Table of Contents
- 2. What is Cloud Hosting?
- 3. The Evolution from Traditional Hosting to Cloud Hosting
- 4. How Cloud Hosting Works
- 5. Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting
- 6. Types of Cloud Hosting
- 7. Types of the Websites Using Cloud Hosting
- 8. Challenges and Considerations
- 9. How does Cyfuture Cloud’s cloud hosting solution help you enhance your business operations?
- 10. Steps to Migrate to cloud hosting
- Step 1: Assessment and Planning:
- Step 2: Choose a Cloud Provider:
- Step3: Design Cloud Architecture:
- Step 4: Data Migration:
- Step 5: Application Migration:
- Step 6: Security and Compliance:
- Step 7: Testing:
- Step 8: Training and Documentation:
- Step 9: Deployment and Cut-Over:
- Step 10: Optimization and Cost Management:
- Step 11: Post-Migration Validation:
- Step 12: Continuous Improvement:
- Step 13: Documentation and Knowledge Sharing:
- 11. Future Trends in Cloud hosting
- 12. Embrace the Future with Cloud Hosting
- 13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
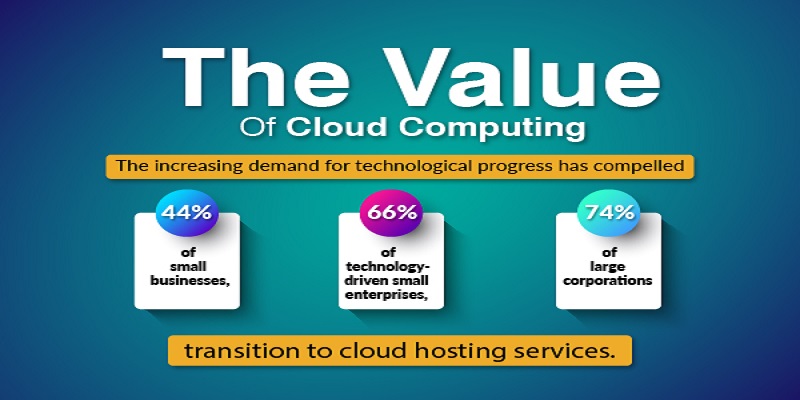
Have you considered how website performance and reliability affect the success or failure of online businesses? If the answer is no, it is time to select how and where to host your website, which is one of the first considerations any new company owner, blogger, or entrepreneur will make. According to the Salesforce survey, 94% of businesses report significant online security improvements after adopting the cloud.
Cloud hosting is like renting space on the internet for your website or software. It’s becoming really popular, and our easy-to-understand guide will help you figure out if it’s a good fit for what you want to do.
In this article, we’ll embark on an enlightening journey into the world of cloud hosting, demystifying its concepts and shedding light on its relevance. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, SMB, or business unicorn, this article will introduce you to the captivating world of cloud hosting. Get ready for an exciting journey into the world of cloud hosting!
2. What is Cloud Hosting?
Before we get into the benefits, features, and types of cloud hosting, it’s important first to grasp what cloud hosting is and how it works. Cloud hosting is a type of hosting service that hosts your website or application on a network of virtual servers. It distributes resources and stores data through a network of interconnected servers.
The purpose of a network of servers is when one server fails, and your website can quickly switch to another server, ensuring that your website remains available and operational.
Cloud hosting also allows you to simply raise or reduce the resources your website requires when traffic fluctuates. Cloud hosting is a popular alternative for organisations of all sizes because it provides a number of advantages that traditional hosting services do not.
When a site takes exceptionally long to load, a visitor will navigate away from it. Then, website loading speed and customer satisfaction are proportionately related. This problem is best tackled by CDN services in India.
According to the Cloud adoption survey, 94% of enterprises use cloud services.
Unlike traditional hosting solutions that rely on a single server, cloud hosting enables businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand.
3. The Evolution from Traditional Hosting to Cloud Hosting
Before delving into the complexities of cloud hosting, it’s critical to understand the context in which this technology arose. Traditional hosting techniques, such as shared hosting and dedicated servers, gave a set allocation of resources, resulting in scalability, flexibility, and uptime limits. As websites and applications began to experience fluctuating traffic, these hosting solutions proved insufficient in meeting the dynamic demands of the digital age.
Have a look at the below table to understand the evolution from traditional to cloud hosting.
|
Aspect |
Traditional Hosting |
Cloud Hosting |
|
Infrastructure Ownership |
Organizations own and maintain physical servers |
Infrastructure is owned and managed by providers |
|
Scalability |
Limited scalability; scaling requires hardware procurement |
Highly scalable; resources can be provisioned on-demand |
|
Resource Allocation |
Fixed resource allocation; typically over-provisioned |
Flexible resource allocation; pay for what you use |
|
Capital Expenditure |
High upfront capital costs for hardware |
Lower upfront costs; pay-as-you-go model |
|
Maintenance and Management |
Organizations are responsible for server maintenance and updates |
Providers handle infrastructure maintenance and updates |
|
Location Dependency |
Server location-dependent; limited geographic reach |
Geographically distributed data centers for global reach |
|
Redundancy and Reliability |
Reliability depends on in-house setup and redundancy |
High redundancy and reliability offered by providers |
|
Disaster Recovery |
Organizations must plan and implement their own disaster recovery solutions |
Cloud service providers frequently include disaster recovery alternatives. |
|
Security |
Security is the responsibility of the organization |
Providers offer robust security features and compliance options |
|
Flexibility and Agility |
Limited flexibility and agility |
Highly flexible and agile; rapid resource provisioning |
|
Downtime |
May experience downtime during maintenance or hardware failures |
High uptime and availability due to redundancy and failover |
|
Cost Structure |
Fixed costs for hardware, maintenance, and IT staff |
Variable costs based on resource usage |
|
Performance |
Performance may degrade under heavy loads |
Performance remains consistent with scalable resources |
|
Software Updates |
Organizations manage software updates and patches |
Providers handle software updates and patching |
|
Accessibility |
Limited remote accessibility |
Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection |
|
Usage-Based Billing |
Not applicable |
Common usage-based billing models |
4. How Cloud Hosting Works
The cloud is essentially a decentralised place where data is exchanged over satellite networks. Every cloud application needs a host, and the hosting business is responsible for maintaining the vast data centres that offer the security, storage capacity, and processing power required to keep any data sent to the cloud safe.
The principle of virtualization is essential to cloud hosting. Virtual machines (VMs) are produced by splitting the resources of a physical server into separate environments capable of running operating systems and applications independently. A hypervisor then manages these VMs, ensuring effective resource allocation and isolation.
In a cloud hosting environment, multiple VMs are distributed across a cluster of interconnected servers. This solution guarantees redundancy and fault tolerance by effortlessly shifting the workload to another server if one fails. This not only improves dependability but also reduces downtime, which is crucial in the digital environment where every second counts.
The resource pooling idea underpins the cloud hosting architecture; rather than allocating specialized resources to individual websites or apps, cloud hosting aggregates a massive pool of computing power, storage, and bandwidth. This shared resource pool is then dynamically allocated based on demand, ensuring that websites and apps get the resources they require at the precise moment they require them.

5. Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting
Easily scalable – Because you’re utilizing a pool of shared resources, scaling your website up or down in accordance with your business requirements is really simple. If you anticipate an increase in traffic, simply contact the customer care staff, and your hosting plan will be raised in no time.
Flexible pricing – In relation to the scalability problem raised above, cloud hosting has a very flexible price structure. Essentially, you will only ever pay for the bandwidth you use, and you will be able to move between different packages as needed simply.
Performance boost – Cloud hosting is a substantial improvement over shared hosting. It’s considerably less likely to have site slowdown since it’s set up to share resources more fairly and has a pool of backup servers to pull from. Furthermore, it prevents other websites that share your server space from grabbing all of the resources during surges.
Redundant servers – In a shared hosting environment, if your server goes down, your website goes down. Fortunately, in a cloud environment, if one server fails, your site will continue to function by moving to another cloud server. In many cases, you may even migrate to servers situated in a different data centre, considerably boosting the robustness of your business’s continuity.
Access to expert customer service – When you choose cloud hosting, you have a team of specialists who look after your website on a daily basis. They ensure its security and maintain the programme up to date. This means you won’t have to worry about hosting your website and can instead focus on growing your company.
Quick deployment – Cloud hosting options are extremely simple to use, and you can have your website up and running in no time. That is why many individuals, whether they are new to website ownership or have been doing it for a long, choose cloud hosting.
Almost unlimited storage capacity – One of the best features of a cloud arrangement is the ability to expand your storage needs at any time, and the process is quick and straightforward.
6. Types of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting service that is built on a network of virtual servers that are hosted on a cloud infrastructure such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, or Cyfuture Cloud.
These virtual servers may be quickly scaled up or down based on demand, and they come with a variety of capabilities and configurations to fit the demands of a variety of applications and businesses. There are several types of cloud hosting, each catering to a distinct set of requirements:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- IaaS is the most basic form of cloud hosting.
- According to the survey, 67% of enterprise infrastructure is now cloud-based.
- It delivers virtualized computer resources such as storage, virtual machines, and networking through the internet.
- Users have complete control over the operating system, applications, and configurations, making it ideal for enterprises that require infrastructure management.
- Examples: Azure Virtual Machines, AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- PaaS extends cloud hosting by providing developers with a platform and environment to design, deploy, and manage applications without concern for the underlying infrastructure.
- It separates server administration and provides development, testing, and deployment tools.
- Ideal for developers and teams looking to streamline application development and deployment.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- According to 79% of survey respondents, the most popular cloud deployment choice among Indian enterprises is software-as-a-service (SAAS).
- SaaS is a cloud hosting paradigm that delivers it via the internet.
- Users access the programme via web browsers, and the supplier is in charge of all maintenance, upgrades, and infrastructure.
- Commonly used for productivity apps like email, CRM, and collaboration tools.
- Examples: Gmail, Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365.
Function as a Service (FaaS) or Serverless Computing:
- FaaS enables developers to execute code in response to events without having to manage servers or infrastructure.
- Code execution is triggered by events, and you’re billed based on the actual compute resources used during execution.
- Suitable for event-driven applications and microservices.
Container as a Service (CaaS):
- CaaS is a platform for managing containerized applications that makes use of technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes.
- It abstracts the infrastructure while allowing developers to package and deploy applications in containers.
- Provides scalability and flexibility for container-based deployments.
- Examples: Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
Database as a Service (DBaaS):
- DBaaS offers fully managed database services in the cloud, reducing the administrative overhead of database management.
- It includes various database types such as SQL, NoSQL, and NewSQL databases.
- Ideal for organizations looking to offload database maintenance tasks.
- Examples: AWS RDS, Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL.
7. Types of the Websites Using Cloud Hosting
E-commerce stores
- E-commerce websites, which sell products or services online, often experience fluctuating levels of traffic.
- Cloud hosting allows e-commerce stores to scale their resources up during busy periods (like holidays) and scale down during quieter times, ensuring a smooth shopping experience for customers.
- It provides high availability and reliability, crucial for maintaining sales and customer satisfaction.
News publications
- News websites need to handle unpredictable traffic spikes, especially during breaking news events.
- Cloud hosting enables news publications to quickly and automatically allocate more resources when traffic surges, preventing downtime and ensuring news is delivered promptly to readers.
Search engines
- Search engines process vast amounts of search queries and data requests daily.
- Cloud hosting’s scalability and distributed infrastructure allow search engines to handle enormous workloads efficiently.
- Cloud-based search engines can also leverage AI and machine learning for better search results.
Social networks
- Social networks link millions of people throughout the world, and their traffic may be unpredictable.
- Cloud hosting helps social networks manage user data, media files, and real-time interactions while dynamically adjusting resources to accommodate heavy usage patterns.
- It supports features like instant messaging, video sharing, and personalized content delivery.
Any other high-traffic projects
- High-traffic projects encompass a wide range of websites, including streaming platforms, gaming communities, and collaborative tools.
- Cloud hosting is ideal for such projects due to its ability to handle sudden traffic spikes, provide global reach, and offer robust security features.
- Projects can scale resources up or down as needed to match user demand.
Cloud hosting is ideal for any website that requires a large amount of bandwidth, computing power, RAM, and other resources.
The cloud hosting design makes it easy to foresee traffic surges that occur during e-commerce website sales or when a blog post goes viral, causing the website’s traffic to increase. However, the traffic does not exhaust the resources of the virtual servers.
Furthermore, many websites require increased security to protect business-critical and private data such as payment information and client information. In this instance, a customer can also choose private cloud hosting, which provides specialised cloud infrastructure as well as a private network.
8. Challenges and Considerations
Here’s a tabular breakdown of some common challenges and considerations associated with cloud hosting, along with suitable solutions:
|
Challenge/Consideration |
Solution(s) |
|
1. Security and Compliance |
|
|
2. Data Privacy |
|
|
3. Downtime and Availability |
|
|
4. Scalability and Performance |
|
|
5. Data Backup and Recovery |
|
|
6. Cost Management |
|
|
7. Vendor Lock-In |
|
|
8. Performance Monitoring |
|
|
9. Compliance and Governance |
|
|
10. Data Transfer Costs |
|
9. How does Cyfuture Cloud’s cloud hosting solution help you enhance your business operations?
Agility and Scalability: At Cyfuture Cloud, we provide organizations with the agility to rapidly respond to changing market demands. Businesses may scale their operations up or down as needed by using our cloud resources, eliminating the need for large upfront expenditures. This flexibility enables companies to embrace fresh opportunities, create innovative products, and quickly adjust to market changes.
Cost Efficiency: We allow businesses to optimize their IT costs by allowing them to adopt our pay-as-you-go model. With cloud-based services, organizations pay only for the resources they consume, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure maintenance and reducing capital expenses. According to a BusinessWire report, 82% of small and medium businesses report reduced costs after adopting cloud tech.
Furthermore, we enable efficient resource allocation, ensuring businesses use their cloud resources optimally, minimizing wastage and maximizing cost savings.
Enhanced Collaboration and Accessibility: Our cloud hosting services enable cross-team and cross-departmental cooperation and information exchange. Our cloud-based applications and storage allow employees to access data and work collaboratively from anywhere, facilitating remote work arrangements and global teams. This increased accessibility and cooperation encourages creativity, productivity, and effective decision-making. The performance of your website is also enhanced by the Cyfuture Cloud’s CDN services in India.
Robust Security and Data Protection: We incorporate robust security measures and data protection protocols through our cloud hosting solutions. We invest heavily in ensuring security and integrity and offer advanced encryption, identity management, and multi-factor authentication. Businesses may use Cyfuture Cloud to use these security capabilities while offloading the burden of managing security infrastructure, enabling them to focus on their core strengths.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: We play a pivotal role in establishing robust business continuity and disaster recovery plans. By leveraging the cloud’s distributed infrastructure and backup capabilities, organizations can ensure their critical data and applications are secure and recoverable in the event of a disaster or system failure. We empower businesses to replicate and back up data across multiple regions, providing resilience and peace of mind.
10. Steps to Migrate to cloud hosting
Migrating to cloud hosting can be a difficult process, but with appropriate strategy and execution, it can be a simple move. The following are the typical stages for migrating to cloud hosting:
Step 1: Assessment and Planning:
- Assess your current IT infrastructure, applications, and data to determine what should be moved to the cloud.
- Categorize workloads and applications based on their criticality and complexity.
- Define your migration strategy and objectives, including specific goals and timelines.
Step 2: Choose a Cloud Provider:
- Choose a cloud provider that meets your organization’s requirements, such as Cyfuture Cloud.
- Consider factors like service offerings, pricing, compliance requirements, and geographic regions.
Step3: Design Cloud Architecture:
- Create a cloud architecture that supports your workloads, applications, and security requirements.
- Decide on network configurations, security policies, data storage solutions, and disaster recovery plans.
Step 4: Data Migration:
- Plan and execute the migration of your data to the cloud. This may involve transferring files, databases, or other data sources.
- Use data transfer services or tools provided by the cloud provider to move data securely.
- Verify data integrity and consistency after migration.
Step 5: Application Migration:
- Choose the appropriate migration method for each application:
- Rehost (lift and shift): Move applications to the cloud with minimal changes.
- Refactor (replatform): Modify applications to make them cloud-native.
- Rearchitect (rewrite): Completely rebuild applications for the cloud.
- Test applications thoroughly in the cloud environment.
Step 6: Security and Compliance:
- Encryption, access restrictions, and identity management are examples of security measures that should be implemented.
- Ensure that industry rules and best practices are followed.
- Regularly monitor and audit your cloud environment for security and compliance.
Step 7: Testing:
- Conduct comprehensive testing of your workloads and applications in the cloud environment.
- Perform load testing, functional testing, and disaster recovery testing to ensure reliability.
Step 8: Training and Documentation:
- Train your IT team and end-users on how to use and manage the new cloud infrastructure and tools.
- Create documentation for operating and maintaining cloud resources.
Step 9: Deployment and Cut-Over:
- Schedule a migration window during low-traffic periods.
- Execute the migration plan, monitoring closely for any issues.
- Complete the cut-over process, making the cloud resources live.
Step 10: Optimization and Cost Management:
- Continuously monitor resource utilization and costs.
- Optimize resources by adjusting capacity as needed.
- Implement cost management practices to avoid unexpected charges.
Step 11: Post-Migration Validation:
- Validate that all workloads and applications are functioning as expected.
- Conduct user acceptance testing to ensure end-users are satisfied.
- Address any post-migration issues promptly.
Step 12: Continuous Improvement:
- Continuously assess and optimize your cloud environment.
- Stay updated with cloud provider offerings and best practices.
Step 13: Documentation and Knowledge Sharing:
- Maintain documentation for configurations and procedures.
- Share knowledge and experiences within your organization for future reference.
Cloud migration is a complex process, and the specific steps and considerations may vary depending on your organization’s unique needs and goals. It’s important to have a well-thought-out plan and engage with experienced cloud professionals or consultants if needed to ensure a successful migration.
11. Future Trends in Cloud hosting
To satisfy the changing demands of businesses and organisations, the cloud hosting sector is dynamic and constantly evolving. Here are some future trends in cloud hosting that are expected to shape the industry:
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source of data generation (e.g., IoT devices), reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making. Edge cloud providers are emerging to support these requirements, enabling low-latency applications and services.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: Many organizations are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to diversify their cloud providers, avoid vendor lock-in, and optimize cost and performance. Managing workloads across multiple cloud platforms will become more common.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless architectures, such as AWS Lambda and Azure Functions, will continue to gain popularity. They offer event-driven, cost-effective computing without the need to manage servers, making them ideal for microservices and scalable applications.
- Containers and Kubernetes: Containerization and orchestration using tools like Docker and Kubernetes will remain a dominant trend. Containers enable portability, scalability, and efficient resource utilization, making them suitable for modern cloud-native applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML services are being integrated by cloud providers, making it easier for organisations to design and deploy AI-driven applications. These services will continue to evolve and become more accessible.
- Data Analytics and Big Data: Cloud platforms provide robust data analytics and big data solutions. The demand for real-time data processing and analytics, as well as the use of AI for insights, will drive future breakthroughs in this sector.
- Zero Trust Security: As cyber threats continue to evolve, the Zero Trust security model, which assumes no trust within or outside the network, will become more important. IAM (identity and access management) will be critical in safeguarding cloud settings.
- Serverless Databases: Serverless database services like AWS Aurora Serverless and Azure Cosmos DB will simplify database management and scaling, allowing businesses to focus on application development rather than database administration.
- Edge AI: Combining edge computing with AI, Edge AI enables real-time, intelligent decision-making at the edge of the network. This is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, robotics, and IoT.
- Quantum Computing in the Cloud: While still in its infancy, quantum computing is making its way to the cloud. Cloud providers are beginning to offer access to quantum computing resources, opening up new possibilities for solving complex problems.
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS): Blockchain technology is being integrated into cloud platforms, enabling businesses to experiment with blockchain applications without setting up and managing their own nodes.
- Green Cloud Hosting: Sustainability and environmental concerns will drive the adoption of green cloud hosting. Cloud providers are making efforts to reduce their carbon footprint and offer renewable energy-powered data centers.
- 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G networks will facilitate faster and more reliable connections to cloud services, enabling low-latency applications and expanding the possibilities of IoT and edge computing.
These trends reflect the ongoing evolution of cloud hosting to meet the demands of modern businesses and technologies. Staying informed about these developments can help organizations make strategic decisions about their cloud hosting strategies and investments.
12. Embrace the Future with Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is revolutionizing the web hosting industry by providing unmatched scalability, flexibility, and performance. With its ability to handle varying levels of traffic, ensure high availability, and deliver lightning-fast website speeds, cloud hosting has become the go-to solution for businesses of all sizes.
Businesses can unlock the full potential of their websites, improve user experience, and remain competitive in the digital world by embracing cloud hosting. Embrace the potential of cloud hosting to catapult your online presence into the future.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the purpose of cloud hosting?
The capacity to make apps and websites available on the internet via the cloud is referred to as cloud hosting. Cloud hosting aggregates computing resources from a network of virtual and real servers, providing increased scalability and the ability to make changes fast.
What are the requirements for cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting refers to the ability to make software and websites available on the internet via the cloud. Cloud hosting pools computing resources from a network of virtual and physical servers, enabling better scalability and the ability to make changes fast.
Is cloud hosting beneficial for small businesses?
Cloud hosting can help businesses save time and money by boosting productivity, improving collaboration and promoting innovation.
Is cloud hosting cost-effective?
Cloud storage is significantly more cost-effective because cloud providers manage storage infrastructure for their users. Cloud storage consumers often pay a fixed amount for their storage rather than paying for hardware acquisition, installation, and associated charges.
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 





















