 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

“The cloud computing layer encloses Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS).”
Cloud computing is typically divided into three primary layers: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing businesses to avoid managing physical hardware. PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for end-users to install and maintain applications locally. These layers collectively enable businesses and individuals to scale resources efficiently, access applications remotely, and innovate without the overhead of maintaining physical systems or software infrastructure.
A multi-layered architecture supports cloud computing and serves as the foundation for a range of cloud services and applications. Comparable to strata in the technological landscape, these layers each provide a distinct contribution to the smooth operation of cloud-based systems. Comprehending these tiers is essential, acting as the cornerstone for anybody traversing the vast world of cloud computing.
The Physical Layer, which includes the actual infrastructure such as servers, data storage devices, and networking components, is its base. The next layer is virtualization, which is made possible by software and hypervisors that build and maintain virtual computers or containers. These tiers utilize abstraction to optimize the effectiveness of resources.
Moving on, the Control Layer uses management tools and APIs to orchestrate and monitor the whole system. Lastly, the Application Layer provides cloud services and apps while serving as the end-user interface. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are integrated at this layer.
Together, these layers provide an intricate structure that offers scalable, adaptable, and reasonably priced cloud solutions. For developers, IT specialists, and companies looking to maximize cloud operations and provide end users with cutting-edge cloud-based solutions, it is essential to comprehend their roles and interdependencies.
The current computer environment has been completely transformed by the revolutionary technology known as cloud computing. Broadly speaking, it is the provision of diverse computer services, including storage, processing power, apps, and more - via the internet or "the cloud." Cloud computing provides remote access to these services, allowing users to control apps and store data without depending on local servers or personal devices. This has completely changed the way that people and businesses manage their digital operations.
The need for scalable, adaptable, and affordable solutions in the digital world has given rise to the necessity for cloud computing. By addressing the need for readily available, on-demand resources, it helps companies manage data, apps, and services effectively. The need for improved communication, more distant accessibility, and streamlined operations is met by cloud computing—especially in this day and age when quick scaling and worldwide connection are critical. This technology serves as a platform for innovation, enabling businesses to make the most use of their resources, cut down on infrastructure expenses, and quickly adjust to the rapidly changing technological landscape.
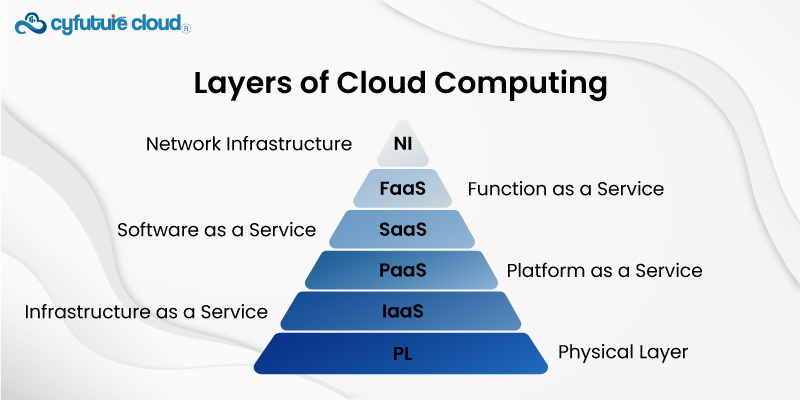
Among the layers of cloud computing, the physical layer forms the foundation. It consists of the hardware infrastructure, including data centers, servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. Data centers house rows of servers, storage units, and networking hardware responsible for managing, processing, and storing data. This physical layer is the bedrock upon which all other cloud layers are built, and its efficiency and stability are crucial for a smooth cloud computing experience. Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust physical infrastructure to ensure optimal performance, security, and availability of cloud services.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a model for separating cloud services. It provides virtualized computing resources via the Internet. IaaS providers give customers the flexibility to scale resources up or down in response to demand by letting them rent servers, networking, and storage. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are notable IaaS providers. By abstracting the challenges of managing physical infrastructure using Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), users can focus on installing their apps and maintaining the virtual infrastructure.
Applications can be developed, hosted, and deployed in an environment provided by the platform as a service (PaaS) layer. It abstracts away from the physical infrastructure, as well as the underlying hardware and software components. PaaS offers developers a fully complete platform to design, launch, and run programs without requiring them to deal with the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure. Vendors, including Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, and Heroku, provide PaaS solutions. It offers infrastructure-free software development tools so that development cycles may be completed more quickly.
The goal of this layer is to provide end users with cloud-based software applications via the Internet. This layer of cloud computing is the most user-friendly as it offers ready-to-use apps that don't need to be installed. SaaS applications offer a broad range of services, including email services, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce, office productivity suites like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, and much more. SaaS provides universal accessibility across devices and streamlines software access by eliminating the requirement for local installs.
With the Function as a Service (FaaS) cloud computing architecture, programmers can manage infrastructure management while executing code in response to events. Among the layers of cloud computing, Functions as a Service (FaaS) enables the execution of discrete functions or code units. The platform manages resource allocation automatically and grows in response to demand. All developers have to do is write the code and submit it to the FaaS provider; the provider will take care of the rest, responding to different triggers. FaaS, which is frequently used in serverless computing, provides a pay-as-you-go pricing model that lowers expenses by only billing for the actual time that code is executed. This makes it a cost-effective choice for completing quick, event-driven operations.
The foundation of cloud services is the network layer. It includes the network infrastructure that makes things possible, enabling communication, resource access, and data transmission amongst cloud components. This covers both private and public networks, such as the public internet, extranets, and intranets. The network layer is essential for providing safe and dependable data transit between users, apps, and cloud resources. It offers the connection required for the whole cloud ecosystem to work.
Comparing the Layers of cloud computing: Key Distinctions Between IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS
|
Criteria |
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) |
PaaS (Platform as a Service) |
SaaS (Software as a Service) |
FaaS (Function as a Service) |
|
Definition |
Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet |
Provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with infrastructure |
Provides software applications over the internet |
Provides a platform for running discrete functions or code snippets without managing servers |
|
Management |
Users manage applications, data, runtime, middleware, and OS |
Users manage applications and data, while the provider manages runtime, middleware, and OS |
Users only manage application settings and data |
Users manage code and event triggers, the provider manages the infrastructure |
|
Key Providers |
AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs, Google Compute Engine |
Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, Heroku |
Google Workspace, Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365 |
AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Microsoft Azure Functions |
|
Use Cases |
Hosting websites, virtual data centers, disaster recovery |
Development and deployment of applications, API integration |
Email services, CRM systems, collaboration tools |
Event-driven computing, microservices, data processing |
|
Benefits |
High flexibility, full control over infrastructure |
Simplified development, reduced management overhead |
Easy access to applications, minimal local IT management |
Scalability, cost-efficiency, no server management |
|
Challenges |
Requires significant management and expertise |
Limited control over underlying infrastructure |
Data security and compliance concerns |
Potential cold start latency, limited control over execution environment |
|
Cost Structure |
Pay-as-you-go for virtualized resources (compute, storage, network) |
Pay for platform usage (runtime, storage, databases) |
Subscription-based or pay-per-use for software access |
Pay-per-execution, based on the number of function invocations |
|
Scalability |
High, but requires manual intervention |
High, with automated scaling capabilities |
Automatically scalable |
Automatically scalable, but may be limited by function execution time |
|
Security Considerations |
Requires robust security measures by the user |
Shared responsibility model; the provider handles some security aspects |
Provider handles most security aspects, but user data protection is crucial |
Provider handles most security aspects, but secure code and triggers are the user's responsibility |
|
Integration |
Requires extensive integration efforts |
Easier integration with development tools and services |
Seamless integration with end-user applications |
Integrates with other cloud services and APIs |
|
Future Trends |
Increasing automation, AI for infrastructure management |
Growth in DevOps and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) |
Expansion in AI-driven applications, vertical-specific solutions |
Enhanced support for edge computing, greater adoption in IoT applications |

Understanding these layers of cloud computing is essential to grasping the delivery, management, and accessibility of cloud services. Every layer has a distinct function in providing cloud computing services, which facilitates the use of cloud technology for a variety of objectives by individuals, companies, and organizations.
By understanding the unique responsibilities and interactions across these layers, users may pick the best service models, improve resource usage, and gain insight into how data, applications, and services are processed and provided via the cloud. Gaining the most from cloud-based solutions and realizing their potential for innovation and scalability in the digital world requires having a thorough grasp of cloud computing layers.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more



