Table of Contents
- Are You Struggling to Find the Right Infrastructure for Your AI Workloads?
- Introduction: The AI Infrastructure Revolution
- What Are Dedicated Servers for AI Workloads?
- The GPU Revolution: Why Graphics Cards Became AI Powerhouses
- Server Colocation: The Strategic Middle Ground
- The 2026 AI Server Market Landscape
- Why Dedicated GPU Servers Outperform Cloud for AI
- Cyfuture Cloud: Powering AI Innovation Through Advanced Infrastructure
- Emerging Trends Reshaping AI Infrastructure in 2026
- Challenges and Solutions in AI Server Deployment
- Accelerate Your AI Journey with the Right Infrastructure
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 1. What is the difference between dedicated GPU servers and cloud GPU instances?
- 2. Why is server colocation ideal for AI workloads?
- 3. How much does it cost to deploy dedicated GPU servers for AI?
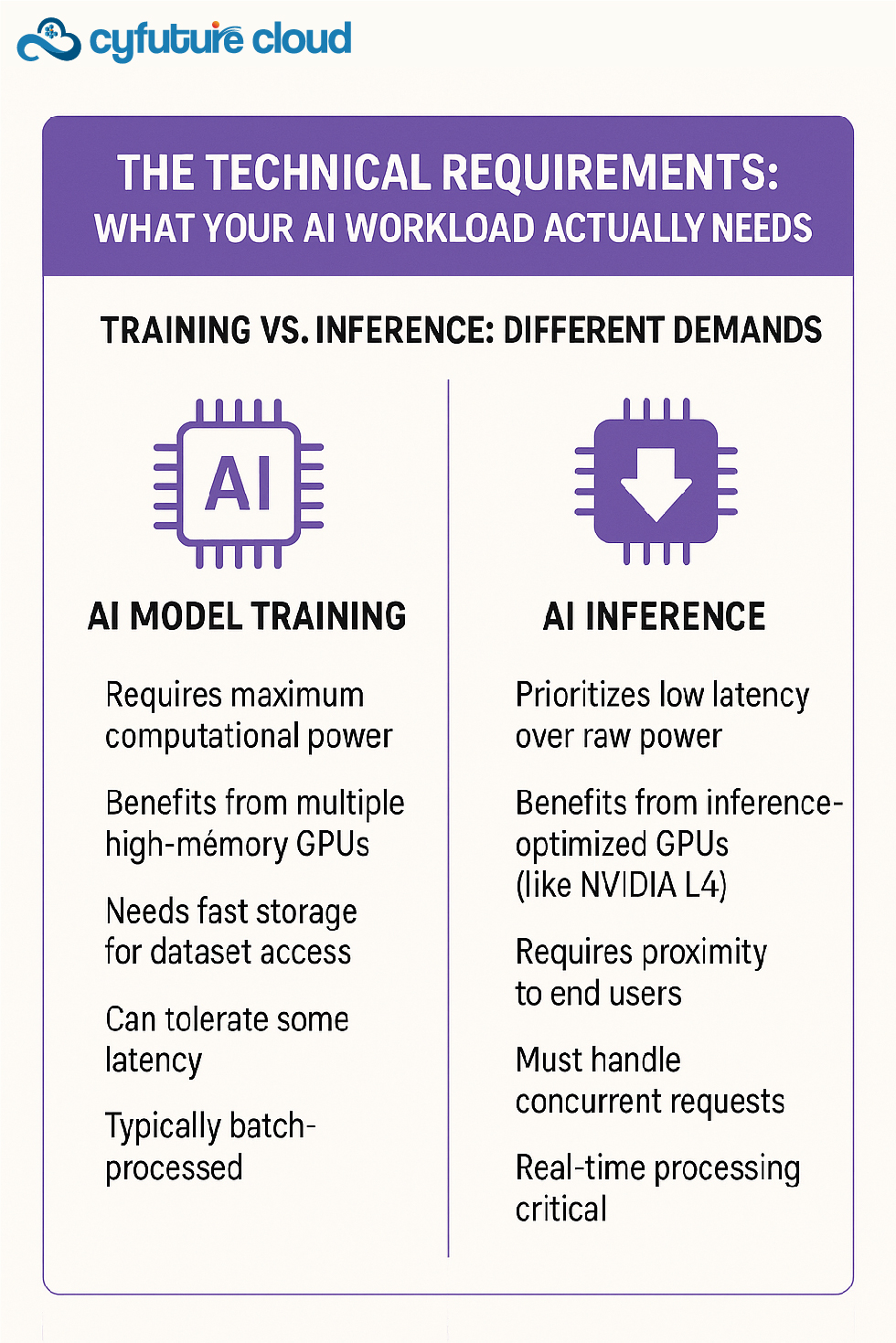
- 4. What GPU specifications do I need for machine learning training vs. inference?
- 5. How does Cyfuture Cloud support AI workloads on dedicated servers?
- 6. What are the main challenges when deploying GPU servers for AI?
- 7. Is dedicated infrastructure more secure than cloud for AI workloads?
- 8. How do I calculate ROI when choosing between cloud and dedicated GPU servers?
- 9. What networking requirements are critical for AI server deployments?
Are You Struggling to Find the Right Infrastructure for Your AI Workloads?
Dedicated servers for AI workloads powered by Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) have emerged as the cornerstone of artificial intelligence infrastructure in 2026, fundamentally transforming how enterprises train machine learning models, process massive datasets, and deploy intelligent applications at scale. As organizations worldwide grapple with the exponential growth of AI adoption—rising from 50% in 2023 to 72% in 2024—the demand for specialized computing infrastructure capable of handling intensive computational demands has reached unprecedented levels.
The artificial intelligence revolution isn’t just changing what we can do with technology—it’s completely reshaping the infrastructure we need to do it. Here’s the thing:
Traditional CPU-based servers simply can’t keep pace with modern AI requirements. And that’s where dedicated GPU servers enter the picture.
Introduction: The AI Infrastructure Revolution
The artificial intelligence landscape has experienced a seismic shift over the past three years. What began as experimental technology for tech giants has rapidly evolved into mission-critical infrastructure for businesses across every sector—from healthcare and finance to autonomous vehicles and smart manufacturing.
But here’s what many don’t realize:
Behind every breakthrough AI application, every intelligent chatbot, and every predictive analytics platform lies a robust infrastructure foundation. And at the heart of this foundation? Dedicated GPU servers, increasingly deployed through server colocation facilities that combine the power of physical hardware with the flexibility of modern cloud architectures.
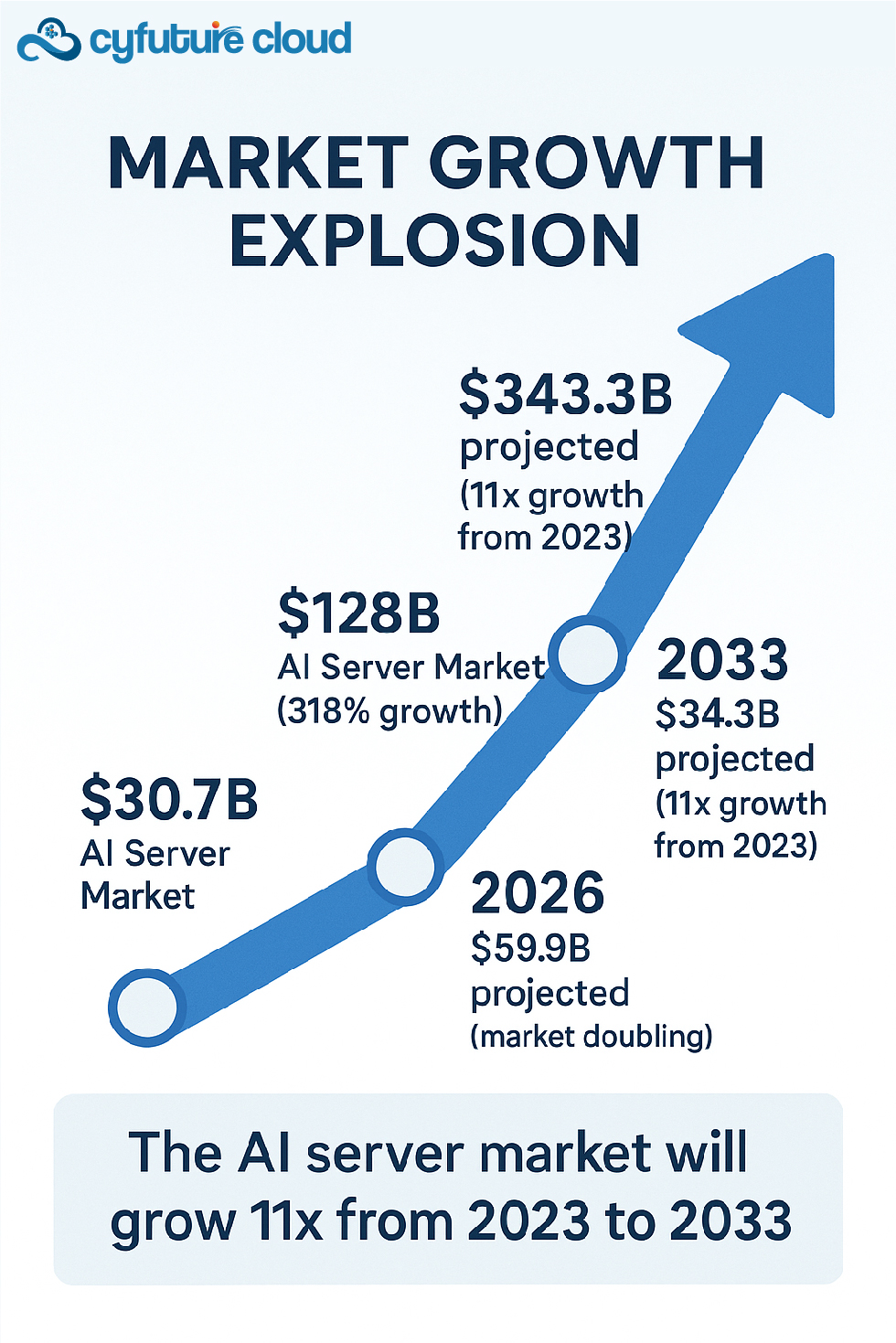
The global AI server market was valued at USD 30,742 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 343,260 million by 2033, representing more than an eleven-fold expansion. By 2026, the market is expected to nearly double compared to 2024, reaching USD 59,907 million.
This explosive growth isn’t happening in isolation. It’s driven by fundamental shifts in how organizations approach AI deployment, data sovereignty, and total cost of ownership.
What Are Dedicated Servers for AI Workloads?
Dedicated servers for AI workloads represent specialized computing systems designed exclusively for artificial intelligence applications. Unlike shared cloud resources where computing power is distributed among multiple tenants, dedicated servers provide complete, unshared access to powerful hardware resources.
Think of it this way:
GPU dedicated servers are specialized servers equipped with powerful GPUs designed to handle computationally intensive tasks, optimized for parallel processing. This makes them ideal for machine learning training, deep learning operations, neural network development, and large-scale data analytics.
The architecture typically includes:
- High-Performance GPUs: NVIDIA H100 gpu, A100 gpu, or AMD MI300 series processors
- Massive Memory Configurations: Often exceeding 1TB RAM for handling enormous datasets
- Ultra-Fast Storage: NVMe SSDs with exceptional I/O performance
- Advanced Networking: 400G Ethernet or InfiniBand for rapid data transfer
- Specialized Cooling Systems: Liquid cooling solutions managing thermal loads exceeding 50kW per rack
The GPU Revolution: Why Graphics Cards Became AI Powerhouses
Understanding GPU Dominance in AI Computing
Here’s a fascinating transformation:
Graphics Processing Units, originally designed for rendering video game graphics, have become the undisputed champions of AI computation. But why?
The answer lies in their fundamental architecture.
In 2024, the GPU segment holds a substantial 44.8% to 58.55% market share in AI server hardware, with projected revenue reaching approximately USD 54.2 billion. The market for GPU cloud server is expected to reach USD 86.3 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.5%.
The Technical Advantage:
CPUs process tasks sequentially, handling one complex calculation at a time. GPUs, conversely, contain thousands of smaller cores designed for parallel processing—simultaneously executing thousands of simpler calculations. For AI workloads involving matrix multiplications and tensor operations, this architectural difference translates to performance improvements of 20x to 1,700x compared to traditional CPUs.
NVIDIA’s Market Dominance
NVIDIA has established an almost unassailable position in the AI GPU market, controlling approximately 80-92% market share in 2024. This dominance stems from several factors:
- CUDA Ecosystem: Over 4 million developers use NVIDIA’s CUDA framework
- Specialized Architecture: Tensor Cores specifically designed for AI acceleration
- Continuous Innovation: H100 and Blackwell series pushing performance boundaries
- Enterprise Integration: DGX systems and HGX platforms for turnkey AI solutions
The NVIDIA H100 GPUs have become the gold standard for high-performance AI computing, despite their hefty price tag reflecting the skyrocketing demand. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon have deployed thousands of these units in their data centers.
But competition is heating up:
AMD is making significant strides with its MI300 series, reporting $1 billion in sales within the first two quarters of 2026, with data center GPU revenue anticipated to exceed $4 billion for the year. Intel is also investing heavily, though their 2026 AI GPU sales are projected around $500 million.
Server Colocation: The Strategic Middle Ground
What Makes Server Colocation Ideal for AI Workloads?
Server colocation represents a hybrid infrastructure approach where organizations own their hardware but house it in specialized third-party data centers. For AI workloads, this model offers compelling advantages:
Here’s why it matters:
A 2024 Foundry study revealed that colocation data centers are the preferred choice among IT and business leaders for deploying enterprise AI workloads, with the majority considering moving these operations from public cloud to colocation.
The Colocation Advantage for AI
- Infrastructure Without Capital Burden
Colocation eliminates the need for organizations to build and maintain their own data centers. Instead, they leverage:
- State-of-the-art cooling systems (essential for GPU thermal management)
- Redundant power supplies with 99.99% uptime guarantees
- Advanced physical security with biometric access
- Carrier-neutral connectivity options
- Power and Cooling at Scale
AI workloads generate extraordinary power demands. NVIDIA’s Blackwell GB300 racks hit 163 kW per rack in 2025, with projections showing Rubin Ultra NVL576 racks may exceed 600 kW per rack by 2027. Google’s Project Deschutes has already unveiled a 1 MW rack design.
Traditional enterprise data centers weren’t engineered for such densities. Purpose-built colocation facilities provide:
- Rack densities exceeding 50kW
- Direct-to-chip liquid cooling systems
- Power delivery of 100+ MW to individual buildings
- Modular cooling zones that scale with deployment
- Low-Latency Network Connectivity
AI inference workloads demand proximity to end users. Even a five-millisecond delay can disrupt real-time applications like voice assistants or recommendation engines. Colocation facilities offer:
- Strategic locations near population centers
- Direct connections to major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- 400G Ethernet and InfiniBand networking
- Dark fiber and peering agreements
Cost Comparison: Colocation vs. Public Cloud
Let’s talk numbers:
Nearly half of IT leaders in a recent survey reported unexpected cloud-related costs ranging from $5,000 to $25,000, with AI workloads being a common culprit.
The Economics:
- Public Cloud: Pay-as-you-go flexibility but costs escalate dramatically for 24/7 AI workloads
- Server Colocation: Predictable monthly costs with transparent pricing for power, space, and bandwidth
- Break-Even Point: For steady, high-utilization workloads, colocation typically becomes more economical within 12-18 months
A comparative analysis shows that a $200/month dedicated server can outperform a $500/month cloud instance when properly optimized for AI workloads.
The 2026 AI Server Market Landscape
Market Size and Growth Trajectories
The numbers tell a compelling story:
- Global AI Server Market (2024): USD 128 billion
- Projected CAGR (2025-2034): 28.2%
- AI GPU Market (2026): USD 17.58 billion, projected to reach USD 113.93 billion by 2033
- Data Center GPU Market (2024): USD 16.94 billion, predicted to reach USD 192.68 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 27.52%
GPU Memory Segmentation
The AI GPU market segments by memory capacity reveal strategic considerations:
- 16/32GB GPUs: Dominate at ~55% market share, ideal for inference and edge AI applications
- 80GB GPUs: Represent ~30% of the market, fastest-growing segment for large-scale model training
- High-Memory Solutions: Essential for training models with trillions of parameters
Application Breakdown
Where are these servers being deployed?
- Data Centers: 40% of AI GPU market share
- Cloud Computing: 35% market share
- Edge Computing: 25%, but growing fastest at over 25% CAGR
Edge computing’s rapid growth reflects the trend toward processing data closer to its source—critical for autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and real-time analytics.
Why Dedicated GPU Servers Outperform Cloud for AI
Performance Consistency
The Problem with Shared Infrastructure:
Public cloud environments use virtualized resources shared among multiple tenants. During peak usage periods, this “noisy neighbor” effect can cause:
- Unpredictable latency spikes
- Inconsistent IOPS performance
- GPU throttling under sustained loads
The Dedicated Advantage:
Dedicated servers provide deterministic performance. Your AI training jobs complete in predictable timeframes. Your inference engines maintain consistent sub-millisecond response times.
For high-frequency trading, low-latency APIs, and real-time AI inference, this consistency is non-negotiable. As one quantitative trading firm noted: “When microseconds matter, dedicated hardware wins, every time.”
Data Sovereignty and Security
Here’s something crucial:
AI systems thrive on data—often sensitive, proprietary, or regulated data. Industries like healthcare, finance, and government face strict compliance requirements:
- GDPR with penalties up to €20 million or 4% of worldwide annual revenue
- HIPAA for healthcare data protection
- SOC 2, ISO 27001 certifications
Colocation facilities offer:
- Physical separation from other tenants
- Complete control over data residency
- Custom security implementations
- Compliance-ready environments with audit trails
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Breaking Down the Economics:
Initial Investment:
- Cloud: Low upfront cost, high ongoing expenses
- Dedicated/Colocation: Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs
Operational Costs:
- Cloud: Bandwidth egress fees, storage charges, compute overages
- Dedicated/Colocation: Flat monthly rates for power, space, bandwidth
Scaling Costs:
- Cloud: Linear cost increase with usage (can become exponential)
- Dedicated/Colocation: Stepped increases at hardware addition points
Real-World Example:
An AI startup training large language models 24/7:
- Year 1 Cloud Costs: $180,000
- Year 1 Dedicated/Colocation: $95,000 (including hardware amortization)
- Year 3 Total Cloud: $540,000
- Year 3 Total Dedicated: $285,000
The savings? $255,000 over three years.
Cyfuture Cloud: Powering AI Innovation Through Advanced Infrastructure
At Cyfuture Cloud, we understand that AI workloads demand specialized infrastructure solutions. Our dedicated server offerings combine the raw power of cutting-edge GPU hardware with the reliability and scalability that modern AI applications require.
What Sets Cyfuture Cloud Apart:
- Latest GPU Technology: Access to NVIDIA H100, A100, H200 GPU and AMD MI300 series GPUs
- Flexible Deployment Models: From bare metal dedicated servers to hybrid cloud colocation solutions
- Optimized Network Performance: Low-latency connectivity with tier-1 carrier access
- 24/7 Expert Support: Our team understands AI workloads and can optimize your infrastructure
- Transparent Pricing: No hidden fees or surprise charges
Our customers have reported up to 60% cost savings compared to major public cloud providers while achieving superior performance for their AI training and inference workloads.
Emerging Trends Reshaping AI Infrastructure in 2026
1. Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling
As rack densities soar beyond 300kW, traditional air cooling reaches physical limits. Direct-to-chip liquid cooling (DLC) systems remove heat directly from the silicon die, enabling:
- Dense GPU configurations without thermal throttling
- Up to 40% reduction in total power consumption
- Quieter data center operations
- Extended hardware lifespan
2. High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) Integration
The integration of HBM3 and next-generation memory architectures by chipmakers like SK Hynix, Samsung, and Micron has become essential for handling large-scale AI model training and inference. This trend enhances processing speed, reduces bottlenecks, and supports massive parallelism.
3. AI-Specific ASICs and NPUs
While GPUs dominate today, purpose-built AI accelerators are gaining traction:
- Google’s TPUs: Optimized for TensorFlow workloads
- AWS Trainium/Inferentia: Cost-effective alternatives for AWS customers
- Custom Silicon: Companies designing proprietary AI chips for specific use cases
By 2026, over 75% of AI models rely on specialized chips, making CPU-based AI training largely obsolete.
4. Edge AI Computing Acceleration
The shift toward edge computing for low-latency inference is reshaping infrastructure strategies. Organizations are deploying AI servers at the network edge for:
- Autonomous vehicle processing
- Industrial IoT and smart manufacturing
- Healthcare diagnostic systems
- Retail analytics and personalization
This trend drives demand for compact, energy-efficient GPU servers optimized for edge deployment.
5. Sustainable AI Infrastructure
Environmental concerns are driving innovation:
- Renewable energy-powered colocation facilities
- AI-driven cooling optimization reducing energy consumption by 30%
- Advanced Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) ratings below 1.2
- Carbon-neutral commitments from major data center providers
Challenges and Solutions in AI Server Deployment
Challenge 1: GPU Supply Constraints
The Problem: Global GPU shortages have led to 6-12 month wait times for high-end processors.
Solutions:
- Pre-order hardware through established partnerships
- Consider alternative GPU vendors (AMD MI300 series)
- Explore GPU as a Service during supply gaps
- Design workloads to be GPU-agnostic when possible
Challenge 2: Skill Gap in AI Infrastructure Management
The Problem: Managing high-performance GPU clusters requires specialized expertise.
Solutions:
- Partner with managed service providers like Cyfuture Cloud
- Invest in team training and certification programs
- Leverage automation and orchestration tools
- Engage consultants for initial setup and optimization
Challenge 3: Cooling and Power Management
The Problem: Modern GPUs generate enormous heat, requiring advanced cooling solutions.
Solutions:
- Deploy liquid cooling systems for high-density racks
- Work with colocation providers specializing in AI workloads
- Implement AI-driven thermal management
- Plan for power capacity growth
Challenge 4: Cost Optimization
The Problem: Balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
Solutions:
- Right-size GPU configurations for specific workloads
- Implement time-sharing for underutilized resources
- Use spot instances for non-critical training jobs
- Monitor utilization metrics to identify optimization opportunities
Accelerate Your AI Journey with the Right Infrastructure
The evidence is clear:
Dedicated GPU servers, particularly when deployed through strategic server colocation partnerships, represent the optimal infrastructure choice for organizations serious about AI in 2026 and beyond.
While public cloud platforms offer undeniable benefits for experimentation and variable workloads, the economics, performance, and control advantages of dedicated infrastructure become compelling for production AI systems operating at scale.
The decision isn’t whether to adopt AI—that ship has sailed.
The critical question is: Will your infrastructure enable or constrain your AI ambitions?
With GPU servers dominating the landscape, the AI server market projected to exceed $343 billion by 2033, and 72% of enterprises already deploying AI systems, now is the time to establish the infrastructure foundation that will power your competitive advantage.
Make the strategic move to dedicated GPU infrastructure.
Partner with providers who understand the unique demands of AI workloads. Leverage server colocation to gain enterprise-grade capabilities without enterprise-scale capital expenditure. And most importantly, don’t let infrastructure limitations slow your innovation.
The future belongs to organizations that can iterate faster, train models more efficiently, and deploy intelligence at scale. Dedicated GPU servers are the engine that powers that future.
Ready to transform your AI infrastructure?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between dedicated GPU servers and cloud GPU instances?
Dedicated GPU servers are physical machines exclusively allocated to your workloads, providing consistent performance, predictable costs, and complete control. Cloud GPU instances are virtual machines sharing underlying hardware, offering flexibility but with variable performance and potentially higher long-term costs. For sustained AI workloads running 24/7, dedicated servers typically provide better ROI after 12-18 months.
2. Why is server colocation ideal for AI workloads?
Server colocation combines the benefits of dedicated hardware ownership with professionally managed data center infrastructure. For AI workloads specifically, colocation provides: advanced cooling systems capable of handling GPU thermal output (30-300kW per rack), redundant power with 99.99% uptime, low-latency network connectivity to major interconnection points, and compliance-ready environments—all without the capital expense of building your own data center.
3. How much does it cost to deploy dedicated GPU servers for AI?
Costs vary significantly based on GPU model and configuration. Entry-level setups with NVIDIA A100 GPUs start around $1,000-2,000 monthly in colocation facilities, while high-end configurations with multiple H100 GPUs can exceed $10,000 monthly. However, for organizations currently spending $15,000+ monthly on cloud GPU instances, dedicated servers typically achieve 50-70% cost reduction within 18 months when factoring in hardware amortization.
4. What GPU specifications do I need for machine learning training vs. inference?
For Training: Choose high-memory GPUs (80GB+) like NVIDIA A100 or H100, multiple GPUs with NVLink connectivity, and maximum compute power. Training benefits from parallel processing across multiple GPUs.
For Inference: Opt for inference-optimized GPUs like NVIDIA L4 or T4, prioritizing low latency over maximum compute power. Single GPU configurations often suffice, with focus on response time and concurrent request handling.
5. How does Cyfuture Cloud support AI workloads on dedicated servers?
Cyfuture Cloud provides comprehensive AI infrastructure solutions including: access to latest NVIDIA and AMD GPU technologies, flexible deployment through bare metal servers or colocation options, optimized network configurations for low-latency AI applications, 24/7 expert support from teams experienced in AI workloads, and transparent pricing models without hidden fees. Our infrastructure is designed specifically for the thermal, power, and performance demands of modern AI applications.
6. What are the main challenges when deploying GPU servers for AI?
Key challenges include: GPU supply constraints (6-12 month lead times for high-end models), power and cooling requirements exceeding traditional data center capabilities (racks can exceed 50kW), skills gap in managing high-performance GPU infrastructure, and optimizing costs while meeting performance requirements. Partnering with experienced providers like Cyfuture Cloud helps overcome these challenges through access to hardware pipelines, purpose-built facilities, and expert guidance.
7. Is dedicated infrastructure more secure than cloud for AI workloads?
For sensitive AI applications handling proprietary data, dedicated infrastructure in colocation facilities offers enhanced security through: physical separation from other tenants, complete control over network architecture and access controls, ability to implement custom security measures meeting specific compliance requirements, and reduced attack surface compared to multi-tenant cloud environments. Industries like healthcare, finance, and government often require this level of control for regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2).
8. How do I calculate ROI when choosing between cloud and dedicated GPU servers?
Calculate 3-year TCO considering: initial hardware costs (if purchasing), monthly colocation fees (space, power, bandwidth), bandwidth and storage costs in both scenarios, management overhead and staffing, expected utilization rates (dedicated servers favor high, consistent utilization), and performance impacts on business outcomes. Use online TCO calculators and request quotes from both cloud providers and colocation facilities. Generally, workloads with >60% consistent GPU utilization over 18+ months favor dedicated infrastructure.
9. What networking requirements are critical for AI server deployments?
AI workloads demand: minimum 25Gbps connectivity, 100Gbps+ for distributed training across multiple servers, low-latency paths (<5ms) for real-time inference applications, InfiniBand or RoCE for GPU-to-GPU communication in training clusters, direct connections to cloud providers if using hybrid architecture, and robust DDoS protection and firewall capabilities. Colocation facilities offering carrier-neutral environments provide maximum flexibility in network architecture design.
10. Should I choose Windows Dedicated Servers or Linux Dedicated Server for AI and GPU workloads?
The choice depends on your application stack and operational preferences. Linux Dedicated Server environments are widely preferred for AI and GPU workloads due to native support for AI frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch), better GPU driver compatibility, lower licensing costs, and superior performance optimization for high-performance computing. Windows Dedicated Servers are ideal for enterprises running Microsoft-based applications, .NET workloads, or AI solutions tightly integrated with Windows ecosystems. Many organizations deploy a hybrid approach, using Linux for AI training and Windows servers for application hosting and visualization, ensuring flexibility, performance, and seamless integration with existing enterprise systems.
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement