Table of Contents
- What is a CDN?
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Outlook
- India Content Delivery Network Market: Regional Insights
- Common Content Delivery Network (CDN) services:
- What Potential Market opportunities could fuel the adoption of CDN India services?
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Market Analysis
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Market Trends 2024
- What Challenges Confront Content Delivery Providers and How Are They Addressed?
- What if you want to do the same and build your own CDN?
The CDN India market has been witnessing substantial growth, driven by the growing appetite for online content, increased digital media consumption, and the expansion of the e-commerce industry.Enhanced internet connectivity, ubiquitous smartphone usage, and the widespread embrace of streaming services have collectively catalyzed the surging demand for CDN services.
CDN India Service providers cater to various sectors, such as media, entertainment, e-commerce, gaming, and education, offering solutions like content caching, website acceleration, security features, video streaming optimization, and load balancing to enhance the delivery of online content to end-users.
But before moving ahead let’s have a sneak peek on what Content Delivery Network is.
What is a CDN?
A Content delivery Network (CDN) is basically a global collection of servers that speed delivery of web content by bringing it closer to users. Data centers use caching, a process that temporarily stores copies of files so that users can access Internet content from a web device or browser more quickly through a server near you. Stored content encompasses web pages, images, and videos within proxy servers positioned closest to end-users. These considerably shorter paths from the source to the destination not only conserve bandwidth but also enhance performance while reducing expenses.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Outlook
The evolution of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) has been an exhilarating and transformative journey, propelled by technological advancements and shifting online habits. CDNs have traversed a remarkable path from their inception during the early days of e-commerce websites and video distribution at the turn of the century.
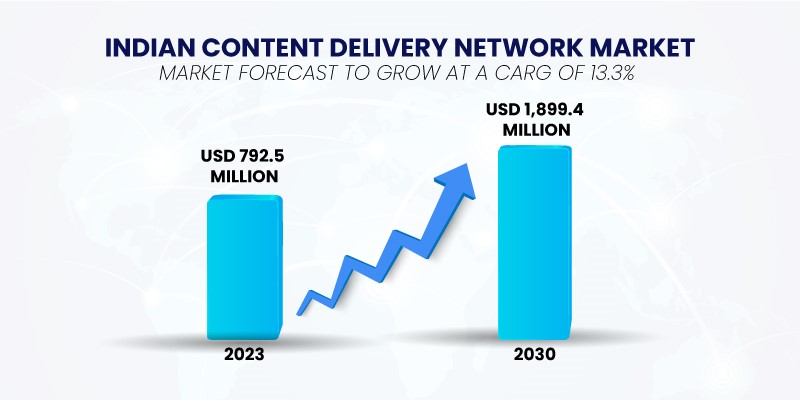
Consider the recent rapid expansion of the CDN sector, marked by the active participation of industry giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon. According to the analysis, the CDN market in India was valued at US$ 792.5 million in 2023, and it is poised to exhibit a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.3% from 2023 to 2030.
India Content Delivery Network Market: Regional Insights
The use of CDN India services has grown significantly throughout various regions of the nation. Because of the presence of e-commerce corporations, media and entertainment enterprises, and IT businesses in the Western area, which encompasses Pune, Mumbai, and Ahmedabad, there is a large market for CDN services. Mumbai, serving as the financial capital, holds a significant position as a pivotal hub for CDN infrastructure in the Indian region.
The Southern region, encompassing cities such as Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad, boasts a flourishing IT and technology sector, playing a pivotal role in fostering the expansion of the CDN industry in the area. The need for CDN services has increased due to the proliferation of IT corporations, research institutes, and media production organisations.
The Northern area, notably the Delhi NCR, has a sizable CDN market. Delhi, along with its neighboring regions like Noida and Gurgaon, stands as pivotal business centers spanning multiple sectors, leading to a significant demand for CDN (Content Delivery Network) services. The significant local population, combined with the existence of prominent e-commerce companies, major media corporations, and government institutions, collectively contribute to the surge in demand for these services.
Cities in the Eastern region, including Kolkata, Bhubaneswar, and Guwahati, are emerging as promising players in the CDN industry. Despite their relatively smaller size compared to other regions, the growing adoption of digital technology, a thriving e-commerce sector, and the presence of educational institutions all contribute to the rising demand for CDN services.
In the Central region, encompassing cities like Jaipur, Indore, and Bhopal, a rapid transformation is underway as it evolves into a thriving market for CDN services. These cities are at the forefront of the digital revolution and are experiencing a surge in online content consumption, which is propelling the demand for CDN infrastructure in the area.
Common Content Delivery Network (CDN) services:
| CDN Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Akamai | One of the oldest and widely used CDN providers, known for its global presence and security features. Offers various solutions for media delivery, web performance, and security. |
| Cloudflare | Known for its easy setup and free tier, providing CDN, DDoS protection, security features, and a wide network of servers worldwide. Also offers additional services like DNS, firewall, and more. |
| Amazon CloudFront | Part of Amazon Web Services (AWS), CloudFront provides low-latency content delivery with the scalability of AWS infrastructure. Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services. |
| Fastly | Offers real-time content delivery, edge computing, and streaming services. Known for its developer-friendly environment and high-speed content delivery through a programmable network. |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure CDN integrates with Azure services and provides global coverage with edge locations worldwide. Offers various caching and delivery options for different content types. |
| Google Cloud CDN | Part of Google Cloud Platform (GCP), it aims to deliver content quickly and securely through Google’s infrastructure. Provides integration with other GCP services. |
What Potential Market opportunities could fuel the adoption of CDN India services?
Numerous promising market opportunities can drive the adoption of Content Delivery Network (CDN) services. These opportunities stem from advancing technologies, shifts in user behavior, and emerging trends in the digital realm.
Here are some market opportunities:
- Surge in Online Video Streaming: The expansion of video streaming platforms, encompassing OTT services, live streaming, and video on demand, offers a substantial prospect. CDN services can enhance the delivery of top-quality video content, minimizing buffering, and ultimately enhancing the user experience.
- E-commerce Expansion: The e-commerce industry is on a continual growth trajectory, and CDNs have the capacity to refine website performance, slash page loading times, and elevate the overall shopping experience. This can drive greater adoption among online retailers.
- Mobile Internet Usage: With the increasing use of mobile devices for internet access, CDN services that prioritize mobile optimization and accelerated mobile page loading will find a growing market.
- Gaming and Esports: Online gaming and esports have seen tremendous growth. CDNs can provide low-latency content delivery for online gaming, and this segment presents a lucrative market for CDN providers.
- Edge Computing: The integration of edge computing with CDN services can unlock opportunities in processing data closer to the user, enabling real-time applications, IoT devices, and interactive content delivery.
- IoT and Smart Devices: The proliferation of IoT devices and smart technology opens up new opportunities for CDN services to support data delivery and reduce latency for connected devices.
- Global Expansion of Online Education: Online education platforms are expanding globally. CDNs can facilitate the delivery of educational content, live classes, and interactive learning, making it a promising market.
- Cloud Services: As businesses migrate their operations to the cloud, CDNs become essential in guaranteeing reliable, low-latency access to cloud-based applications, data, and services.
- Cybersecurity and DDoS Mitigation: Given the increasing cyber threats, CDNs are expanding their array of security services, making them an appealing option for organizations looking to bolster their online security.
- Content Localization: In response to the demand for region-specific content, CDNs can facilitate content localization strategies, ensuring that users receive content in their preferred languages and formats.
- 5G Rollout: The deployment of 5G networks will lead to faster internet speeds and greater user expectations. CDN services can help meet these expectations by delivering content efficiently and reducing latency.
- Green Initiatives: As environmental concerns grow, CDNs that focus on energy efficiency and sustainability can appeal to organizations seeking eco-friendly technology solutions.
- Media and Entertainment: The growth of digital media, including music streaming, podcasts, and digital publications, creates opportunities for CDNs to deliver content to a global audience.
To capitalize on these market opportunities, CDN providers should continually innovate, improve their service offerings, and adapt to the changing demands of a digital-centric world.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Market Analysis
The content delivery network (CDN) market is like a super-fast internet delivery system. Right now, it’s worth about $15 billion, and it’s expected to grow to $36.5 billion soon. This is because more people are watching videos online, there are more internet users, and many businesses are moving their stuff online.
A CDN is like having copies of internet stuff stored on many computers all over the place. When you want to see something online, the CDN finds the closest copy and shows it to you really fast. It’s like magic internet speed.
CDNs are used for all kinds of things on the internet, like text, pictures, videos, and even online shopping. So, they make sure everything loads quickly and works smoothly when you’re online.
Watching videos online is changing because the internet is getting better and the companies that make online shows are making them more interesting. They’re doing this without spending too much money, and they’re giving you good stuff to watch.
Also, more people are watching videos on their phones, and they like watching on big TVs too. These companies are also making their own shows. Because more people are watching online videos, the companies that help deliver those videos online are in high demand.
According to Cisco’s visual networking index, IP video is projected to have 79% of the online traffic by 2024. This suggests the growing trend of online video services.
Playing games online is getting even more popular because the games look better and more amazing. The companies that make these games want to make sure they run smoothly, so they use special internet technology. This technology helps you quickly download game stuff like updates and new features. It also prevents the game from crashing, and it makes the game look even better.
When you use the internet on your phone or other devices, a lot of data is created, and it needs to be managed well. Some solutions help make the internet work faster, and this is important for big companies like stores and the entertainment industry.
However, in some places, it’s tricky because there isn’t enough internet or the network is not very good. Companies have to get enough customers to pay for everything, and this can be hard in areas where the internet is not great.
Lately, more people in rural areas are getting better internet, from 60% to over 90% of them now have it. This varies because some places have more older people, some have more people who come and go, and some get extra help from the government.
COVID-19 also had an effect on the internet market. The companies that help deliver internet stuff, like videos and games, need the economy to be doing well and for banks to lend them money. Even with these challenges, the internet will keep getting faster and better because more data is being shared on the internet, and we’re getting faster internet networks.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Market Trends 2024
Media Delivery is Expected to Have a Significant Market Share
- About 56.3% of people around the world use the internet, and this is making the internet grow. This is because we now have really clear and sharp TVs, cool stuff for our smart devices, and the internet is getting better, so we all expect to see really good stuff online.
- Lots of media companies are changing how they share their stuff – they’re putting copies of their videos and shows closer to you so they play without pausing or crashing. This also helps them from overloading their main computer, which makes watching stuff online more reliable. This change is good for companies that help with this and make the internet work better.
- CDN providers are now giving more attention to improving web performance, especially for mobile devices and dynamic content needs.
- According to the Global Internet Phenomena Report, streaming videos now account for a significant 53.7% of all internet data traffic, marking a nearly 5% increase compared to the previous year. Businesses that offer access to content delivery networks (CDNs) – these networks consist of high-speed servers that enhance internet speed – have reaped substantial benefits from this trend. The volume of data transmitted through CDNs is on the rise, driven by technological advancements like peer-to-peer sharing, the proliferation of 5G, the use of wearable devices, the integration of smart technologies, and the emergence of virtual reality and augmented reality experiences.
- Mobile usage for consuming media content constitutes approximately 45% of all internet traffic, and this percentage is anticipated to continue growing. As more data is consumed, especially through activities like watching videos on mobile devices, companies are actively working to ensure a seamless mobile experience. The projected data usage for individuals is expected to reach about 4.5 gigabytes per month, which is more than three times the current average of approximately 1.5 gigabytes per month.
- Media content delivery networks (CDNs) are employing advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to empower users with greater control over their viewing experiences. For instance, while watching a sports game, viewers can access real-time statistics and data, and even make purchases related to the content they are viewing.
What Challenges Confront Content Delivery Providers and How Are They Addressed?
1. Latency and Slow Load Times:
Challenge: Slow loading times can deter users and harm the user experience. Latency issues occur when content must travel long distances to reach the end-user.
Solution: To combat this, CDPs should optimize server distribution by strategically placing servers closer to end-users. Additionally, they can employ edge caching to store content closer to users, and adopt faster protocols like HTTP/2.
2. Scalability Issues:
Challenge: As traffic and demand increase, CDPs can face scalability challenges. Servers may not handle the load efficiently.
Solution: CDPs can address scalability issues by utilizing a scalable infrastructure, implementing load balancing to distribute traffic evenly, and using auto-scaling solutions that automatically adjust server capacity based on demand.
3. Security Threats and DDoS Attacks:
Challenge: CDPs need to safeguard content and servers from various security threats, including Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Solution: Robust security measures, such as Web Application Firewalls (WAF), DDoS mitigation services, and strong encryption protocols, can help protect against security threats.
4. Origin Server Failures:
Challenge: Origin server failures can disrupt content delivery. If the origin server is down, users may not access the content.
Solution: CDPs can ensure high availability by implementing redundancy with failover mechanisms, using backup servers, and utilizing load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple origin servers.
5. High Bandwidth Costs:
Challenge: High bandwidth costs can be a significant expense for CDPs.
Solution: To reduce costs, CDPs can employ cost-effective data transfer solutions, peer with internet exchange points (IXPs) to reduce transit costs, and optimize content delivery routes to minimize data transfer costs.
6. Geographic Content Distribution Challenges:
Challenge: Ensuring optimal content delivery to users in different geographic locations can be a challenge.
Solution: CDPs can address this challenge by strategically expanding server locations, using a CDN with a vast network to reach a global audience, and employing dynamic content optimization based on user location to deliver content efficiently.
7. Real-time Content Delivery:
Challenge: Delivering real-time content or dynamic content efficiently can be complex.
Solution: CDPs can utilize edge computing for dynamic content generation and distribution, reducing the need to fetch data from the origin server and enabling real-time content delivery.
8. Caching Stale Content:
Challenge: Stale or outdated content may be served to users if not managed properly.
Solution: CDPs should implement cache invalidation mechanisms, use cache purging to remove outdated content, and set appropriate cache headers for content freshness.
9. Mobile Optimization:
Challenge: Ensuring content is optimized for mobile devices is crucial as mobile usage continues to rise.
Solution: CDPs can optimize content for mobile devices through responsive design, adaptive streaming for video content, and efficient mobile-focused caching strategies.
10. Dynamic Content Delivery:
Challenge: Efficiently delivering dynamic content, such as personalized content, can be challenging.
Solution: CDPs can address this challenge by leveraging edge computing, implementing a CDN with dynamic content optimization capabilities, and reducing server-side processing by caching and using content delivery optimizations.
What if you want to do the same and build your own CDN?
If you aspire to create your own CDN, you can achieve this through the utilization of Kubernetes services. This is where kubeCDN comes into the picture. kubeCDN serves as a content delivery network running on Kubernetes and is self-hosted by you. Consequently, you retain complete autonomy over your configuration. There is no necessity for an external service to oversee content delivery, granting you the authority to govern the flow of data from your servers to end-users’ devices.
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 




















