Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
Top 10 Web Server Security Secrets You Must Know
Table of Contents
- What is Server Security?
- Why is Server Security so Important??
- What are Common Server Security Threats?
- 10 Key Steps to Make Your Web Server Secure
- Keep Your Server Software Updated
- Enable Firewall Protection
- Implement Strong Password Policies
- Disable Unused Services and Ports
- Encrypt Data and Connections
- Set Proper File and Directory Permissions
- Enable Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
- Backup Data Regularly
- Monitor Server Logs
- Restrict Remote Access
- Conclusion
Did you know over 30,000 websites are hacked every single day? (Source: Forbes). Yes-this staggering number highlights the reality of the digital age: cyberattacks are becoming smarter, faster, and more frequent. If your web server security isn’t a priority, you could be an easy target for hackers.
Your web server isn’t just a technical tool; it’s the foundation of your online presence. So, whether you run a personal blog or a business site, it holds valuable information—from user data to business-critical files. One breach can do more than compromise data—it can cripple operations and destroy the trust you’ve worked hard to build.
In this blog, we’ll explore the top 10 web server security secrets you need to protect your server and stay ahead of cybercriminals. We’ll simplify complex threats, share actionable tips, and reveal best practices that are easy to implement.
This isn’t just another blog; it’s your first step to a safer digital presence. Ready to learn how to protect your server, your data, and your reputation? Let’s dive in!
What is Server Security?
Server security refers to the processes and measures implemented to protect a server from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, data breaches, and other potential threats. A server is a critical component of any IT infrastructure, hosting sensitive information, applications, and resources that users and systems rely on daily. Ensuring web server security is essential to safeguard data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
Why is Server Security so Important??
Server security is vital because it ensures the protection of sensitive data, maintains operational continuity, and safeguards an organization’s reputation. A server acts as the backbone of any online system, hosting critical information such as customer data, financial records, and proprietary assets. Without robust web server security, businesses face risks like data breaches, cyberattacks, and malware infections, which can lead to severe financial losses and legal consequences. Additionally, server downtime caused by threats like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks disrupts operations and erodes customer trust.
Strong security measures also help organizations comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, avoiding legal penalties and reinforcing customer confidence. In an era of growing cyber threats, prioritizing server security is not just a precaution but a necessary step toward building a resilient and trustworthy digital presence.
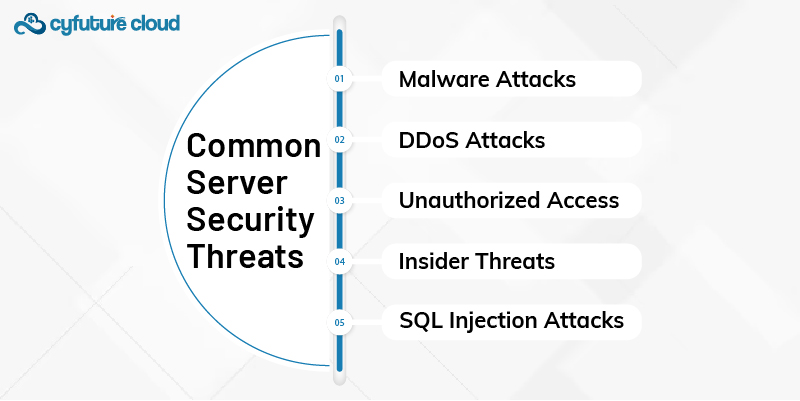
What are Common Server Security Threats?
Server security threats come in various forms, aiming to exploit vulnerabilities in a server to compromise data or disrupt operations. Understanding these threats is critical to building strong web server security measures. Below are the most common threats:
Malware Attacks
Malware, such as viruses, ransomware, and spyware, can infiltrate your server to steal sensitive data, corrupt files, or disrupt services. These attacks exploit weak defenses to spread quickly and cause widespread damage.
Key Points:
- Malicious software that compromises server data.
- Can lead to data theft, corrupted files, and ransom demands.
- Often spreads through unpatched vulnerabilities or phishing emails.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm a server with traffic, rendering it inaccessible. These attacks disrupt website availability and damage user trust.
Key Points:
- Overloads the server with fake traffic to crash services.
- Disrupts business operations and website availability.
- Often targets unprotected servers.
Unauthorized Access
Hackers exploit weak passwords or unpatched systems to gain unauthorized access to servers. This can lead to stolen data, altered configurations, or a total system takeover.
Key Points:
- Occurs due to weak passwords or outdated software.
- Allows hackers to control and misuse server resources.
- Compromises sensitive data and server integrity.
Insider Threats
Insider threats involve malicious actions by employees or contractors who misuse their authorized access to steal data or harm the server.
Key Points:
- Caused by disgruntled employees or careless insiders.
- Leads to intentional or accidental data breaches.
- Harder to detect due to authorized access.
SQL Injection Attacks
SQL injection attacks occur when attackers exploit input fields on a website to inject malicious code into the server’s database, stealing or altering sensitive data.
Key Points:
- Targets databases through website input fields.
- Can steal, delete, or manipulate critical data.
- Exploits poorly secured forms and queries.

10 Key Steps to Make Your Web Server Secure
Here’s how you can improve web server security and protect your data from cyber threats. Each step highlights critical measures to ensure your server remains secure and reliable.
Keep Your Server Software Updated
Outdated software often has vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Regularly update your server’s operating system, applications, and plugins to patch security gaps and reduce risks. Automating updates can save time and ensure consistency.
Key Points:
- Regularly apply updates and security patches.
- Use automatic updates for critical components.
- Monitor for new releases from software vendors.
Enable Firewall Protection
Firewalls act as the first line of defense by filtering and blocking malicious traffic. Configure network firewalls to monitor incoming and outgoing data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Key Points:
- Configure firewalls to block suspicious traffic.
- Use both hardware and software firewalls.
- Regularly review firewall logs for unusual activity.
Implement Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are a major security risk. Enforce policies requiring complex passwords, regular updates, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure only authorized access to your server.
Key Points:
- Use unique, strong passwords for each account.
- Enforce periodic password updates.
- Enable MFA for added security.
Disable Unused Services and Ports
Unused services and open ports can be exploited by attackers. Regularly audit your server to identify and disable unnecessary features, reducing its attack surface.
Key Points:
- Perform regular service and port audits.
- Disable unused or unnecessary features.
- Limit access to essential services.
Encrypt Data and Connections
Encryption protects data from being intercepted or stolen during transmission. Use HTTPS (SSL/TLS certificates) and encrypt sensitive files to enhance web server security.
Key Points:
- Install SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS.
- Encrypt sensitive files on the server.
- Use secure protocols for data transfer (e.g., SFTP).
Set Proper File and Directory Permissions
Misconfigured permissions can lead to unauthorized access. Assign minimal privileges necessary for files and directories to prevent accidental or malicious changes.
Key Points:
- Use “least privilege” principles for permissions.
- Restrict write access to critical files.
- Monitor permissions for unauthorized changes.
Enable Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
These systems monitor traffic for signs of malicious activity and automatically respond to threats. IDS/IPS tools provide real-time defense against evolving cyberattacks.
Key Points:
- Install IDS/IPS tools to detect anomalies.
- Regularly update detection rules.
- Combine with firewalls for layered security.
Backup Data Regularly
Backups ensure you can recover from data loss caused by attacks or technical failures. Automate backup as a service and store them securely to maintain business continuity.
Key Points:
- Schedule regular automatic backups.
- Store backups in secure, offsite locations.
- Test backups periodically for reliability.
Monitor Server Logs
Logs provide insight into server activity and can help identify suspicious behavior. Regularly review and analyze logs to detect and mitigate threats early.
Key Points:
- Enable logging for all server activities.
- Analyze logs for unusual patterns.
- Use automated tools for efficient monitoring.
Restrict Remote Access
Remote access is a common target for hackers. Use secure protocols like SSH, limit IP access, and disable root login to tighten web server security.
Key Points:
- Use SSH with key-based authentication.
- Restrict remote access to trusted IPs.
- Disable direct root access for added protection.
Conclusion
By following or top 10 web security secrets outlined in this blog—keeping software updated, enabling firewalls, enforcing strong passwords, encrypting data, and more—you can create a robust defense against hackers. If you’re looking for reliable, secure, and easy-to-manage hosting solutions, Cyfuture Cloud has you covered. With top-notch security features, robust infrastructure, and 24/7 monitoring, Cyfuture Cloud ensures your web server stays protected against evolving threats.
A secure server is the foundation of a successful digital presence, and with the right measures in place, you can confidently focus on growing your online footprint. Explore Cyfuture Cloud today and make web server security simple, reliable, and stress-free!
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 



















