 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

In today’s knowledge base, we will discover the main difference between Hexa Core and Ocata Core. Let’s get started!
We must understand multi-core processors before we get to the details of hexa-core and octa-core processors. A core is a processor or microprocessor processing component on which instructions are performed. There used to be humble beginnings of cloud computing where it was not divided into cores as processors only contained one core.
However, due to technological advancements, techniques were used to incorporate more than one core in one processor; thus, the improvements were implemented.
A Hexa-core processor is a CPU (Central Processing Unit) that has 6 independent cores inside a single chip.
Each core works like a small processor, capable of executing instructions on its own. With 6 cores, the processor can handle more tasks at the same time compared to dual-core or quad-core processors.
1. 6 Processing Cores
◾ Each core processes tasks independently.
◾ Improves multitasking and parallel processing.
2. Clock Speed
◾ Performance also depends on the GHz (speed) of each core.
3. Multithreading Support
◾ Some Hexa-core CPUs support Hyper-Threading (Intel) or Simultaneous
◾ Multi-Threading (AMD), allowing up to 12 threads (6 cores × 2 threads each).
4. Balanced Performance
◾ Provides a middle ground between Quad-core (4 cores) and Octa-core (8 cores).
|
Benefit |
Explanation |
|
Better Multitasking |
Run multiple applications (browsing, streaming, office apps) smoothly. |
|
Gaming |
Handles modern games at 1080p and 1440p with good frame rates. |
|
Productivity |
Supports moderate video editing, 3D rendering, and coding tasks. |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Balanced performance without consuming as much power as Octa-core CPUs. |
1. Desktop CPUs:
◾ Intel Core i5-11400 (6 cores, 12 threads)
◾ AMD Ryzen 5 5600X (6 cores, 12 threads)
2. Mobile CPUs:
◾ Qualcomm Snapdragon 650/653
◾ Apple A11 Bionic (Hexa-core: 2 high-performance + 4 efficiency cores)
|
Processor Type |
Core Count |
Best For |
|
Dual-Core |
2 |
Basic tasks (browsing, office apps) |
|
Quad-Core |
4 |
Entry-level gaming, moderate multitasking |
|
Hexa-Core |
6 |
Mid-range gaming, video editing, multitasking |
|
Octa-Core |
8 |
High-end gaming, heavy multitasking, 4K editing, AI apps |
In simple terms:
A Hexa-core processor = 6 brains inside your CPU, giving a balance of performance, efficiency, and affordability. It’s stronger than quad-core but not as powerful as octa-core.
- Improved multitasking capabilities
- Better performance in multi-threaded applications
- Energy efficiency compared to higher core count processors
- Lower heat generation compared to octa-core processors
An octa-core processor is a CPU (Central Processing Unit) that has 8 separate cores inside a single chip.
Each core is like a small processor that can handle tasks on its own. With 8 cores, the processor can run many tasks at the same time, which makes devices faster and more efficient.
1. 8 Cores = More Power
◾ Each core processes instructions independently.
◾ More cores help with multitasking, gaming, and running heavy applications.
2. Big.LITTLE Design (in smartphones)
◾ Some octa-core mobile processors use a mix of:
◾ High-performance cores for demanding tasks (like gaming, video editing).
◾ Power-efficient cores for light tasks (like texting, browsing).
3. Better Multitasking
◾ Lets you stream videos, browse the internet, and run apps together smoothly.
4. Examples
◾ Mobile: Snapdragon 8 Gen series, MediaTek Dimensity, Samsung Exynos.
◾ Desktop: AMD Ryzen 7 (8 cores), Intel Core i7 (8 cores).
◾ Quad-Core (4 cores): Good for light tasks.
◾ Hexa-Core (6 cores): Balanced for gaming and multitasking.
◾ Octa-Core (8 cores): Best for heavy tasks, gaming, editing, and future-proofing.
In simple terms:
An octa-core processor is a CPU with 8 brains working together, making your device faster, smarter, and more efficient for multitasking and high-performance applications.
- Superior multitasking capabilities
- Excellent performance in heavily multi-threaded applications
- Future-proofing for upcoming software demands
- Potential for better performance in specific scenarios
Now that we've covered the basics of hexacore and octa-core processors, let's examine the key differences between them:
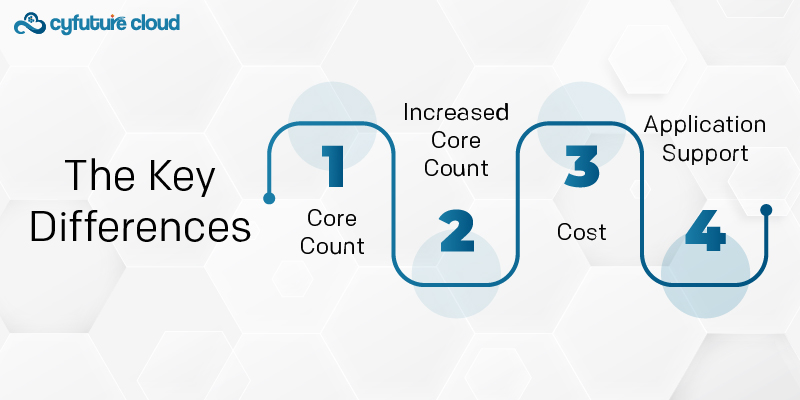
Core Count: The primary distinction is the quantity of cores. Hexa-core CPUs possess six cores, and octa-core processors contain eight.
Increased Core Count: A higher number of cores produces more tremendous heat. Octa-core processors generally generate more heat than hexa-core processors, which should be considered in device design and cooling systems.
Cost: Octa-core CPUs are often more expensive than Hexa-core processors due to their enhanced complexity and performance capabilities.
Application Support: Not all apps can fully utilize eight cores. In numerous instances, the performance disparity between hexacore and octa-core processors may be minimal for routine work.

The decision between a hexa-core and an octa-core CPU depends on your requirements and applications. Consider the following factors:
Application: A hexacore CPU is likely adequate for users whose primary activities involve fundamental tasks such as web browsing, social media engagement, and light productivity. An octa-core processor is preferable for intensive multitasking, gaming, or professional content creation.
Budget: Octa-core processors generally incur higher costs. Hence, it is essential to evaluate your budget during the decision-making process.
Future-Proofing: An octa-core processor may provide more excellent durability if you wish to guarantee your device can accommodate forthcoming software requirements.
Device Type: An octa-core CPU may be more advantageous for desktop computers, as power consumption and heat generation are less critical factors. Nonetheless, the compromises between performance and efficiency become increasingly significant for mobile devices.
| Feature | Hexa-Core Processor (6 Cores) | Octa-Core Processor (8 Cores) |
| Core Count | 6 independent cores | 8 independent cores |
| Threads (with Hyper-Threading/SMT) | Up to 12 threads | Up to 16 threads |
| Performance | Balanced – great for mid-range gaming, productivity, and multitasking | Higher performance – best for heavy multitasking, 4K gaming, and professional workloads |
| Power Efficiency | More efficient, consumes less power compared to octa-core | Slightly higher power consumption (more cores active) |
| Gaming | Good for 1080p and some 1440p gaming | Better for 1440p and 4K gaming, supports ray tracing and advanced graphics |
| Workload Handling | Handles medium workloads (video editing, coding, office apps) | Handles heavy workloads (3D rendering, AI, machine learning, virtualization) |
| Use in Smartphones | Often used in mid-range smartphones | Common in flagship/high-end smartphones |
| Price | More affordable | More expensive |
| Best For | Users who need good performance at a budget-friendly price | Power users, gamers, and professionals who need maximum performance |
No definitive victor emerges in the competition between hexacore and octa-core CPUs. Both configurations deliver remarkable performance and can effortlessly manage the majority of workloads. The decision ultimately hinges on your particular requirements, financial constraints, and the nature of the gadget you use or acquire.
Remember that core count is only one facet of a processor's comprehensive performance. Additional elements such as clock speed, cache size, and manufacturing method also influence considerably. When selecting a device or CPU, evaluate the complete package instead of concentrating exclusively on the core count.
As technology progresses, more significant core counts may become the norm. Both hexa-core and octa-core CPUs deliver exceptional performance for various users and applications. Select the option that most adequately meets your requirements, and experience the capabilities of contemporary multi-core computing!

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


