Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
Introduction to Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Table of Contents
- What is Healthcare Hosting
- Cloud Computing: What is it?
- Cloud Computing in the Medical Field
- How is cloud computing applied in the medical field?
- Principal advantages of cloud computing for healthcare
- 1. Improved safety.
- Features of Healthcare Cloud Hosting:
- Implementing cloud computing in healthcare presents challenges.
- Conclusion
The adoption of healthcare cloud hosting is not a new development. Did You Know? According to MarketsAndMarkets, the medical cloud computing and cloud server hosting industry will reach $65 billion by 2025 with an average CAGR of 18%. The necessity for technical modernization, increased emphasis on digitization, and enhancement of healthcare procedures can all be linked to the increased adoption of cloud computing in the sector.
The ongoing pandemic simply makes the pattern worse. The introduction of previously slow-growing fields like telemedicine has increased as social estrangement has become the new norm. Despite this, healthcare professionals will keep using these tools long after the crisis has passed.
We at Cyfuture have examined the factors that make an introduction to cloud computing so alluring for the hosting healthcare cloud, and we are prepared to share our findings with you. To learn more, continue reading.
What is Healthcare Hosting
Healthcare hosting is a specialized Cloud hosting solution tailored to the unique needs of the healthcare industry, providing secure and compliant storage and management of sensitive patient data. It includes robust security measures, data encryption, and adherence to regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to ensure the privacy and integrity of patient information. Healthcare hosting plays a crucial role in maintaining the confidentiality and availability of critical medical records, facilitating telemedicine, and supporting healthcare organizations in delivering high-quality and secure services to patients.
Cloud Computing: What is it?
A form of on-demand collaboration known as cloud computing entails a vendor offering customers online access to reconfigurable computer resources for a negligible monthly fee. In layman’s terms, it involves offering IT services using a cloud architecture that consists of servers, storage, databases, networks, and/or applications.
The majority of the time, customers only pay for the capacities they really use. This enables cutting operating expenses, improving infrastructure management, and growing in accordance with business requirements. However, not all clouds are created equal, and not all cloud computing models are appropriate for all users. You can select the cloud computing model and type that is best for your company from a variety available in the healthcare industry.
Cloud Computing in the Medical Field
Cloud computing has transformed the medical field by offering scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, sharing, and analysis. Healthcare providers leverage cloud platforms to securely store and access patient records, diagnostic images, and other critical data from anywhere, facilitating telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. Furthermore, cloud-based tools enable advanced data analytics, accelerating medical research and diagnostic processes. While offering convenience and flexibility, cloud computing in the medical field also raises concerns about data security and privacy, necessitating robust measures to adhere to healthcare regulations and protect sensitive patient information.
How is cloud computing applied in the medical field?
Clouds are well-established and ubiquitous tools nowadays. Of course, there are implementation-specifics in every sector. The healthcare industry has led the way in several developments. Likewise with cloud computing.
Democratizing and guaranteeing access to this information is crucial in a sector that produces large volumes of data every day. What causes this to occur? Let’s start by examining the advantages of cloud computing in medicine to provide a response to this query.
Principal advantages of cloud computing for healthcare
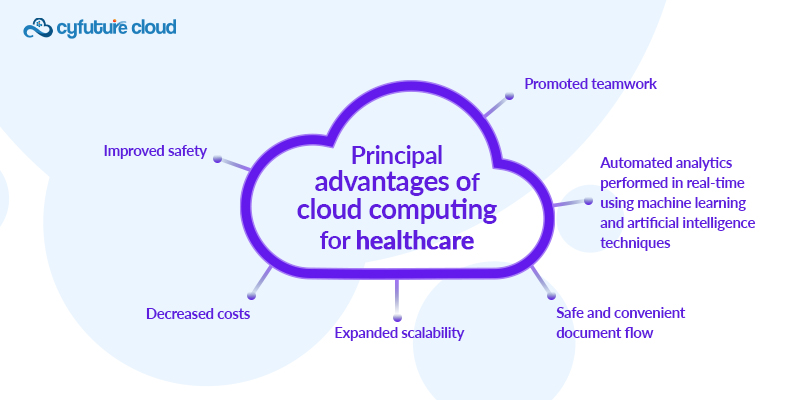
The use of cloud computing in the healthcare industry is beneficial in many ways, including streamlining the development and upkeep of telemedicine apps and facilitating the safer and easier transmission of medical records. The following are the main benefits of cloud computing for healthcare:
1. Improved safety.
The European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the CSF HITRUST Alliance industry standard all support and regulate the protection of users’ personal information in online services.
2. Decreased costs
Healthcare companies can save money on pricey systems and equipment since modern cloud computing services operate on flexible subscription models. Using a dedicated cloud server with pre-established capabilities is one way to increase resilience.
3. Expanded scalability
The allocated processing power can be dynamically increased or decreased depending on the current load and requirements thanks to cloud technology.
4. Safe and convenient document flow.
The service is available from any internet-connected device and allows for the storage and analysis of electronic health records, patient lists, test results, and other relevant information. It also offers a wide range of security and access rights choices.
5. Automated analytics performed in real-time using machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques.
These features can be crucial for supporting massive database administration, clinical decision making, and treatment time reduction due to the busy schedules of healthcare workers.
6. Promoted teamwork.
Healthcare professionals can exchange knowledge and expertise using a number of means by using cloud-based messaging and collaboration services, which will both raise the quality of healthcare services and advance the medical sciences.
The healthcare sector benefits from cloud computing’s global remote access, automated backups, and quick recovery. In order to guard against illegal access, the majority of cloud service providers also provide risk management and monitoring services.
These are some advantages of cloud computing in the medical field. Let’s talk about risks and difficulties now.
Features of Healthcare Cloud Hosting:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Compliance | Adherence to industry standards (HIPAA, GDPR) |
| Encryption | Data encryption at rest and in transit |
| Access Controls | Role-based access, authentication mechanisms |
| Data Backup | Regular backups, disaster recovery planning |
| Scalability | Ability to scale resources based on demand |
| Performance | Reliability, low latency, high availability |
| Healthcare Specific Tools | Integration with EMR/EHR systems, PACS, etc. |
| Audit Trails | Logging and tracking of user actions |
| Service Level Agreements | Defined uptime, support, and response times |
| Compliance Reporting | Generation of compliance-related reports |
| Cost and Pricing Model | Transparent pricing, cost-effective solutions |
Implementing cloud computing in healthcare presents challenges.
Users’ mistrust of the security and privacy protections offered, organisational inertia, the loss of data control, and lax safety standards are some of the major obstacles facing cloud computing in healthcare.
The clause allowing the customer to audit and manage their data freely may occasionally be missing from the service agreement. There are situations when the provider cannot adhere to the necessary compliance regulations (for example, safety standards, contracts, or policy change statements). Certain common services are occasionally not available to customers (for example, credit card payments).
Some cloud service providers overuse computing resources, limit access, or employ outmoded hardware or software due to intense competition. Rarely, users could not have access to the virtual architecture of the service being offered.
One of the most major issues is data blockage. Cloud consumers occasionally have the option of moving their data or services to an other provider or the on-premise IT environment. Sadly, the majority of cloud infrastructures offer very little interoperability.
Large amounts of data may need to be frequently uploaded or downloaded by some users (like biological research laboratories), but this may be hindered by a lack of available physical bandwidth. Debugging issues in large dispersed infrastructures is also more challenging.
Open-source management interfaces, inadequate encryption key management, and privilege misuse pose the biggest hazards associated with cloud computing in the healthcare industry. Cloud computing is often accessible to a wide range of clients. Ineffective resource distribution by the vendor may result in security and performance problems.
Conclusion
The field of healthcare as a whole reaps significant benefits from current technologies. Its advancement is significantly aided by the sciences of optics, nanotechnology, robotics, machine learning, and other fields. One of these scientific domains is cloud computing, which enables cost savings, improves the safety and security of the data accumulated, analyses enormous information arrays in real-time, and offers many other significant and minor advantages.
In this post, we gave a quick definition of cloud computing, talked about its difficulties, and gave some examples in the field of healthcare.
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 


















