Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
What is Backup as a Service (BaaS)?
Table of Contents
In today’s digital-first world, data is the backbone of every business—from startups to global enterprises. Yet, with cyber threats, accidental deletions, and hardware failures on the rise, safeguarding this data has never been more critical. Enter Backup as a Service (BaaS): a modern, cloud-powered solution that’s transforming how organizations protect and recover their vital information.
Understanding Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Backup as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based, fully managed backup and recovery service. Instead of relying on traditional, on-premises backup infrastructure, businesses use third-party providers to automatically and securely back up their data to remote, cloud-based repositories. This approach not only ensures data safety but also offloads the complexity of backup management to experts.
Key features of BaaS:
- Automated, scheduled backups of files, databases, and entire systems
- Secure, encrypted data transmission and storage
- Centralized management dashboards for monitoring and restoring data
- Scalability to match growing data volumes without hardware investments
- Disaster recovery capabilities for rapid restoration after data loss events
Why is BaaS Essential?
Data loss—whether from cyberattacks, accidental deletion, or natural disasters—can cripple business operations. For small and medium businesses (SMBs) in particular, the stakes are high: downtime means lost revenue, reputational damage, and potential legal consequences.
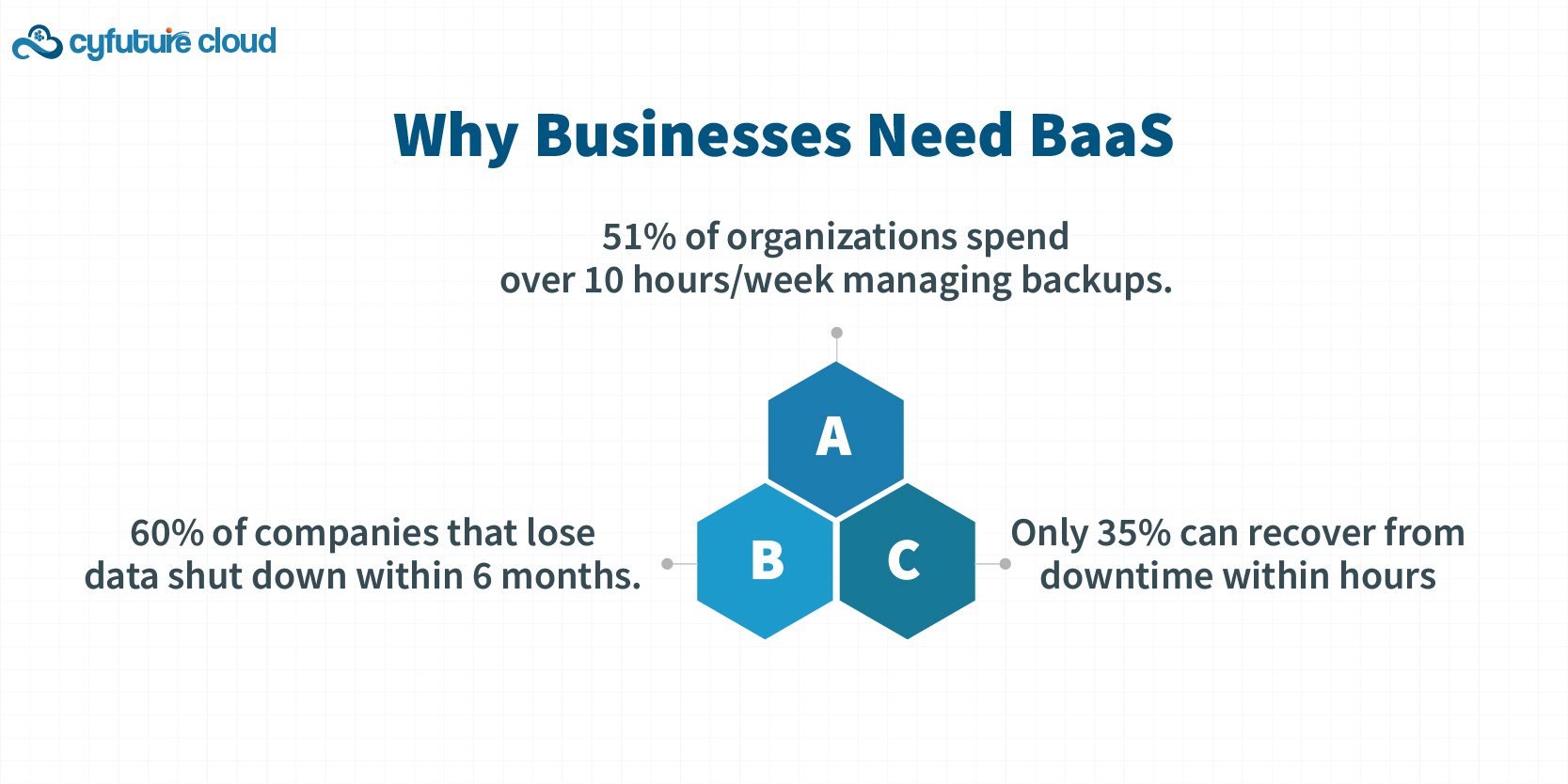
Why Businesses Need BaaS
- 51% of organizations spend over 10 hours/week managing backups.
- Only 35% can recover from downtime within hours.
- 60% of companies that lose data shut down within 6 months.
Statistics highlight the urgency:
- 51% of organizations spend over 10 hours per week managing backups—a significant drain on IT resources.
- Only 35% of organizations can recover from a downtime event within hours, despite over 60% believing they can.
- The BaaS market is booming, valued at $5.69 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $33.18 billion by 2030, growing at a staggering 31.8% CAGR.
How Does Backup as a Service (BaaS) Work?
1. Initial Setup
Businesses connect their servers, endpoints, databases, and applications to the BaaS provider’s cloud backup platform. This onboarding process is quick and requires no additional hardware, allowing organizations to begin securing data immediately.
2. Configuration & Policy Management
Through a user-friendly dashboard, IT teams define backup schedules, retention policies, encryption settings, and data categories to be protected. These customizable policies ensure compliance with industry standards and internal governance.
3. Continuous or Scheduled Backups
BaaS automatically captures data either in real time or at scheduled intervals. This automation minimizes human error, reduces administrative overhead, and ensures that the most recent version of business-critical data is always protected.
4. Secure Data Transmission
Before leaving the source system, data is encrypted using advanced security protocols, then transferred over secure channels (TLS/SSL) to the cloud. This prevents interception, tampering, or unauthorized access during transit.
5. Cloud Storage & Intelligent Management
Backups are stored in highly secure, geographically distributed cloud repositories to ensure resilience and disaster recovery readiness. The provider manages all backend operations—including maintenance, patching, scaling, and monitoring—so businesses don’t have to manage any infrastructure.
6. Fast, Flexible Data Recovery
When data loss, corruption, ransomware, or accidental deletion occurs, businesses can restore individual files, folders, databases, or entire systems within minutes. Most BaaS platforms offer point-in-time recovery, enabling organizations to revert to an earlier, clean version of their data with just a few clicks.
BaaS vs. Traditional Backup Methods
|
Feature |
BaaS (Cloud-Based) |
Traditional Backup (On-Premises) |
|
Setup Cost |
Low (subscription-based) |
High (hardware/software purchase) |
|
Management |
Provider-managed |
In-house IT required |
|
Scalability |
Instantly scalable |
Limited by hardware |
|
Disaster Recovery |
Offsite, rapid recovery |
Onsite/offsite, slower recovery |
|
Security |
Encrypted, multi-layered |
Varies, often less robust |
|
Accessibility |
Remote, anytime access |
Local/network access only |
Key Benefits of BaaS
- Cost-Effectiveness: No need for expensive hardware or dedicated backup teams; pay only for what you use.
- Automation & Reliability: Reduces risk of missed backups and human error—backups are performed consistently and automatically.
- Expert Management: Providers offer specialized expertise, ensuring optimal performance, compliance, and security.
- Disaster Resilience: Offsite, cloud storage protects data from local disasters, ransomware, and cyberattacks.
- Rapid Recovery: Quick restoration of data minimizes downtime and business impact.
How does BaaS ensure data security during transmission and storage in the cloud?
Backup as a Service (BaaS) ensures data security during transmission and storage in the cloud primarily through robust encryption and strict access controls.
How BaaS Secures Data
Encryption During Transmission
Before data leaves your systems, it is encrypted using strong encryption algorithms. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted while being sent to the cloud, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Encryption at Rest
Once the data reaches the cloud storage, it remains encrypted while stored (“at rest”). This protects it from unauthorized access, even if someone gains physical access to the storage infrastructure.
Secure Network Protocols
Data is transmitted over secure network connections, often using protocols like SSL/TLS, which further protect the data from interception or tampering during transfer.
Access Controls and Key Management
Only authorized personnel have access to decryption keys, and access to backup data is tightly controlled through user authentication and permissions. Encryption keys are managed securely, reducing the risk of unauthorized decryption.
Physical and Digital Security in Data Centers
BaaS providers store backup data in secure, often geographically distributed, data centers with strong physical and digital security measures to guard against theft, fire, or natural disasters.
Regular Monitoring and Compliance
Continuous monitoring ensures the integrity of backup data, and providers often comply with industry standards such as ISO 27001 and SOC2, which mandate strict security protocols.
Choosing the Right BaaS Provider
When evaluating BaaS solutions, consider:
- Security features: End-to-end encryption, immutability, and compliance certifications.
- Scalability: Ability to handle your current and future data needs.
- Recovery options: Granular restore capabilities and disaster recovery support.
- Cost transparency: Clear pricing models based on storage, bandwidth, and recovery frequency.
- Support and SLA: 24/7 support and guaranteed uptime.
The Future of BaaS
With the exponential growth of data and increasing cyber risks, BaaS adoption is set to accelerate. By 2030, the global BaaS market is expected to surpass $33 billion, driven by organizations seeking robust, scalable, and cost-effective data protection.
In summary
Backup as a Service (BaaS) empowers businesses to secure mission-critical data, streamline IT operations, and maintain uninterrupted business continuity in an era where cyberattacks, system failures, and accidental deletions are inevitable. With Cyfuture Cloud’s advanced BaaS platform, organizations benefit from automated, scalable, and enterprise-grade data protection without the complexity of managing traditional backup infrastructure. Cyfuture Cloud ensures fast recovery, compliance-ready storage, and future-proof resilience, enabling businesses to confidently safeguard their digital assets. For companies aiming to strengthen operational continuity and build a robust, secure IT ecosystem, BaaS from Cyfuture Cloud is not just a modern solution—it is an essential cornerstone of long-term digital strategy.
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 



















