 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

Virtualization is an essential technology that underpins modern-day cloud computing. It allows the creation of digital variations of computing assets, together with servers, garage gadgets, networks, and even running structures. In cloud computing, virtualization performs a vital function in maximizing resource utilization, enhancing flexibility, and allowing the scalability and efficiency that define cloud services.
At its core, virtualization entails developing a digital (instead of real) model of something. In computing, this indicates using software programs to create an abstraction layer over computer hardware, allowing the hardware factors of a single pc—processors, memory, storage, and more—to be divided into more than one virtual computer system, generally referred to as digital machines (VMs).
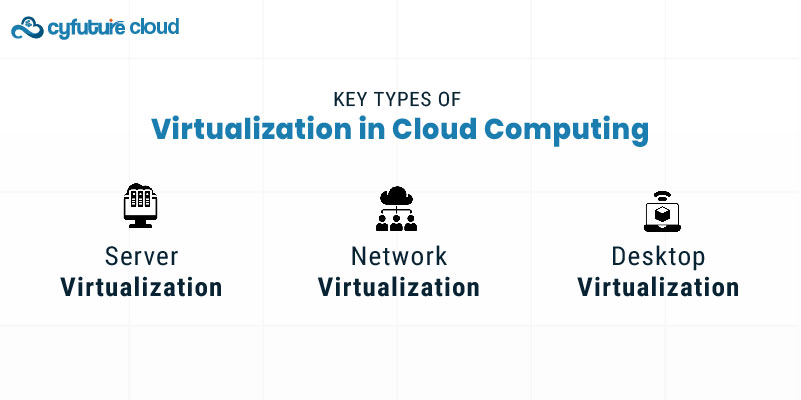
Server Virtualization: Divides one physical server into multiple virtual servers.
Storage Virtualization: Pools physical storage from multiple devices into a single, manageable unit.
Network Virtualization: Creates virtual networks that are decoupled from the underlying network hardware.
Desktop Virtualization: Separates a desktop environment from the physical device used to access it.
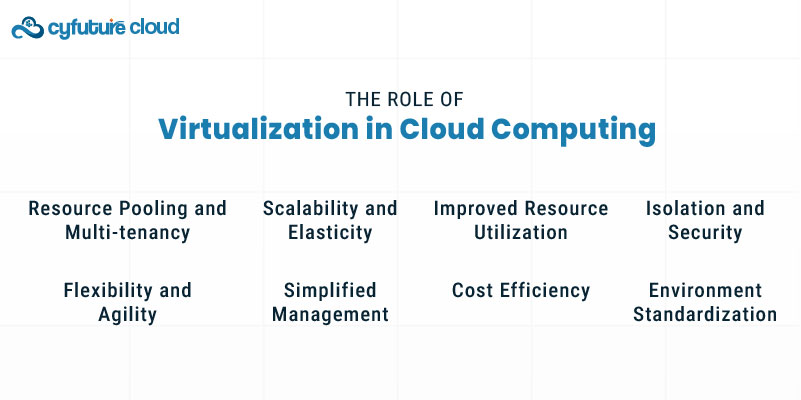
Virtualization is essential to cloud computing for several reasons:
They make it possible in that physical resources owned by multiple cloud providers can be combined into physical resource pools, and then virtual slices can be assigned to different tenants.
This multi-tenant model is inherent in the public cloud model to allow diverse customers the use the same computational resources.
2. Scalability and Elasticity
Since creating virtual resources, it is easy to create or dispose of them depending on the organization’s needs, hence scalability is easily achieved.
This flexibility is typical for cloud services, thus allowing efficiently adapting the businesses’ capacities to the varying loads.
3. Improved Resource Utilization
Hypervisors can host one or several virtual machines on a single physical computer, and since this essentially enhances the use of the hardware the rates of utilization are notably boosted.
This results in the benefits of cost optimization and efficiency for cloud providers and users and consumers of cloud services.
4. Isolation and Security
Virtualization still has an ability of paravirtualization where numerous virtual machines can side by side on one piece of physical apparatus yet remain independent of each other.
It increases security because problems affecting one VM do not have a domino effect on other VMs, thus increasing stability.
5. Flexibility and Agility
Server operation can be done with relative ease since the virtual machines can be migrated from one physical server to another with reduced downtime hence enabling one to perform maintenance and load balancing easily.
These informatics make the management of infrastructures more flexible and the processes of disaster recovery more effective.
6. Simplified Management
Virtualization refers to a provision that hides the complexities and details of the underlying hardware and infrastructure hence making it easier to administer and allocate the resources required in the computing process.
It also centralizes the management of infrastructures hence minimizing the administrative costs.
7. Cost Efficiency
From the above discussion, it is clear that virtualization optimizes the use of hardware resources thus cutting the cost of capital and operation.
8. Environment Standardization
The general advantage of virtualization is that it implies the ability to build application environment replicas that are consistent with development, testing, and production environments.
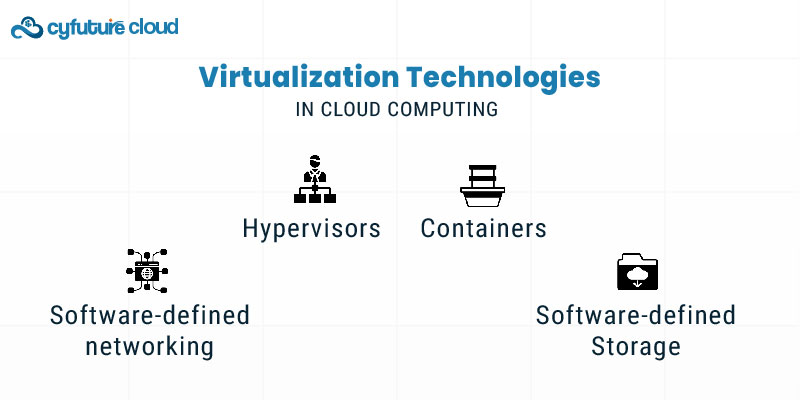
Several virtualization technologies are commonly used in cloud computing:
Hypervisors: Software layers that manage virtual machines. Examples include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM.
Containers: Lightweight virtualization era that programs programs with their dependencies. Docker and Kubernetes are popular box technologies.
Software-defined networking (SDN): Virtualizes community functions for greater flexible and programmable network management.
Software-defined Storage (SDS): Abstracts garage sources from the underlying hardware for extra flexible and efficient garage management.
While virtualization offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges:

Performance Overhead: There are costs associated with virtualization though; this is in terms of performance which has however reduced over the years as technology progresses.
Complexity: They also pointed out that managing virtualized environments may be difficult, time-consuming, and might call for skills as well as tools that are different from standard ones.
Security: Although virtualization positively impacts security, it raises new concerns that involve the protection of the hypervisor and traffic between virtual machines.
Resource Contention: In environments where virtualization is extremely implemented, there might be competition for some of the resources thus leading to some instability.
Conclusion
Virtualization is a cornerstone era in cloud computing, permitting the power, scalability, and performance that outline cloud services. It allows for extra efficient use of hardware resources, provides the foundation for multi-tenant architectures, and enables the rapid provisioning and de-provisioning of resources which might be essential to cloud elasticity. As cloud computing continues to conform, virtualization technology will in all likelihood continue to increase, in addition to enhancing the talents and efficiency of cloud services.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


