 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


SAN storage is a sea change in data handling and organization. It is a highly evolved architecture targeted toward serving high-demand enterprise applications. In its essence, at the core of the concept, storage is a special, high-speed network entity that provides block-level network access to storage. This type of architecture, in contrast with the conventional file-level storage systems, offers unprecedented performance, scalability, and reliability-valued above everything else in today's data-driven world.
The architecture of SAN storage works on a well-thought architecture that comprises several vital components of the solution.
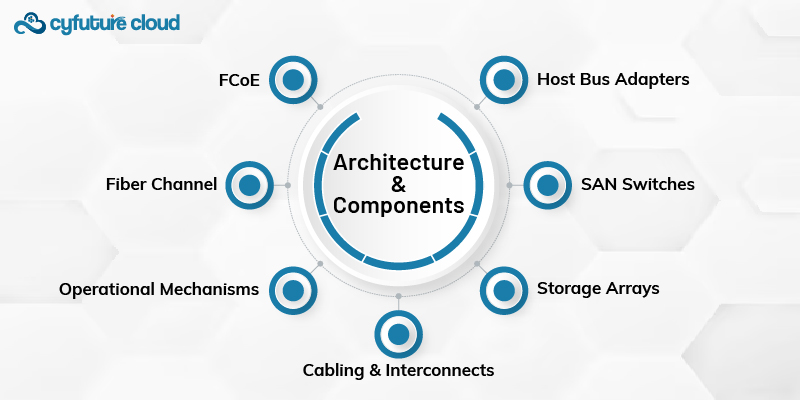
These are interface cards that are fitted in servers and storage devices. They are essentially used to connect the host system with the SAN fabric. HBAs form the basis of any good-speed data transfer with low latency.
These switches are supposed to be the backbone of the infrastructure of the SAN. They connect several storage devices and servers for effective routing and management of data between them. Some extended SAN switches have also provided features like zoning and port aggregation that optimize performance and security.
These are groups of storage devices, such as hard drives or solid-state drives, configured for redundant and scalable storage solutions. Storage arrays within a SAN can be designed for specific performance and capacity needs, thus suitable for a wide variety of applications in an enterprise environment.
The interconnects in a SAN are designed to support substantial data throughput by using fiber optic cables or high-speed Ethernet to provide the potential for seamless communications throughout all parts of the network.
The use of block-level storage protocols has been widely used in the operation of SAN storage, and three major protocols have been widely in operation: Fiber Channel (FC), Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI), and Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE):
This is the high-speed networking technology that offers very low latency and high-throughput data transfer, FC is viewed as the standard in high-performance SAN environments. iSCSI: Additionally, based on the pervasive TCP/IP protocol, iSCSI allows transporting SCSI commands over IP networks at an economical and flexible price without performance loss.
This is the protocol that encapsulates Fiber Channel frames in Ethernet packets; this allows SAN to run over high-speed Ethernet infrastructures already implemented with minimal network management and cost.
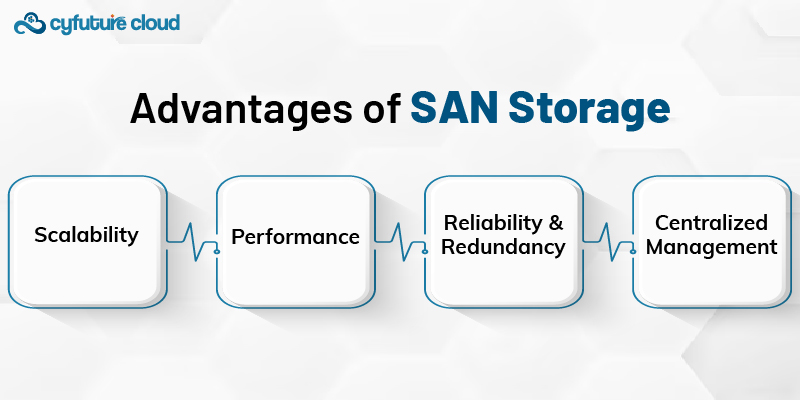
This is one of the key factors in the use of SAN. It offers unlimited scalability. The storage capacity can be extended easily by enterprises without affecting ongoing operations. For those businesses working with exponentially growing data volumes, this scalability characteristic is a key factor.
SANs allow direct block-level access to storage devices for better performance compared with traditional NAS solutions. This makes them very well-suited for latency-sensitive applications such as databases and virtualization.
The architecture of a SAN is essentially designed to make itself highly available and fault-tolerant. RAID configurations, redundant paths, and failover capabilities in place maintain data integrity and continuous operation even if hardware failures were to occur.
Centralized management makes unified control over storage simpler, lessening the administration burden while improving data governance. At the same time, advanced management tools provide an efficient means of provisioning, monitoring, and performing routine maintenance of storage resources.
SAN storage is indispensable in environments where high performance, reliability, and scalability are indispensable:
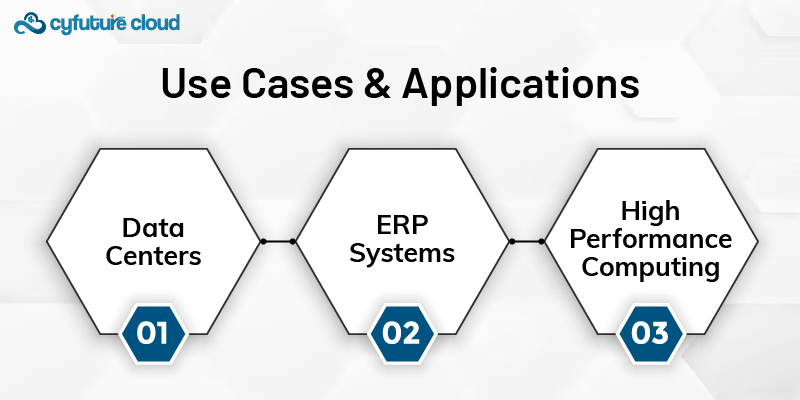
The SAN acts as the backbone of the modern data center with its ability to support mission-critical applications, virtualized environments, and large-scale databases.
They require heavy-duty performance coupled with the reliability of the SAN, making the latter perfect for enterprise resource planning systems, which assure smooth business operations and data integrity.
Applications in HPC require the highest rate of data access and processing; hence, they find ultimate support and infrastructure in the form of SANs.
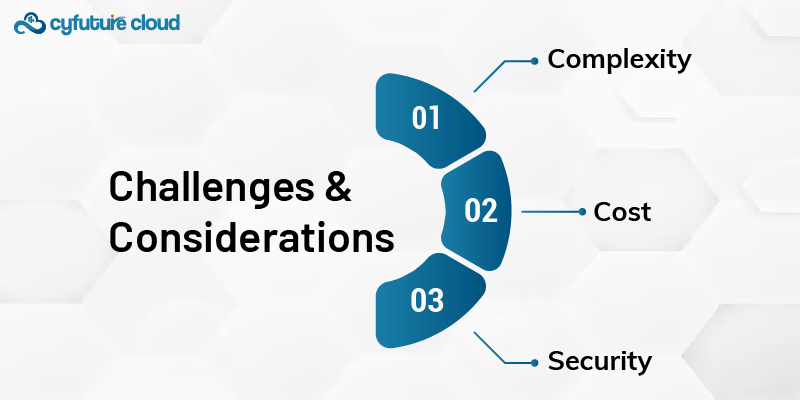
While SAN storage does have a great many advantages, there are some challenges associated with this type of data storage:
A complex aspect lies in the design and administration of SANs, which includes professional training and experience for proper management. It is only then that correct configuration and maintenance would be able to tap into the full potential of SAN storage.
Setting up a SAN infrastructure could become pretty pricey as a large investment would be required for hardware, software, and sometimes even training personnel. Yet, the long-term benefits derived usually outweigh the initial expenditure.
Ensuring the security of data within a SAN environment involves several measures that require strong action, including encryption, access controls, and audits regularly to guard against unauthorized access and data breaches.
As time passes, technology is also changing and evolving. There have been various emerging trends that tend to shape the future of the SAN storage system. These include:
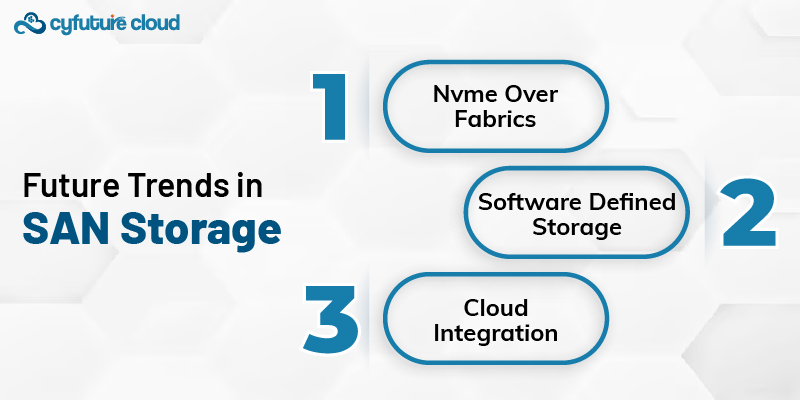
This is an emerging technology that will surely bring evolution in the area of SAN storage. The ultra-low latency and high throughput make it ideal for applications that are next in a generation.
SDS abstracts the storage hardware from the software and has provided more flexible, cost-efficient storage solutions that are easier to manage and scale.
Merging on-premise SAN with cloud storage solutions continues to become popular, offering the best of both worlds in performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
Since the world of data management keeps on growing and expanding, it offers an advanced solution with power, reliability, and scalability. Its mainstays are its sophisticated architecture, unparalleled performance, and top-of-the-line features that position it as a core building block for modern enterprise infrastructures. As organizations scale to produce and deploy voluminous amounts of data, the approach of SAN storage will increasingly become the key to this effort toward managing the data efficiently, securely, and scalable.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


