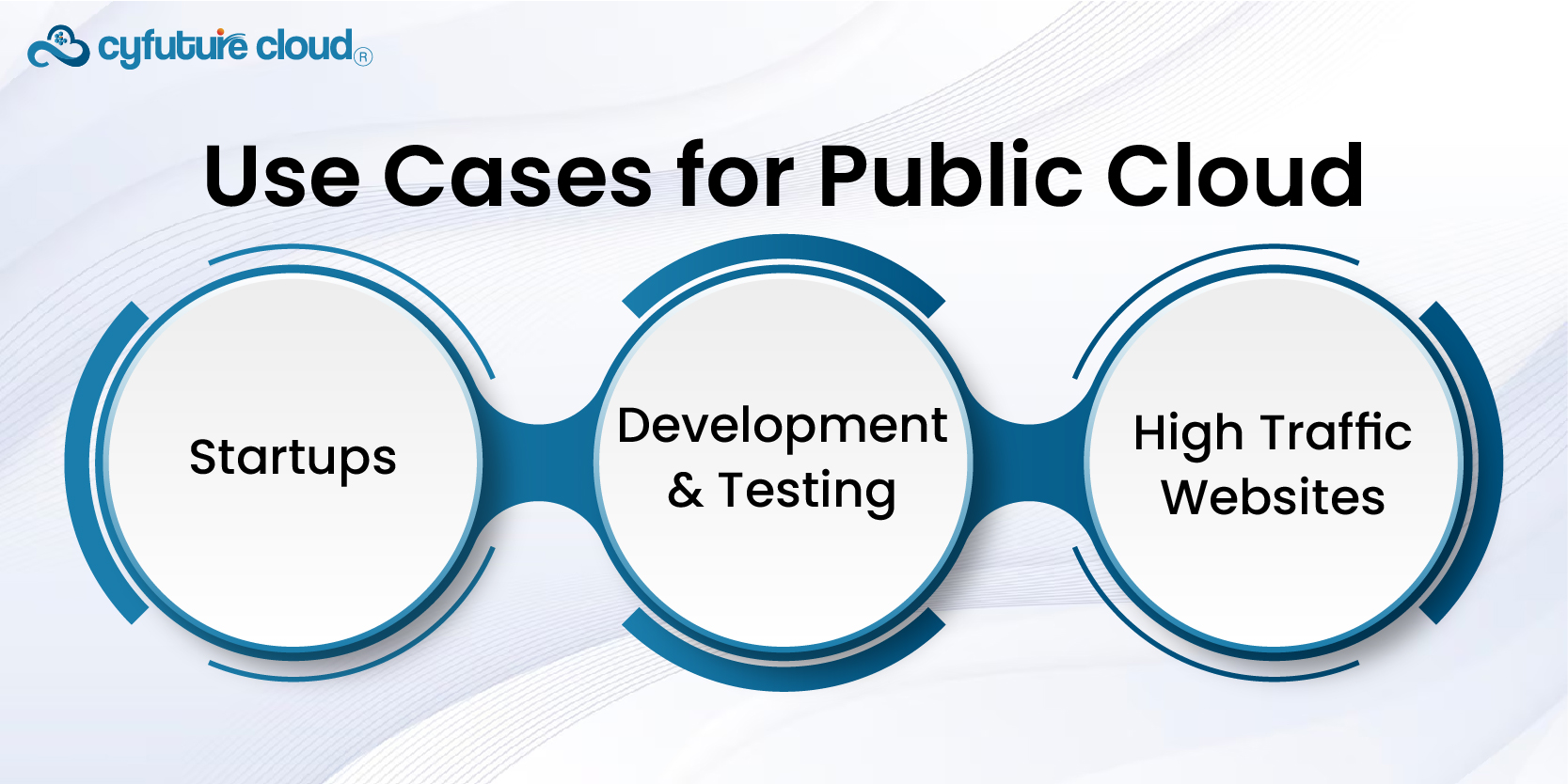
- Startups: They often need to scale quickly without significant upfront investment.
- Development and Testing: Developers can spin up resources quickly for short-term use.
- High Traffic Websites: Businesses that experience fluctuating traffic can benefit from the elasticity of the public cloud.
- Security: Since resources are shared, there is a higher perceived risk of data breaches, although providers implement robust security measures.
- Customization: Compared to other cloud models, there are fewer customization options. You may have to conform to the provider’s configurations.
Managed Cloud refers to a cloud hosting solution where a third-party service provider manages a business’s cloud infrastructure. This includes setup, configuration, maintenance, and support. The managed cloud can be applied to public, private, or hybrid clouds. The key aspect is the management and support provided by the vendor.
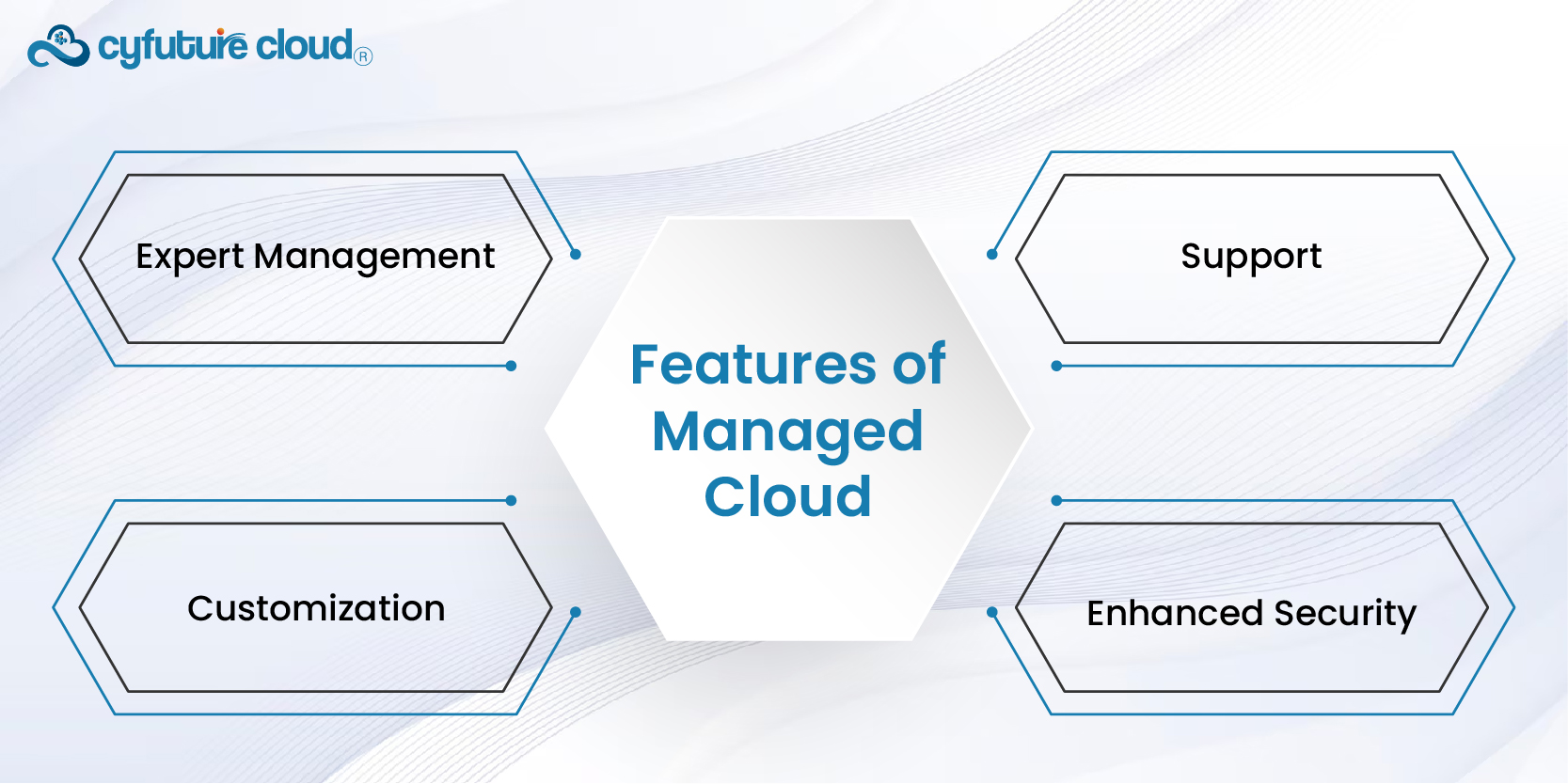
- Expert Management: The managed cloud solves the concern with the eligibility of the cloud provider by providing expert management of the cloud infrastructure. This also involves the process of monitoring, general backup, and disaster backup.
- Customization: Controllable cloud solutions can be particularly deployed to satisfying organization’s requirements through customization hence flexibilities in implementation.
- Support: Subscribers are served by separately staffed support teams to give help and guarantee improved functionality.
- Enhanced Security: Through using managed cloud services, security is enhanced due to the providers’ commitments towards offering deep security solutions and compliance assistance that are unique to industries.

- Businesses with Limited IT Resources: Hiring managed services that assist in dealing with other tough managerial duties on clouds act as a boon to companies that may not have specialized staff.
- Highly Regulated Industries: IT sectors that involve high regulation and policy compliance, data sensitivity, or simply require a stable and predictable cloud solution can leverage managed cloud solutions.
- Mission-Critical Applications: As a result, high-availability and high-reliability applications can employ managed cloud infrastructure and management requirements.
- Cost: Managed cloud services tend to be more expensive than public cloud because they include management and support fees.
- Vendor Dependency: Businesses may become dependent on the managed service provider for ongoing support and changes.
Understanding the differences between managed and public cloud is crucial for selecting the right solution for your business.
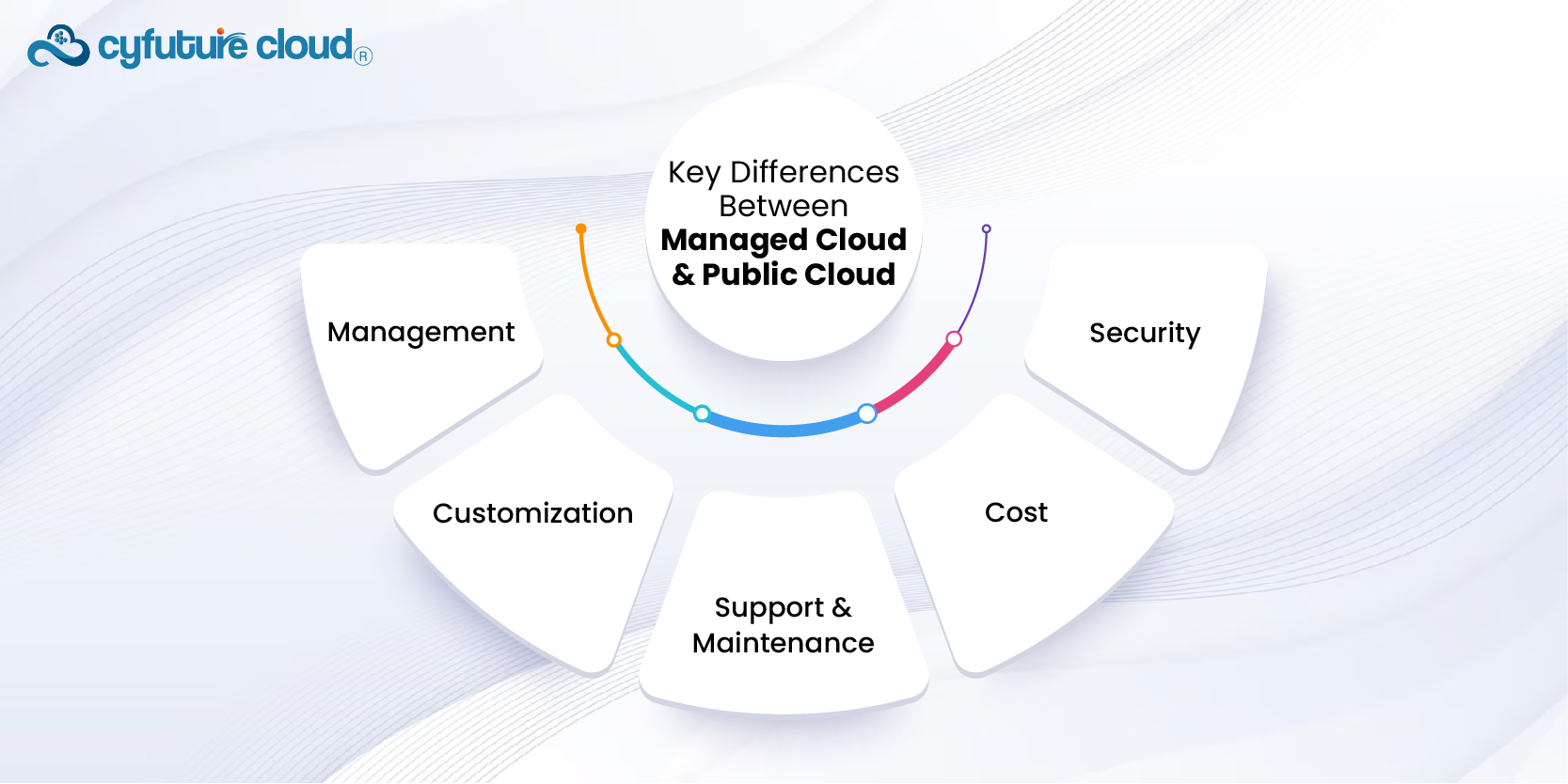
- Public Cloud: You manage your resources. Public cloud providers handle infrastructure, but you are responsible for managing your applications, data, and services.
- Managed Cloud: The service provider manages your resources. This includes infrastructure, applications, and support, allowing you to focus on your core business activities.
- Public Cloud: Offers limited customization. You have access to standardized services and configurations.
- Managed Cloud: Offers high levels of customization. Services can be tailored to fit specific business requirements and needs.
- Public Cloud: Basic support and maintenance are included. You may need to purchase additional support plans for more comprehensive assistance.
- Managed Cloud: Comprehensive support and maintenance are part of the package. Providers handle all aspects of cloud management, including updates and troubleshooting.
- Public Cloud: Typically cheaper upfront. You pay for what you use with lower overall costs due to shared resources.
- Managed Cloud: More expensive due to added management services. Costs include not only usage but also the expertise and support provided by the vendor.
- Public Cloud: Security is robust but may not meet all compliance needs for certain industries.
- Managed Cloud: Enhanced security and compliance options are available. Providers often offer advanced features to meet specific regulatory requirements.
Choosing between managed and public cloud depends on your business needs:
- Public Cloud is ideal if you:
- Need to minimize costs.
- Have in-house IT expertise to manage cloud services.
- Require flexibility and scalability without additional management.
- Managed Cloud is better if you:
- Lack the resources or expertise to manage your cloud environment.
- Need advanced security and compliance features.
- Prefer a tailored solution with ongoing support.
Both managed and public clouds offer valuable benefits depending on your business needs. The public cloud is cheaper and provides virtually unlimited resources that can be acquired promptly with less overhead in comparison to the managed cloud, which provides detailed solutions for a company as well as managing the cloud requirements for the company at a much higher cost. Determining one’s unique needs ensures that you select the most suitable platform for your organization. When choosing between IAAS options, it helps to understand the differences, focusing on your business objectives and available streams of income.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


