Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
What Is a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)-A Complete Overview
Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how the internet stays organized? Domain names help with this. They’re like addresses that help us find websites easily. A unique domain name is a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). What’s an FQDN? In this guide, we’ll explain:
► What FQDN means
► How it helps with Internet networks
► How it’s different from other domain names
► Some examples of FQDNs
► How to make an FQDN for your website
Ready to learn about FQDNs? Let’s start!
What is FQDN?The full term for FQDN is a Fully Qualified Domain Name. An FQDN can be described as a complete address similar to the internet address of a computer. It has two parts: the hostname, the computer’s name, and the domain name. This makes it possible to locate the specific computer model in the market. To view the FQDN of your computer, you can do this on Mac or Linux using Terminal or Windows in the advanced system settings. This can be defined as a method of identifying the full Internet address of your computer. |
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Structure
An FQDN always works as an independent and unique reference to a particular resource on the internet. It is highly structured, and its nature is to give successively more specific data as one reads from right to left. Let’s delve into each component in detail:
Top-Level Domain (TLD):
– This is the rightmost part of the FQDN.
– Examples include.com,.org,.net,.edu.
– The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority manages top-level domains.
- Domain Name:
– This is the name registered under a TLD.
– The website owner or organization usually chooses it.
– Example: In “example.com,” “example” is the domain name.
- Subdomain:
– This is an optional part that comes before the domain name.
– It allows for further organization within a domain.
– Subdomains include “www” for web servers, “mail” for email servers, or department names like “sales” or “support.”
- Hostname:
– This is the leftmost part of the FQDN.
– It often refers to a specific machine or service.
– In many cases, especially for websites, “www” is the hostname.
Here’s an example of a complex FQDN broken down:
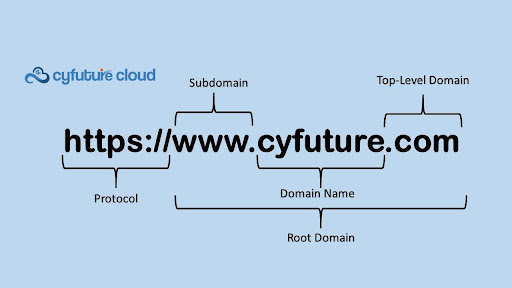
How FQDNs Are Used
Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) play a crucial role in various aspects of Internet communication and network management. Here’s a detailed look at how FQDNs are used:
Web Browsing:
When you enter a website URL into your browser, you frequently use a FQDN. The browser utilizes this to find the appropriate web server and display the webpage. For example, when you type “www.example.com,” your browser recognizes which server to contact.
- Email Routing:
FQDNs are essential for email systems. The domain part of an email address (after the @ symbol) is an FQDN. Mail servers use this to determine where to send emails. For instance, in “,” the mail server uses the FQDN to route the email correctly.
- Network Configuration:
System administrators use FQDNs to identify devices on a network. This is particularly useful in large networks where multiple devices might have similar hostnames. The FQDN in networking ensures that each device has a unique identifier.
- SSL/TLS Certificates:
In SSL/TLS certification, when protecting the websites, the FQDN gives the domain on the correctness of the produced certificate. This is essential, especially while establishing secure, encrypted sessions between the browsers and web servers.
- DNS Management:
FQDNs are crucial to the Domain Name System, or DNS. They are used in DNS records to convert domain names to IP numbers, making it easier for humans to type than numerical IP numbers.
- Server Administration:
FQDNs identify and manage different servers and services in server environments. This is especially important in cloud computing and distributed systems, where numerous servers may run simultaneously.
- API and Web Services:
Many APIs and web services use FQDNs in their endpoints. This allows for precise identification of different services within an organization’s infrastructure.
- Virtualization and Hosting:
In virtual hosting environments, FQDNs help differentiate between multiple websites hosted on a single IP address. Each website can have its own FQDN, allowing the server to direct traffic appropriately.
- Network Troubleshooting:
FQDNs are valuable in network diagnostics. Tools like ping and traceroute can use FQDNs, making it easier for technicians to identify and resolve network issues.
- Access Control:
FQDNs help define access to resources, ideally in security configurations. Firewalls and other security applications have options to allow or drop traffic according to FQDNs.
It becomes essential to know how FQDNs are utilized for anyone associated with web development, network admin, and IT infrastructure. FQDNs offer a clear taxonomy or naming structure that shapes how people act upon and organize devices connected to the internet.
How to Find an FQDN?
Finding a device or website’s Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) can be helpful in various networking tasks. Here’s a guide on how to find FQDNs in different scenarios:
For Your Computer:
- a) On Windows:
– Open Command Prompt
– Type “ipconfig /all” and press Enter
– Look for the “Host Name” and “Primary DNS Suffix” entries
– Combine these (hostname.primary_dns_suffix) to get your FQDN
- b) On macOS or Linux:
– Open Terminal
– Type “hostname -f” and press Enter
– The output is your computer’s FQDN
- For a Website:
- a) Using Command Line:
– On Windows, open Command Prompt
– On macOS or Linux, open Terminal
– Type “nslookup example.com” (replace with the website you’re checking)
– Look for the “Name” field in the output
- b) Using Online Tools:
– Many online DNS lookup tools can provide FQDN information
– Enter the domain name, and these tools will display various DNS records, including the FQDN
- For a Remote Server:
– If you have SSH access, log in and use the “hostname -f” command
– If it’s a web server, you can often find the FQDN in the server response headers
- In a Corporate Network:
– Check with your IT department, as FQDNs may follow a specific naming convention
– Use network discovery tools provided by your organization
- Using WHOIS Lookup:
– Perform a WHOIS lookup on a domain registrar’s website
– The FQDN is often listed in the domain information
- Checking SSL Certificates:
– For HTTPS websites, view the SSL certificate details
– The FQDN is typically listed in the “Common Name” or “Subject Alternative Name” fields
- Using DNS Management Panels:
– If you manage the domain, check your DNS management panel
– The FQDN will be listed in the DNS records
- Network Scanner Tools:
– Use network scanning tools like Nmap
– These can often reveal FQDNs of devices on a network
Keep in mind that your approach may vary depending on the circumstances and your degree of access. Sometimes, FQDNs are not readily discoverable or publicly available, notably due to security concerns.
Why Do You Need an FQDN?
Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) are essential for various reasons in the digital world. Let’s explore why you might need an FQDN:
Unique Identification:
An FQDN provides a unique identifier for your website or server on the internet. This uniqueness is crucial in a vast network where millions of devices and websites coexist.
Improved Network Management:
FQDNs assist system administrators in enhancing the administration and organization of network resources. This system gives unique and well-ordered names to help in identifying a distinct device or service.
3.Enhanced Security:
FQDNs are fundamentals of security protocols. They are applied in SSL/TLS certificates to ensure a secure connection is created with the right servers. This aids in checking for man-in-the-middle attacks or even phishing.
4. Professional Appearance:
Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) are required globally for various reasons.
5. Email Functionality:
FQDNs are crucial for email systems. They ensure emails are routed correctly and help set up email servers and services appropriately

How Can Cyfuture Cloud Help?
Thus, Cyfuture Cloud DNS is an integral component of contemporary networks, providing effective connections to services. Our DNS solution offers the ultimate high performance and is the foundation of service availability. It excels at managing query responses with advanced scalability, effortlessly handling sudden spikes in DNS query volume to keep your applications highly available across multiple instances and hybrid environments.
Cyfuture Cloud DNS stands out with its user-friendly management interface, providing easy visibility and programmability. This simplifies network architecture maintenance, leading to faster web browsing and reduced latency. With Cyfuture Cloud DNS, it goes deeper than providing DNS service alone; it connotes a solution that optimizes the network, thereby improving users’ experience and web browsing and guaranteeing the overall performance of the existing network environment. Let’s connect and discuss your business today!
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 


















