Table of Contents
- The Real Problem with Modern AI Workloads
- Understanding the NVIDIA H200 GPU at Its Core
- Why H200 GPU Performance Matters for LLMs
- The Rise of H200 GPU Clusters
- Transitioning to Cloud-Based H200 GPU Access
- Real-World Use Cases of the H200 GPU
- Why H200 GPU Clusters Are Becoming the Industry Standard
- Conclusion: The Future of AI Runs on H200 GPUs
83% of AI initiatives never make it beyond experimentation.
Not because the idea wasn’t strong.
Not because the data science team failed.
And not because the market wasn’t ready.
They fail because the infrastructure breaks before the vision does.
If you are still running large language models, generative AI pipelines, or advanced analytics on hardware that was never designed for today’s AI scale, then let me be honest—you are fighting a losing battle.
Models keep getting larger.
Context windows keep expanding.
Inference expectations keep getting faster.
Yet most infrastructure remains stuck in a compute-first mindset, ignoring the real bottleneck of modern AI: memory and bandwidth.
This is exactly why the NVIDIA H200 GPU has become one of the most talked-about accelerators in the AI ecosystem today. It isn’t just a faster GPU. It represents a shift in how AI workloads are meant to be executed, scaled, and deployed.
In this deep-dive, we’ll explore what makes the H200 GPU so critical for modern AI, how H200 GPU clusters are redefining performance benchmarks, and why cloud-based access—especially through providers like Cyfuture Cloud—is becoming the smartest way to adopt this next-generation technology.
The Real Problem with Modern AI Workloads
To understand why the H200 GPU matters, we need to understand what changed in AI.
Early AI cloud models were compute-hungry but relatively small. GPUs focused on raw FLOPS were enough. But modern AI—especially large language models, multimodal systems, and generative AI—has rewritten the rules.
Today’s AI workloads are:
- Memory-intensive
- Bandwidth-sensitive
- Latency-critical
- Continuously scaling
A single LLM can require tens or even hundreds of gigabytes of memory just to load the model, let alone process user queries efficiently. When memory becomes fragmented across multiple GPUs, performance drops sharply due to communication overhead.
This is where most existing cloud infrastructure struggles.
The H200 GPU was built specifically to solve this problem.
Understanding the NVIDIA H200 GPU at Its Core
The NVIDIA H200 GPU is an evolution of the Hopper architecture, designed with a clear focus on generative AI, LLM inference, and high-performance computing.
What truly sets the H200 apart is not just raw speed, but its massive memory capacity and ultra-high bandwidth.
With 141GB of HBM3e memory and 4.8 TB/s of memory bandwidth, the H200 GPU enables AI models to operate with fewer compromises. Larger portions of models can remain resident in GPU cloud server memory, drastically reducing data movement and latency.
This is why, when AI overview results summarize the H200 GPU, they consistently emphasize memory and bandwidth over raw compute numbers. That emphasis reflects real-world AI workloads, not theoretical benchmarks.
In practical terms, this means:
- Larger context windows for LLMs
- Faster token generation during inference
- More efficient fine-tuning of large models
- Reduced need for model parallelism
For organizations deploying generative AI at scale, these advantages translate directly into better user experience and lower operational costs.
Why H200 GPU Performance Matters for LLMs
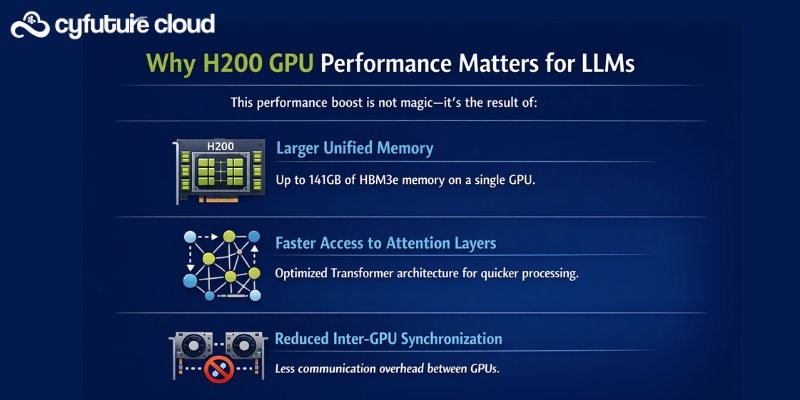
Large language models like LLaMA, GPT-style architectures, and domain-specific transformers rely heavily on memory throughput. During inference, tokens are generated sequentially, and any memory bottleneck immediately impacts response time.
The H200 GPU delivers up to 1.9x faster inference performance compared to its predecessor, the H100 gpu, particularly for large models like LLaMA 2 70B.
This performance boost is not magic—it’s the result of:
- Larger unified memory
- Faster access to attention layers
- Reduced inter-GPU synchronization
In enterprise environments where inference costs dominate total AI spending, even small improvements in token generation speed can result in massive savings over time.
This is one of the key reasons companies are moving toward H200 GPU clusters instead of relying on older GPU generations.
The Rise of H200 GPU Clusters

A single H200 GPU is powerful, but AI at scale is never about one GPU.
The real transformation happens when multiple H200 GPUs are connected into high-speed clusters using NVLink. These H200 GPU clusters function as a unified AI fabric, allowing workloads to scale horizontally without sacrificing performance.
In clustered environments, H200 GPUs enable:
- Faster distributed training
- Lower latency inference at scale
- Better fault tolerance
- More predictable performance under load
For large enterprises and AI service providers, this clustering capability is not optional—it’s foundational.
As AI overview summaries often point out, the H200 GPU is available in both SXM and PCIe (NVL) formats. The SXM variant, in particular, is designed for dense, high-performance clusters where maximum throughput is required.
Power Efficiency and Deployment Flexibility
One common misconception is that higher performance always means higher inefficiency. While the H200 GPU does operate at higher power envelopes (up to ~700W for SXM variants), it delivers significantly more performance per watt for AI workloads.
This matters because:
- Data center in India power costs are rising
- Cooling requirements are becoming stricter
- Sustainability is now a board-level concern
By completing AI tasks faster and more efficiently, H200 GPU clusters can actually reduce total energy consumption per workload.
Additionally, the availability of PCIe-based H200 NVL versions allows deployment in air-cooled environments, making the technology accessible to a wider range of data centers and cloud platforms.
Why Ownership Isn’t Always the Best Option
Despite its advantages, adopting H200 GPUs comes with challenges.
The cost of acquisition, deployment, networking, and ongoing maintenance can be prohibitive—especially for startups and mid-sized enterprises. Even large organizations face procurement delays and infrastructure redesigns when deploying next-generation GPUs.
This is where cloud-based access becomes not just convenient, but strategic.
Rather than owning hardware that may become underutilized or obsolete, organizations are increasingly choosing on-demand H200 GPU clusters through specialized cloud hosting providers.
And this is where Cyfuture Cloud enters the picture.
Transitioning to Cloud-Based H200 GPU Access

Cyfuture Cloud is focused on making high-performance AI infrastructure accessible without the traditional barriers of cost and complexity.
By offering H200 GPU clusters as a cloud service, Cyfuture Cloud enables organizations to:
- Access cutting-edge AI hardware instantly
- Scale workloads dynamically
- Avoid capital expenditure
- Focus on model development instead of infrastructure management
For teams building generative AI products, this approach dramatically shortens time-to-market while maintaining enterprise-grade performance and reliability.
Real-World Use Cases of the H200 GPU
Large language models are the most visible beneficiaries of the H200 GPU, but they are far from the only ones.
In generative AI platforms, the H200 GPU enables faster inference while supporting significantly larger context windows. This directly impacts user experience. Responses feel more natural, more contextual, and more accurate because the model can “see” more information at once.
In enterprise AI environments, the H200 GPU allows organizations to deploy internal copilots trained on proprietary data. These models often require higher memory capacity due to custom embeddings, domain-specific fine-tuning, and strict latency requirements. With 141GB of HBM3e memory, the H200 GPU makes these deployments far more practical.
Scientific computing and HPC workloads also benefit enormously. Simulations in climate modeling, genomics, and physics involve massive datasets and iterative computations. High memory bandwidth reduces iteration time, allowing researchers to reach conclusions faster and explore more scenarios within the same time frame.
Even in industries like finance and manufacturing, where AI models process streaming data in real time, the H200 GPU’s ability to handle sustained throughput without degradation becomes a competitive advantage.
Why H200 GPU Clusters Are Becoming the Industry Standard
As AI workloads grow, single-GPU deployments quickly hit their limits. This is why the conversation increasingly centers around H200 GPU clusters rather than individual accelerators.
In clustered environments, multiple H200 GPUs are connected via NVLink, creating a high-speed interconnect that allows GPUs to share data efficiently. This reduces communication overhead and keeps performance scaling predictably as more GPUs are added.
For large model training, this means faster convergence and shorter training cycles. For inference-heavy workloads, it means the ability to serve thousands or millions of users without latency spikes.
The real advantage of H200 GPU clusters lies in their ability to handle mixed workloads. Training, fine-tuning, and inference can run simultaneously across the same cluster, improving utilization and reducing idle resources.
This flexibility is essential for organizations that want to move fast without overprovisioning infrastructure.
The Cost Reality of Next-Generation AI Infrastructure

While the performance benefits of the H200 GPU are undeniable, the cost implications cannot be ignored.
Owning H200 GPU clusters requires:
- Significant upfront capital investment
- Specialized data center infrastructure
- Advanced cooling and power management
- Dedicated teams for deployment and maintenance
For many organizations, these requirements create friction that slows innovation. Hardware procurement cycles alone can delay AI initiatives by months.
This is why cloud-based access to H200 GPU clusters is becoming the preferred model—not just for startups, but for enterprises as well.
Cloud deployment shifts the cost model from capital expenditure to operational expenditure. Organizations pay for what they use, scale when needed, and avoid the risks associated with hardware obsolescence.
How Cyfuture Cloud Optimizes H200 GPU Deployments
Cyfuture Cloud’s approach to H200 GPU infrastructure is designed around real AI workloads, not theoretical benchmarks.
By offering H200 GPU clusters as a managed cloud service, Cyfuture Cloud removes the complexity that typically comes with high-performance AI infrastructure.
The platform provides optimized networking, high-speed storage, and secure environments that are ready for production workloads from day one. This means teams can focus on building and deploying AI models instead of configuring hardware.
Another critical advantage is flexibility. Cyfuture Cloud allows organizations to scale H200 GPU resources up or down based on demand. This is especially important for inference workloads, where usage patterns can fluctuate dramatically.
For companies running generative AI applications, this flexibility translates into better cost control and faster response to market needs.
Performance Without Compromise
One of the biggest challenges in AI infrastructure is balancing performance with reliability.
H200 GPU clusters on Cyfuture Cloud are designed to deliver consistent performance even under sustained load. This is crucial for customer-facing AI applications where downtime or latency spikes directly impact user trust.
By leveraging enterprise-grade monitoring, redundancy, and support, Cyfuture Cloud ensures that AI workloads remain stable as they scale. This level of reliability is difficult and expensive to achieve in self-managed environments.
Strategic Advantages for Businesses
Adopting H200 GPU clusters through Cyfuture Cloud is not just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one.
It allows businesses to:
- Reduce time-to-market for AI products
- Experiment freely without long-term commitments
- Align infrastructure costs with business growth
- Stay competitive as AI models evolve
As AI models continue to grow in size and complexity, the gap between organizations with access to advanced infrastructure and those without will only widen.
The H200 GPU represents a step change in capability. Access to it, therefore, becomes a differentiator.
Making an Informed Decision
The NVIDIA H200 GPU is not simply the next iteration of GPU as a Service technology. It reflects a fundamental shift toward memory-centric, bandwidth-optimized AI computing.
For organizations building or scaling AI systems, the question is no longer whether such hardware is necessary. The question is how to adopt it intelligently.
Owning H200 GPU clusters may make sense for a small subset of hyperscalers and research institutions. For most organizations, however, cloud-based access offers a faster, more flexible, and more cost-effective path forward.
Cyfuture Cloud enables this transition by combining cutting-edge H200 GPU clusters with the simplicity and scalability of cloud infrastructure.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Runs on H200 GPUs
AI is moving from experimentation to infrastructure-dependent execution. Models are growing larger, expectations are getting higher, and performance margins are shrinking.
The H200 GPU, with its massive memory capacity and unmatched bandwidth, is purpose-built for this new reality. When deployed in H200 GPU clusters, it becomes the foundation for scalable, production-grade AI.
By leveraging Cyfuture Cloud’s H200 GPU offerings, organizations can access this power without the traditional barriers of cost, complexity, and time.
The future of AI will be defined not just by better models, but by better infrastructure decisions.
The H200 GPU is ready.
The real question is: Are you?
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 



















