 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway


In today’s digital age, businesses rely heavily on data, applications, and IT infrastructure to maintain smooth operations. Managing this infrastructure internally can be both expensive and complex. That's where colocation comes in as a strategic solution, providing businesses with a cost-effective, secure, and scalable environment for their IT needs.
In this article, we'll dive into what colocation is, how it works, and why it's a smart choice for companies seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure.
Colocation is a service where businesses rent space for their servers and networking equipment in a third-party data center. Instead of maintaining costly in-house server rooms, companies place their hardware in a secure, professionally managed facility that offers reliable power, cooling, high-speed internet, and physical security. Colocation allows businesses to scale their IT infrastructure easily while benefiting from enhanced uptime, disaster recovery, and lower maintenance costs. By leveraging colocation services, companies can focus on growth and innovation while ensuring their critical data and applications remain accessible and protected.
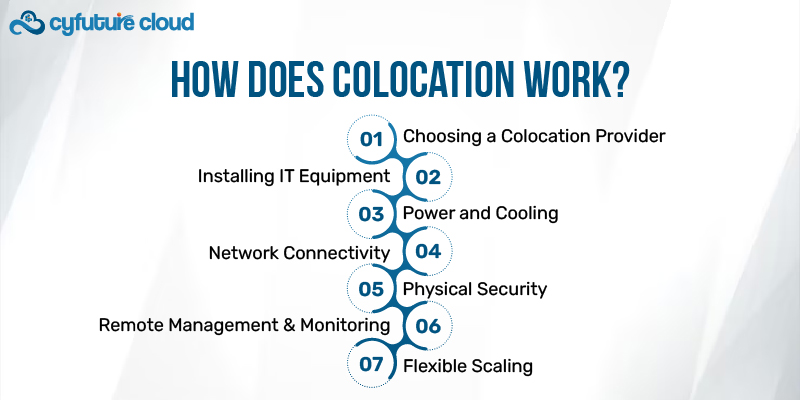
The colocation model involves a few key elements that make it distinct from traditional IT infrastructure management or cloud hosting services. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how colocation works:
Businesses select a colocation provider based on various factors such as location, available space, power requirements, security features, and connectivity options. Companies can choose a colocation facility that best suits their geographic and operational needs, whether it’s close to their headquarters for easy access or in a different region for redundancy and disaster recovery.
Once a business selects a colocation provider, they bring their own IT hardware (servers, storage devices, etc.) and physically install it in the provider’s data center. Colocation facilities typically offer different levels of service depending on the customer’s requirements:
Rack Space: Businesses can rent individual racks for their equipment.
Cages: For enhanced security and privacy, companies may choose dedicated cages.
Private Suites: Large enterprises or companies with high demands may opt for entire rooms or suites for their equipment.
One of the critical services that colocation providers offer is continuous power supply. This includes:
Redundant Power Sources: Colocation facilities have multiple power feeds, backup generators, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to ensure consistent power in case of outages.
Cooling Systems: Data centers are equipped with advanced cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures for IT equipment, preventing overheating and ensuring peak performance.
Colocation providers offer a range of network services, giving businesses high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity. Many colocation facilities are carrier-neutral, meaning they allow businesses to choose from multiple internet service providers (ISPs). This helps ensure reliable and flexible network connections.
Security is a top priority for colocation providers. Data centers are built with multiple layers of physical and digital security measures, including:
24/7 Monitoring: Security personnel and video surveillance continuously monitor the facility.
Controlled Access: Only authorized personnel can access specific areas, and businesses often get their own access controls for their equipment.
Biometric Scanning & Keycards: High-tech access controls like fingerprint or retina scans and electronic keycards are common in colocation facilities.
While businesses are responsible for managing their IT equipment, colocation providers offer remote hands services to assist with certain tasks like rebooting servers, replacing hardware, or diagnosing issues. This allows companies to manage their IT infrastructure even if they are located far from the data center.
As a business grows, colocation offers the flexibility to scale up or down based on changing needs. Whether you need to add more server racks, increase bandwidth, or expand power capacity, colocation providers allow you to adjust your infrastructure without the need for costly upgrades or new facilities.

Now that we understand how colocation works, let’s explore why businesses choose colocation over other IT infrastructure models.
Building and maintaining a private data center can be prohibitively expensive, especially for small- and medium-sized businesses. Colocation eliminates the need for large capital expenditures on infrastructure (power, cooling, physical space), allowing businesses to focus their budget on critical IT hardware and software.
Colocation offers flexibility to scale as your business grows. Whether you need to add a few extra servers or significantly increase your infrastructure, colocation providers offer the space, power, and connectivity to accommodate growth without long delays or major investments.
Colocation data centers are built with strict physical and digital security protocols. With 24/7 monitoring, biometric access controls, and robust firewalls, businesses can ensure that their IT infrastructure is protected against both physical breaches and cyberattacks. Additionally, colocation providers often comply with industry standards and regulations, helping businesses meet compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
Colocation facilities are designed with redundant power supplies, cooling systems, and network connectivity, ensuring that downtime is kept to an absolute minimum. In the event of a local outage, backup generators and redundant networks ensure continuous operation, allowing businesses to maintain uptime and avoid disruptions.
By outsourcing the physical management of IT infrastructure, businesses can concentrate on what they do best. Colocation frees up internal IT teams from managing the physical aspects of data centers, allowing them to focus on strategic tasks such as software development, innovation, and improving customer experiences.
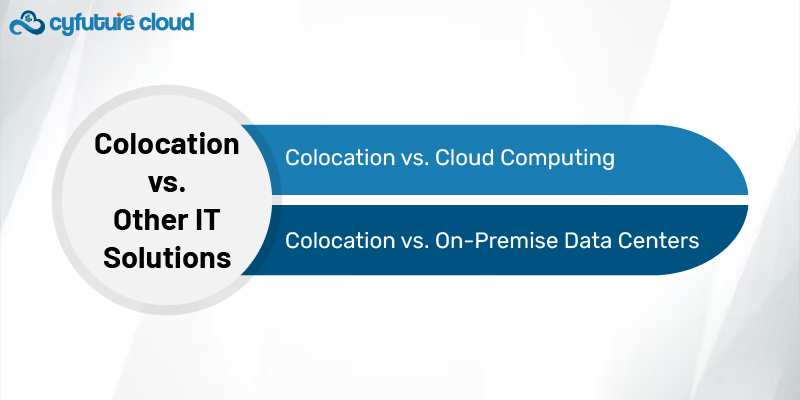
It’s important to understand how colocation compares to other IT infrastructure models:
Colocation vs. Cloud Computing: In cloud computing, businesses rent virtual servers from a provider who manages both the hardware and software. With colocation, businesses maintain control over their physical hardware, which can be crucial for companies with specific performance, compliance, or customization requirements.
Colocation vs. On-Premise Data Centers: While on-premise data centers give businesses full control, they require substantial investments in building, power, cooling, and maintenance. Colocation provides a middle ground, allowing businesses to control their hardware while outsourcing the facility management to experts.
Managed Colocation Hosting businesses with a flexible, cost-efficient, and secure way to manage their IT infrastructure. By leveraging third-party data centers, companies can scale their operations, reduce capital expenditures, and benefit from robust physical security and high availability. For businesses that require control over their hardware but want to avoid the complexities and costs of managing a data center, colocation offers the perfect balance between autonomy and outsourced expertise.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


