 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


A control panel in Microsoft Windows is a specific function that lets users track and modify multiple settings and options of the personal computer. It makes the system's performance, security, and usability manageable in a simple manner.
Definition: A control panel is a collection of administrative tools and configuration options that expose the operating system’s settings in an organized way.
Purpose: Make system configuration accessible—so users can perform tasks (install software, update drivers, set network options, manage accounts) without using low-level commands or editing configuration files manually.
Audience: Both end users (desktop/laptop owners) and IT administrators (who need centralized or automated management).
Most control panels present settings grouped by purpose. Typical categories include:
◾ System & About — OS version, updates, system information, device name.
◾ User Accounts & Access — add/remove users, passwords, permissions, parental controls.
◾ Network & Internet — Wi-Fi, Ethernet, VPN, proxy, DNS.
◾ Hardware & Devices — printers, storage, audio, displays, device drivers.
◾ Programs / Apps — install/uninstall programs, default applications.
◾ Security & Privacy — firewall, antivirus, encryption (BitLocker/FileVault), privacy permissions.
◾ Storage & Backup — disks, partitions, snapshots, scheduled backups.
◾ Accessibility — screen readers, high contrast, keyboard/mouse accessibility options.
◾ System Management — startup items, scheduled tasks, services, performance monitoring.
Accessing the Control Panel in computer can be slightly different depending on the specific version of Windows:
◾Windows 7:
To obtain the Control Panel in Windows 7, click 'Start' and then 'Control Panel'.
◾ Windows 8 or 8. 1:
* Right click on the start menu to display the app bar
* Select all apps and scroll right to the windows apps section
* select control panel
◾ Control Panel in Windows 10:
* Go to the Search box on the taskbar
* Type control panel
* Then select Control panel from the result
◾ For Windows 11, as in Windows 10:
the Control Panel in the Computer can be accessed through the described method.
◾ Log in to Windows with the user account that you want to block access to the Control Panel.
◾ Open the Windows registry.
◾ Navigate to the following registry key:
◾HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies
◾ Check for a subkey named Explorer under the Policies key. If the it exists, skip to the next step. If the subkey does not exist, right-click the Policies key and select New > Key. Type Explorer as the name of the new subkey.
◾ Right-click on the Explorer subkey and select the New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Type No Control Panel as the name of the DWORD value.
◾ Double-click on the No Control Panel value, change the 0 to a 1 in the Value data box, and click OK to save the value change.
◾ Close the Windows registry.
The appearance and organization of the Control Panel differs across Windows versions:

Windows 11, 10, 8, 8.1 & 7: Applets are arranged by categories, grouping them logically, and can also be displayed individually as large or small icons.
Windows Vista: The Control Panel Home displays applets in groups, while the Classic View shows each applet individually.
Windows XP: Category View groups the applets, while Classic View lists them individually.
The Control Panel consists of eight primary components, each with various sub-components:
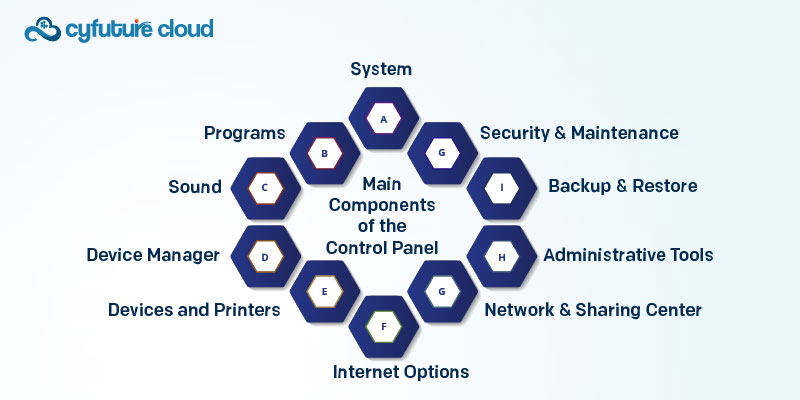
System: View system information and adjust properties
Security and Maintenance: Check security status and manage updates
Backup and Restore: Create backups and restore files
Administrative Tools: Access advanced system tools
Network and Sharing Center: View and manage network connections
Internet Options: Configure settings for Internet Explorer
Devices and Printers: View and manage connected devices
Device Manager: Access detailed hardware information and troubleshoot issues
Sound: Adjust audio settings and manage playback/recording devices
Programs
Programs and Features: Uninstall programs and turn Windows features on/off
User Accounts
User Accounts: Change user account settings and passwords

Personalization: Customize desktop background, colors, and themes
Fonts: Manage installed fonts
Date and Time: Set date, time, and time zone
Region: Change regional format settings
Ease of Access Center: Optimize display, sound, and input settings for accessibility
The Windows Control Panel in Computer has been in use since the early versions of the operating system, with each version of the operating system coming with newer applets and controls. Some notable changes include:

Windows 95: The Control Panel became a folder containing shortcuts to various applets.
Windows ME and XP: The Control Panel home screen was changed to a categorized navigation structure.
Windows Vista and 7: It was in Windows Vista and 7 that other layers of navigation were added, with the Control Panel being the main window that displays all the options that can be tweaked.
Windows 10: The operating system is gradually removing the Control Panel in favor of the Settings app, designed to help you tweak Windows settings on a touch screen.
Even though the Control Panel is essential in Windows, specific hardware devices and software applications have control panels for extra settings and features. For example:
Mouse or keyboard control panels for advanced configuration
Graphics card control panels for customizing display settings
Audio control panels for managing sound effects and equalizer settings
These third-party control panels are often installed alongside the corresponding hardware or software and can be accessed from the Control Panel or through their shortcuts.
The Control Panel in Computer is essential for overseeing and personalizing a Windows PC. Its key advantages include:
Efficiency: It is done in such a manner that many administrative-related operations are made possible via the Control panel, thus eradicating the need for other programs.
Centralized Management: It provides a central ground to manage the entire system, hardware aspects, software, and system configurations.
Personalization: The user can configure the operating system in terms of the look, feel, and performance of the computer.
Therefore, the Control Panel is one of the practical tools for collecting, analyzing, and managing PC performance in Windows. Both beginners and advanced users find its user-friendly interface and extensive feature set to be a valuable tool.
Q: Where is the Control Panel in Windows 11?
A: Start → type Control Panel, or press Windows + R and run control. Modern settings are in Start → Settings.
Q: Can changes in the Control Panel be reverted?
A: Often yes—use System Restore (Windows) or Time Machine (macOS). For servers, roll back via configuration management snapshots.
Q: Is Control Panel being removed from Windows?
A: Microsoft is gradually migrating settings to the modern Settings app, but many legacy Control Panel items remain for compatibility.
Q: How do I automate control-panel-like tasks across many machines?
A: Use PowerShell, configuration management tools (Ansible, Puppet, Chef), or enterprise MDM/GPO for Windows domains

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


