Table of Contents
Are you staying ahead of the curve, or just catching up with the rest?
Let’s face it—cloud computing is no longer a “nice-to-have.” It’s the backbone of almost every industry today, driving innovation and keeping businesses competitive. But here’s the thing: just using the cloud isn’t enough anymore. The real question is—are you tapping into the trends that will shape its future?
If your answer is “not yet” or even “maybe,” don’t worry. You’re in the right place. Cloud computing is evolving so rapidly that keeping up feels like running a race where the finish line keeps moving. But the good news? We’ve researched for you.
Cloud computing has become the backbone of digital transformation, with global spending on cloud services projected to exceed $1.3 trillion by 2025. This rapid growth underscores the critical role of the cloud in driving innovation, efficiency, and scalability across industries.
So,
In this blog, we’ll explore the top 10 cloud computing trends to watch in 2025, highlighting the key innovations and shifts that are set to redefine the cloud industry.
Let’s get started!
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations and individuals manage and access computing resources. In simple terms, cloud computing provides computing resources—such as databases, storage, servers, and software solutions—via the Internet on demand.
This means you can access and utilize powerful computing capabilities without needing to invest heavily in physical infrastructure or data centers. Instead, users only pay for the resources they need, when they need them, and they can scale up or down easily based on demand.
This model provides significant advantages in terms of scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. With cloud computing, all you need is a device with a stable internet connection to access a vast array of computing resources, making it easier than ever for businesses and individuals to perform tasks, store data, and run applications remotely.
Organizations no longer need to maintain complex in-house IT infrastructures. Cloud computing allows them to leverage external servers, networks, and software without the hefty investment in hardware, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Types of Cloud Computing
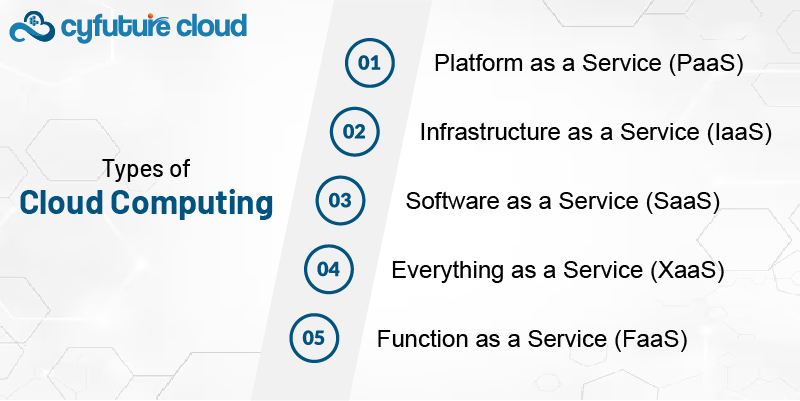
Cloud computing offers several service models that cater to different business and technological needs. These models allow users to select the level of control, flexibility, and management that best suits their requirements. The five main types of cloud computing services are:
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure. This service eliminates the need for developers to manage operating systems, servers, or storage while providing the tools to build custom applications. Examples include Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS offers the most basic level of cloud service. It provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Users have the flexibility to install and manage any software or operating system they choose. With IaaS, businesses avoid the need to invest in physical servers and other hardware. Prominent IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. Instead of downloading and installing software on individual computers, users can access it directly through a web browser. SaaS is ideal for software that needs to be accessed remotely, like email, CRM systems, or collaborative tools. Examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
Everything as a Service (XaaS)
XaaS is a broad term that refers to the delivery of any IT service or resource over the Internet. It includes all the other service models (PaaS, IaaS, SaaS) and can encompass a wide range of offerings, from data storage to advanced AI solutions. XaaS represents the trend of turning everything into a service that can be consumed on-demand, ensuring businesses can access the right tools whenever needed.
Function as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS, also known as serverless computing, takes cloud computing a step further by allowing users to run code in response to specific events without managing the underlying server infrastructure. This “event-driven” approach enables developers to focus solely on writing the code, while the cloud provider takes care of the execution environment. This can be more cost-effective as users only pay for the actual time the code runs. Examples include AWS Lambda and Azure Functions.
Top 10 Cloud Computing Trends in 2025
Discover the top 10 cloud computing trends to watch for in 2025.
Edge Computing Takes Center Stage
Edge computing is about processing data closer to where it is generated rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This trend is gaining traction due to the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and the need for real-time data processing.
- Why it matters: By reducing latency and improving data speed, edge computing enhances user experiences, especially in areas like autonomous vehicles, healthcare devices, and smart cities.
- Impact: It’s expected to complement traditional cloud computing, enabling faster and more efficient data management.
AI-Powered Cloud Solutions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cloud computing are forming a powerful combination. Cloud hosting providers are increasingly embedding AI tools to automate tasks, analyze vast datasets, and deliver smarter solutions.
- Why it matters: AI in cloud computing enables personalized customer experiences, better predictive analytics, and more efficient operations.
- Examples: Platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure offer AI-powered solutions for machine learning, natural language processing, and image recognition.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Organizations are moving towards multi-cloud and hybrid cloud approaches, using multiple cloud providers or combining private and public clouds.
- Why it matters: This strategy helps businesses avoid vendor lock-in, improve redundancy, and optimize costs.
- Impact: Multi-cloud strategies ensure better flexibility and reliability, allowing organizations to choose the best solutions from different providers.
Cloud Security Innovations
As cloud adoption grows, so do security concerns. In 2025, cloud computing trends point to advanced security measures like Zero Trust architecture, AI-driven threat detection, and encrypted data processing.
- Why it matters: Businesses need to protect sensitive data while maintaining compliance with regulations.
- Impact: Cloud providers are investing heavily in tools to enhance security, build trust, and safeguard against cyber threats.
Green Cloud Computing
Sustainability is becoming a key priority for businesses, and cloud providers are stepping up with green initiatives.
- Why it matters: Energy-efficient data centers and renewable energy solutions are reducing the environmental footprint of cloud computing.
- Impact: Companies are increasingly choosing providers that align with their sustainability goals, making green cloud computing a competitive advantage.
Rise of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), eliminates the need for managing underlying server infrastructure.
- Why it matters: Developers can focus purely on code while the cloud provider manages the backend. This trend offers scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Examples: AWS Lambda and Azure Functions allow businesses to execute code only when needed, paying for the actual execution time.
Industry-Specific Cloud Solutions
Cloud providers are offering solutions tailored to specific industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing.
- Why it matters: These specialized solutions address unique challenges and compliance needs, making it easier for businesses to adopt cloud computing.
- Impact: Industry-focused clouds provide better tools and services, boosting efficiency and innovation within sectors.
Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native development focuses on creating applications specifically designed for the cloud using microservices, containers, and Kubernetes.
- Why it matters: These technologies make applications more scalable, reliable, and easier to update.
- Impact: Cloud-native approaches allow businesses to innovate faster and adapt to changing market needs.

Data Sovereignty and Localization
With stricter data privacy regulations worldwide, data sovereignty is a growing concern. Cloud providers are building more localized data centers to comply with regional laws.
- Why it matters: Businesses need to store and process data within specific geographic boundaries to meet legal requirements.
- Impact: Localized cloud solutions ensure compliance while offering faster performance for users in specific regions.
Quantum Computing in the Cloud
Quantum computing is emerging as the next frontier in cloud computing. While still in its early stages, it promises to revolutionize industries with unparalleled computational power.
- Why it matters: Quantum computing can solve complex problems that traditional computers cannot, such as advanced simulations and encryption.
- Impact: Cloud providers like IBM and Google are already offering quantum computing as a service, paving the way for groundbreaking innovations.
Challenges Facing Cloud Adoption in 2025
As cloud computing continues to evolve and expand, businesses face several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure smooth adoption and long-term success. In 2025, three key challenges are expected to stand out: scalability and interoperability, cybersecurity risks, and cost management in complex environments.
Scalability and Interoperability Issues
While cloud computing is celebrated for its scalability, managing rapid growth efficiently remains a significant challenge. Businesses often struggle to seamlessly scale resources without encountering technical bottlenecks or performance issues.
- The Challenge: As organizations adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments, ensuring different platforms and services work together (interoperability) becomes increasingly complex. Lack of standardization across cloud providers can result in integration difficulties.
- Impact: Companies may face delays, higher costs, and limited flexibility when scaling operations or integrating new services.
- Solution: Businesses need to invest in tools and platforms that support cross-cloud compatibility and focus on selecting providers that adhere to global interoperability standards.
Addressing Cybersecurity Risks in an Increasingly Complex Environment
As cloud adoption grows, so does the complexity of securing sensitive data and systems. Cyber security threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and insider threats, are becoming more sophisticated.
- The Challenge: Businesses must safeguard their data while navigating compliance requirements across different regions. Managing security across multi-cloud and hybrid environments adds another layer of complexity.
- Impact: A single vulnerability could lead to data loss, operational disruptions, or reputational damage. With stricter regulations, non-compliance could also result in heavy fines.
- Solution: Implementing advanced security measures such as Zero Trust architecture, AI-driven threat detection, and encryption can help. Regular security audits and employee training are also crucial for mitigating risks.
Managing Costs in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Cloud computing’s pay-as-you-go model is highly appealing, but managing costs across multiple providers or hybrid setups can quickly become overwhelming.
- The Challenge: Organizations often find themselves with underutilized resources, hidden fees, or unexpected expenses due to a lack of visibility into their cloud usage. Balancing costs between public and private clouds in hybrid setups adds another layer of difficulty.
- Impact: Poor cost management can eat into budgets, reducing the financial benefits of cloud computing. This is particularly challenging for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) operating with limited resources.
- Solution: Businesses should use cloud cost management tools that provide detailed insights into resource usage and expenses. Regularly reviewing and optimizing workloads can prevent overspending.
Bottom Line

As we venture further into 2025, it’s clear that cloud computing isn’t just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic imperative. From the rapid evolution of edge computing to the game-changing potential of quantum computing, the trends shaping the cloud industry offer incredible opportunities for businesses to innovate and grow.
However, staying ahead requires more than awareness of trends. It calls for proactive decision-making, strategic investments, and a commitment to overcoming the challenges of scalability, security, and cost management. By understanding the shifting landscape of cloud computing and aligning your business goals with these trends, you can unlock unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Now is the time to act. Whether you’re a tech leader, a business owner, or an industry enthusiast, use these insights to drive meaningful digital transformation and ensure your organization is not just catching up, but leading the way. The future of cloud computing is here—are you ready to embrace it?
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 



















