Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud- What is the basic Difference?
Table of Contents
In today’s digital world, cloud computing has transformed how businesses manage their IT needs. Two main types of cloud setups—private and public—offer distinct ways to store, process, and access data.
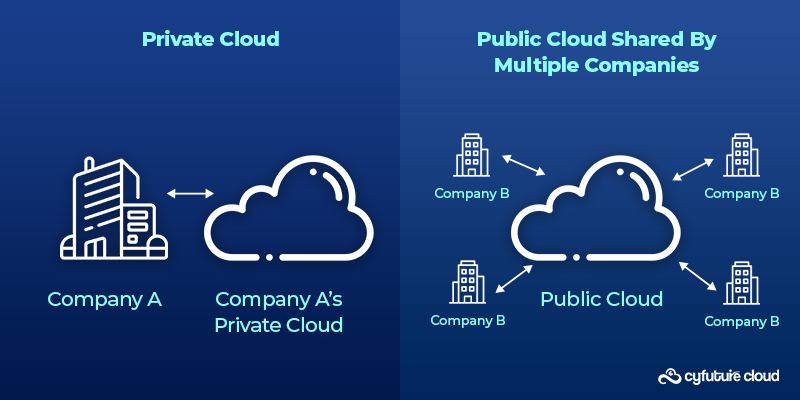
Private Clouds are dedicated systems used exclusively by one organization. They provide strong control over security and can be customized to fit specific needs. Companies that require high levels of security or have strict rules about how data is handled often choose this setup.
Public Clouds, on the other hand, are shared systems provided by companies like AWS or Google Cloud. They offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness because resources are shared among many users. Public clouds are popular with startups and small businesses looking for scalable solutions without large upfront costs.
In this blog, we’ll explain the key difference between private cloud vs public cloud.
Let’s get started!
Public cloud
In a public cloud model, cloud resources and services are provided by a third-party cloud service provider (CSP) and distributed online via a subscription model, such as platform-as-a-service (PaaS), infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), or software-as-a-service (SaaS) (SaaS). In this model, the cloud provider owns, operates, and maintains all of the hardware, software, and other supporting cloud infrastructure, which is then shared with other users. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are a few examples of public clouds (GCP)
Advantages:
- Savings: Since they don’t have to buy, run, or maintain hardware or software, enterprises using a public cloud model typically incur cheaper IT expenditures. Additionally, because the majority of cloud computing plans are based on consumption pricing, businesses only pay for the resources they really utilize.
- Limited maintenance: All cloud environment and related asset maintenance is the responsibility of the public cloud provider.
- Scalability: Businesses that use the public cloud can easily scale workloads up or down in accordance with their operational requirements and have access to nearly endless cloud computing resources on demand.
Reliability: In the event of a failure or other performance issue, workloads in the public cloud can be swiftly transferred from one server to another.
Disadvantages:
- Security: The public cloud model uses a shared responsibility approach or SRM. This means that while a third-party service provider keeps an eye out for threats to the cloud infrastructure and takes appropriate action, they are not in charge of protecting the data, applications, workloads, or operating systems of individual clients. The consumer alone is responsible for that effort. Many customers might not be aware of their part in the shared responsibility model, and they might not have embraced reliable cybersecurity procedures tailored to the cloud. Companies that use the public cloud are likewise exposed to security vulnerabilities caused by other tenants because it is a shared resource.
- Compliance: Due to the multi-tenancy issue, certain firms may find it difficult or impossible to comply with tight regulatory compliance norms in a public cloud environment.
Visit Cyfuture.Cloud to learn more
Private Cloud
A private cloud, also known as an on-premises private data center, is a type of cloud computing where a single entity has exclusive access to the cloud, its services, and the infrastructure that goes along with them. Even while a CSP may still host a private cloud, its resources are always reserved for just one user.
The majority of companies that need highly adaptable and secure IT environments employ private clouds. For instance, private clouds are frequently utilized by institutions like financial institutions, hospitals, and government agencies that manage sensitive data and are held to high compliance standards.
Advantages:
- Privacy As the name suggests, a single tenant has total control over the cloud environment because the private cloud is not shared with other tenants.
- Security: As long as the user has adopted a thorough security policy specifically tailored for the cloud, the private cloud tends to provide far greater control, privacy, and security because it is not shared with any other users.
- Customization: In a private cloud model, businesses have total control over their cloud environment and can alter their network to suit their own business requirements or adhere to legal requirements.
- Performance: The private cloud offers better performance for most users because it is not a shared resource.
Disadvantages: - Cost: Using a private cloud almost always costs more than using a public cloud because the company must either develop and manage its own network in-house or pay a third party to do it for them.
- IT burden: To set up, run, and maintain the cloud environment, the majority of private cloud users need significant IT resources.
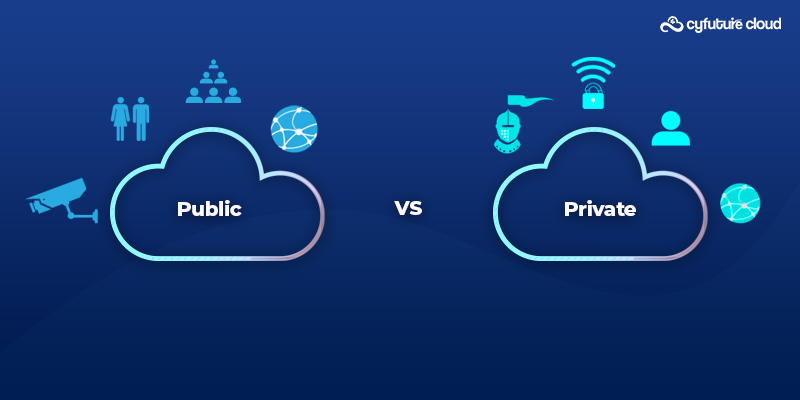
Difference Between Public and Private Cloud
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned and managed by a third-party service provider. | Owned and managed by the organization or a dedicated provider. |
| Accessibility | Accessible via the internet from anywhere. | Accessible within an organization’s data center or through a secured network. |
| Resource Sharing | Shared infrastructure with multiple users. | Dedicated infrastructure for exclusive use. |
| Cost Structure | Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing. | Higher upfront costs, but more predictable expenses. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable to meet variable workloads. | Scalable, but typically with limitations based on dedicated resources. |
| Customization | Limited customization options. | Extensive customization and configuration. |
| Control | Less control over infrastructure and security. | Greater control over infrastructure, security, and compliance. |
| Security | Security measures managed by the service provider. | Organization has more control over security measures. |
| Compliance | Compliance may be more challenging to achieve. | Easier to implement and maintain compliance standards. |
| Use Cases | Suited for cost-effective, flexible, and less sensitive workloads. | Ideal for sensitive data, compliance requirements, and specific use cases. |
How Do Hybrid Clouds Work?
Due to the inherent benefits (and drawbacks) of private and public cloud models, many businesses are turning more and more to the hybrid cloud model, which is an IT setting that combines components of a public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises infrastructure into a single, universal architecture. Organizations may run and scale workloads in the best environment in a hybrid cloud environment, and they also have the freedom to swiftly and simply migrate workloads across various environments.
A hybrid cloud architecture, for instance, enables businesses to use the public cloud for high-volume, low-risk tasks like hosting web-based programs like email or instant messaging. While this is going on, the private cloud can be set aside for tasks that need more protection, such as handling payments or keeping personal information. By doing this, the company is able to take advantage of the public cloud’s financial benefits while simultaneously upholding a higher standard of security or compliance for some tasks.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
Many enterprises can benefit from the “best of both worlds” with a hybrid cloud architecture. Benefits include
- Flexibility: A hybrid cloud computing paradigm enables the company to execute a workload in the best environment while also allowing it to be moved dependent on pricing, capacity, or demand.
- Cost-effectiveness: In a hybrid architecture, businesses can reduce expenses by choosing the most appropriate computing environment for each activity.
- Elasticity: A hybrid cloud infrastructure is dynamic, which enables resources to be swiftly changed and distributed in accordance with the demands of the moment. Furthermore, the company can handle demand spikes using a public cloud service in the event of unanticipated ones.
- Business Agility: By increasing the use of Agile and DevOps processes, a unified hybrid cloud platform helps speed up time to market.
- Improved Security and Compliance: An integrated hybrid cloud platform enables the organization to adopt a comprehensive strategy for cybersecurity and legal compliance. Companies can create a complete plan and implement tooling uniformly throughout the entire environment because they are operating in a single IT environment. A hybrid cloud strategy also makes sure that the company correctly hosts sensitive data, such as customer or patient records, in a private cloud setting as required by laws or industry standards.
Take Away:
That’s It!
This guide has provided you with a clear difference between private cloud vs public cloud
A number of variables use cases, and constraints influence the decision between public, private, and hybrid cloud systems. Real-world enterprises typically use all three types of cloud solutions due to their unique value propositions, thus, this is rarely an either/or problem.
Even though you probably already utilize the cloud, it is worthwhile to create a deliberate cloud strategy to make the most of each cloud environment. Prioritize your workloads by first identifying their requirements and then weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 


















