Table of Contents
By 2024, it is predicted that there will be more than 16.7 billion IoT devices globally, with expectations to increase to 27 billion by 2025. This rapid expansion highlights the urgent requirement for effective instant data handling, as the large amount of data produced by these devices can be too much for conventional cloud systems.
Edge cloud computing emerges as a transformative solution. It enables data to be processed closer to its source. Thereby reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Organizations can optimize their IoT data processing and analytics by harnessing the power of this technology. Thus unlocking valuable insights in real time.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing technology is a distributed computing method that moves computation and data storage closer to where they are used instead of depending only on a central data center. It reduces the distance data needs to travel by processing it at or close to the point of origin. Thus improving processing speed and data handling efficiency. This method is especially advantageous for tasks needing instant analysis and decision-making, like those in the Internet of Things (IoT).
How Edge Computing Works?
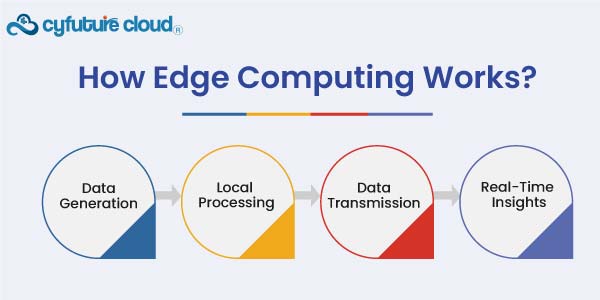
The process of edge computing architecture involves several key components and steps:
-
Data Generation
IoT devices, sensors, and other endpoints produce large quantities of real-time data.
-
Local Processing
Instead of sending all this data to a centralized cloud server, edge computing enables local processing at the device level or nearby edge servers. This can involve filtering, aggregating, or analyzing data on-site.
-
Data Transmission
Only the most relevant or processed data is sent to the cloud or centralized systems. It aids in additional analysis or storage in the long run. This decreases the amount of data required to be transmitted across the network.
-
Real-Time Insights
By processing data locally, organizations can achieve real-time insights and responses. This is crucial for applications where immediate action is often required, such as:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart Manufacturing
- Healthcare monitoring
The Role of IoT in Modern Technology
IoT is a large network of connected physical devices equipped with:
- Sensors
- Software
- Other technologies
It is used to gather, share, and process data online. The best IoT platform enables devices to communicate smoothly and carry out different tasks independently and effectively. Today, its importance in the technology world cannot be emphasized enough. It is changing the way we engage with our surroundings. Thus improving productivity across different sectors and facilitating more informed decision-making using immediate data analytics.
The expansion of IoT is estimated to have the potential to add $12.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030. This demonstrates its transformative power in different industries.
How Edge Computing Improves IoT?
Edge computing is essential for improving the Internet of Things (IoT) by addressing key data processing and management challenges. Achieving this involves:
-
Real-Time Data Processing
One key benefit of edge computing solutions is their capability to enable immediate data processing. It significantly decreases latency by handling data locally on edge devices or gateways instead of transmitting it to centralized cloud servers. This is essential for applications that require immediate comprehension and reactions, such as self-driving cars, factory automation, and medical monitoring. In industrial settings, edge computing helps with predictive maintenance by analyzing machine data locally, enabling timely interventions to avoid breakdowns.
-
Efficient Bandwidth Usage
Edge computing reduces bandwidth usage by minimizing the data sent to the cloud. Rather than transmitting all raw data from IoT devices, edge computing filters and sends only the most important or summarized information to centralized systems. This method helps ease network congestion and lower expenses related to data transmission, which is especially essential as the quantity of interconnected IoT devices keeps increasing. Limiting the amount of data transmitted through the network can help organizations improve performance and ensure smooth operations within their IoT systems.
-
Local Data Storage
Local data storage is another critical feature of edge computing that enhances IoT functionality. It enables faster access and analysis by storing data near where it is generated. This is especially advantageous when cloud connectivity has limitations or inconsistencies. Storing data locally improves security and privacy by allowing sensitive information to be handled and kept on the premises instead of sent over possibly insecure networks. This capacity is crucial for sectors dealing with confidential or delicate information, guaranteeing adherence to data protection laws while upholding operational effectiveness.
Data Processing and Analytics at the Edge
-
Data Processing
Data processing at the edge is important for applications that need instant insights and actions as it involves managing data near its origin. Data from IoT devices is processed locally on edge devices or gateways in an edge-computing architecture instead of being sent to a central cloud server. This on-site data processing enables real-time filtering, aggregation, and analysis, decreasing latency and bandwidth consumption.
When data is generated, edge devices can quickly analyze it to extract meaningful information, discarding irrelevant data before it is transmitted to the cloud. This method is especially advantageous when network connection is limited or unreliable. Thus guaranteeing important data is handled promptly. For example, edge computing in industrial environments analyzes machine data on-site to enable predictive maintenance, which helps prevent equipment failures through timely interventions.
-
Edge Analytics
Performing analytics at the edge offers several benefits:
- Reduced Latency
Edge analytics offers instantaneous insights by analyzing data on-site, which is vital for time-critical functions like autonomous vehicles and live monitoring systems. This feature enables organizations to address evolving circumstances or irregularities promptly.
- Enhanced Efficiency
Edge analytics cuts down on the amount of data that must be sent to the cloud. Thus preserving bandwidth and decreasing expenses related to data transmission. This effectiveness is especially crucial in settings with restricted connectivity or increased data creation rates.
- Enhanced Data Security
Storing sensitive information at the edge reduces the chance of being exposed while being transferred. Organizations can handle and examine important data on-site, ensuring they comply with data privacy rules and minimizing the chances of being targeted for cyber attacks.
- Operational Resilience
Edge analytics enables systems to function independently of cloud connectivity, allowing continued operation even during network disruptions. This is vital for applications in remote locations or critical infrastructure.
Comparison with Cloud Computing
While both edge computing and cloud computing have their advantages, they also present distinct pros and cons:
Pros of Edge Computing
- Lower Latency
Edge computing involves processing data near where it is generated. It leads to quicker response times for applications needing instant analysis.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage
By filtering and aggregating data locally, edge computing minimizes the data sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth and reducing costs.
- Enhanced Security
Processing data locally minimizes the volume of sensitive data sent via the Internet, lessening the potential for data breaches.
Cons of Edge Computing
- Limited Processing Power
Edge devices often have less computational capacity than centralized cloud servers, which may limit the complexity of analytics performed at the edge.
- Management Complexity
Managing a distributed network of edge devices can be more challenging than maintaining a centralized cloud infrastructure, requiring sophisticated orchestration and monitoring solutions.
Pros of Cloud Computing
- Scalability
Cloud computing provides endless resources. This enables companies to expand their operations effortlessly without requiring a substantial initial investment in hardware.
- Advanced Analytics
The cloud can support more complex analytics and machine learning models that require substantial computational resources.
Cons of Cloud Computing
- Higher Latency
Transmitting data to the cloud for analysis may cause delays, which is not ideal for applications needing instant feedback.
- Bandwidth Costs
Transmitting large volumes of data to the cloud can incur significant costs, especially in environments with high data generation rates.
To Sum it Up!
As the quantity of IoT devices rapidly increases, the need for reliable and productive data processing solutions becomes more urgent. Edge computing is becoming increasingly important as it deals with the issues caused by conventional cloud systems by handling data near where it is generated. This method decreases latency and bandwidth consumption while providing immediate insights crucial for autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, and healthcare monitoring applications.
Through edge computing, businesses can improve their processing and analysis of IoT data, accessing valuable information that leads to more intelligent decision-making and increased operational effectiveness. As we progress, the combination of edge computing and IoT will keep changing industries, promoting creativity and allowing for new abilities that were once out of reach. Embracing this technological collaboration is not a choice but a requirement to remain competitive in a world that is becoming more interconnected.
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 


















