 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
 Linux Cloud
Hosting
Linux Cloud
Hosting
 VMware Public
Cloud
VMware Public
Cloud
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
 API Gateway
API Gateway

Google is not just a search engine—it is one of the most powerful technology companies in the world, reshaping how we access knowledge, connect with people, and grow businesses. From its humble beginnings in a Stanford dorm room to becoming a trillion-dollar enterprise under Alphabet Inc., Google has established itself as the backbone of the digital economy.
Whether you’re an individual looking for information or a business leveraging cloud solutions, Google plays a central role in daily life.
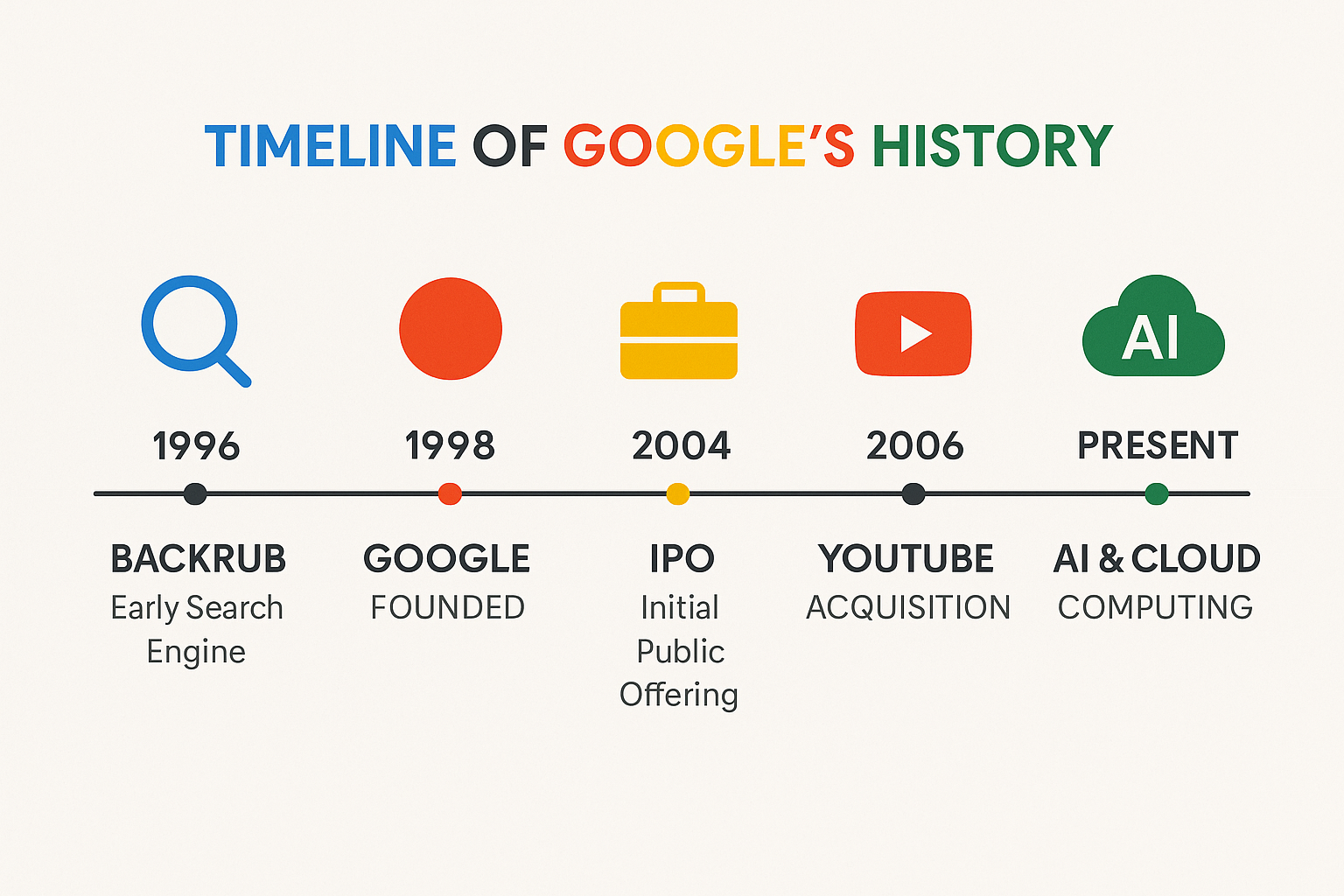
- 1996 – Larry Page and Sergey Brin developed BackRub, a search engine that analyzed website backlinks.
- 1998 – Google Inc. was officially founded. Its mission: “To organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
- 2000 – Launched Google AdWords (now Google Ads), revolutionizing online advertising.
- 2004 – Released Gmail and went public with an IPO, instantly becoming one of the most valuable tech firms.
- 2005 – Acquired Android Inc., laying the foundation for the world’s most popular mobile OS.
- 2006 – Purchased YouTube, transforming digital media.
- 2008 – Launched Google Chrome, now the world’s leading web browser.
- 2015 – Reorganized under Alphabet Inc. to manage diverse business units.
- 2020–Present – Expanded aggressively into AI, cloud computing, and quantum technology.
Google’s offerings can be broadly divided into consumer services, business solutions, and developer platforms.
- Google Search – The world’s #1 search engine with 90%+ market share.
- Gmail – A secure, free, and widely adopted email service.
- Google Maps – Navigation, traffic updates, and location-based services.
- Google Photos – Cloud-based photo storage with AI-powered features.
- YouTube – Largest video platform with over 2.7 billion monthly users.
- Google Chrome – Fast, secure browser with billions of users.
- Android OS – Mobile operating system running on 70%+ smartphones worldwide.
- Google Play Store – App marketplace with millions of apps.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) – Productivity suite including Gmail, Drive, Docs, Sheets, and Meet.
- Google Ads & AdSense – Core of Google’s advertising revenue model.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – Infrastructure, storage, AI, and big data analytics.
- Google Analytics – Website and app performance tracking tool.
- Google Tag Manager – Simplifies marketing and analytics integrations.
- TensorFlow – Open-source AI and machine learning framework.
- Firebase – Backend solutions for mobile and web app development.
- Dialogflow – Conversational AI platform for chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Google Bard (now Gemini) – AI chatbot competing with ChatGPT.
- Quantum Computing Initiatives – Advancing futuristic computational models.
Google’s primary source of revenue is advertising, but its income streams have diversified:
|
Revenue Stream |
Contribution |
Examples |
|
Advertising |
~80% |
Google Ads, YouTube Ads |
|
Cloud Services |
~10% |
Google Cloud Platform, Workspace |
|
Hardware |
~5% |
Pixel smartphones, Nest devices |
|
Other Bets |
~5% |
Waymo (self-driving cars), Verily (life sciences) |
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a fast-growing division competing with AWS and Microsoft Azure. It offers:
- Compute Engine (virtual machines)
- Kubernetes Engine (container orchestration)
- BigQuery (data analytics)
- AI/ML APIs (Vision AI, Speech AI, etc.)
- Security & Compliance Tools
Businesses choose GCP for its AI-driven innovations, flexible pricing, and integration with Google Workspace.
For businesses, Google is the gateway to online visibility.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Ranking on Google Search defines a brand’s digital presence.
- Google Ads: Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns help businesses reach targeted audiences.
- Google Analytics: Data-driven insights optimize marketing strategies.
- YouTube Marketing: Video SEO and ads expand reach globally.
Understanding Google’s algorithms (like PageRank, Panda, Penguin, and Helpful Content Updates) is crucial for anyone in digital marketing.
Despite its success, Google faces global challenges:
- Monopoly Concerns: Accused of dominating online search and ads.
- Privacy Issues: Criticized for data collection and tracking.
- Antitrust Investigations: Ongoing legal scrutiny in the US and EU.
- Misinformation Control: Struggles with fake news and harmful content.
Google’s roadmap is shaped by emerging technologies:
- AI & Generative AI (Gemini, Bard) – Redefining human-computer interaction.
- Quantum Computing – Solving complex problems beyond classical computing.
- Autonomous Vehicles (Waymo) – Pioneering self-driving cars.
- Healthcare & Life Sciences – Through Verily and DeepMind.
- Sustainability – Pledging to operate on carbon-free energy by 2030.
1. What is Google best known for?
Google is best known for its search engine, but it also leads in advertising, cloud computing, mobile OS, and AI.
2. How does Google make money?
Most of Google’s revenue comes from advertising (Google Ads & YouTube Ads), followed by cloud services, hardware, and other innovations.
3. What is Alphabet Inc.?
Alphabet Inc. is Google’s parent company, created in 2015 to manage multiple business units like Waymo, Verily, and DeepMind.
4. What is Google Cloud used for?
Google Cloud is used for hosting, storage, big data analytics, AI, and enterprise-level IT solutions.
5. Why is SEO important for Google?
SEO ensures businesses rank higher in Google search results, improving visibility, traffic, and conversions.

Let’s talk about the future, and make it happen!
By continuing to use and navigate this website, you are agreeing to the use of cookies.
Find out more


