 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

PostgreSQL is a feature-filled and free, relational database management system. It is a tool used for managing enormous population data with it comes many numbers.
This knowledge base section will provide a step-by-step approach to installing PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 18.04.
So, let us get started!
And also we need to know that your Ubuntu is easily updated and the latest. Open a terminal window and run the following commands:
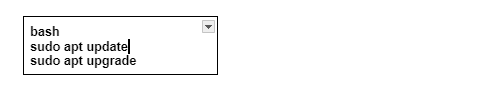
It will update your system's package list. Moreover, upgrade any outdated packages to the latest versions.
To install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 18.04–use the following command:
|
Bash sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib |
This command will install both the PostgreSQL database server and additional utilities.
You can verify it by checking the PostgreSQL service status. Use the following command:
|
bash systemctl status postgresql |
If PostgreSQL has been installed correctly, you will see output indicating that the service is active and running.
By default, PostgreSQL creates a system user named "postgres" with administrative privileges. To access the PostgreSQL prompt, switch to this user by running:
|
bash sudo -i -u postgres |
Now, you can access the PostgreSQL prompt by typing:
|
bash psql |
You are now connected to the PostgreSQL server. Now, you can begin executing SQL commands.
To improve security, set a password for the default PostgreSQL user "postgres". While remaining signed in as the "Postgres" user, execute the following command:
|
bash \password postgres |
Enter your desired password and confirm it when prompted. Make sure to choose a strong password to protect your database.
Establish a new user with limited access. Use the following command:
|
SQL CREATE USER username WITH PASSWORD 'password'; |
Replace "username" with the desired username and "password"
Now, you can create a new database and assign ownership to the newly created user. Run the following command:
|
Sql CREATE DATABASE dbname OWNER username; |
Replace "dbname" with the desired name.
You need to modify the PostgreSQL configuration file to allow remote connections. Open the PostgreSQL configuration file using a text editor:
|
bash sudo nano /etc/postgresql/12/main/pg_hba.conf |
Find the line that reads:
|
sql # TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD |
Below this line, add the following line to allow access from any IP address:
|
css host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 |
Save the file and exit the text editor. Then, restart the PostgreSQL service to apply the changes:
|
bash sudo systemctl restart postgresql |
That’s It!
Follow our above step-by-step guide to install PostgreSQL on your Ubuntu 18.04 server. Now, you can also configure it for basic use. For more information contact our support team.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


