Table of Contents
- What is Network Function Virtualization (NFV)?
- What is NFV in Networking
- How does network functions virtualization work?
- Benefits of Network Function Virtualization
- Use of Network Function Virtualization
- Challenges of Network Function Virtualization
- Future of Network Function Virtualization
- NFV in Cloud and Networking:
- Conclusion
With the increasing demand for fast, reliable, and secure network services, network infrastructure has become a critical component of many organizations’ operations.
As a customer, you can have your cloud network service provider add a new network function by deploying encryption software on an existing standardized server or switch, rather than introducing new hardware appliances. They can achieve this by spinning up a new virtual machine to perform the function.
It’s worth noting that Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is different from virtualized networks since it focuses only on offloading network functions, rather than the whole network.
As a result, businesses are always looking for ways to enhance their network performance, reduce costs, and increase agility.
This blog will discuss how Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is reshaping modern networks and the role of NVF in IoT.
What is Network Function Virtualization (NFV)?
Organizations can achieve their goals of virtualizing network functions through the use of Network Function Virtualization (NFV) technology. Virtualizing network services, such as routers, firewalls, and load balancers, enables them to be deployed on any hardware or software platform.
The concept underlying NFV is the separation of software from hardware. By decoupling network functions from specialized hardware devices, NFV enables organizations to deploy network services more quickly and flexibly while reducing the need for costly specialized equipment.
What is NFV in Networking
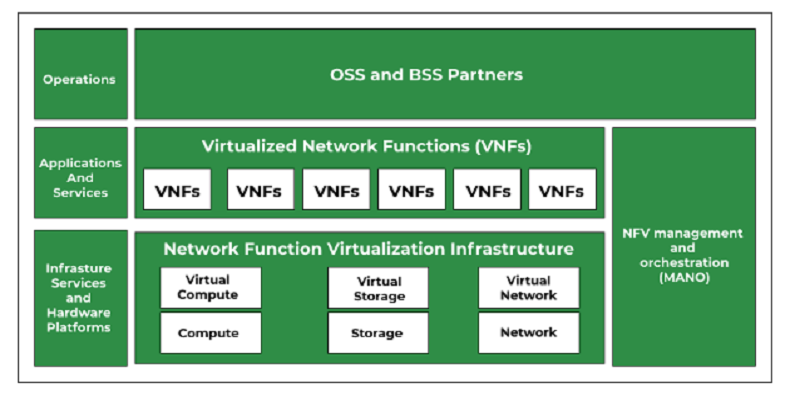
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) in networking refers to the concept of virtualizing and abstracting network functions, traditionally performed by dedicated hardware appliances, into software-based instances that run on standard hardware. By decoupling network functions from specialized hardware, NFV Cloud enables increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in deploying and managing network services. It leverages virtualization technologies to create nfv networking that can be dynamically orchestrated and scaled, leading to quicker service deployment, improved resource utilization, and easier network management for operators and service providers.
How does network functions virtualization work?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) replaces the need for individual hardware networking components by running software on virtual machines to perform the same networking functions.
The Software handles load balancing, routing, and firewall security, and network engineers can program and automate the virtual network using a hypervisor or software-defined the networking controller. This approach enables IT managers to configure various aspects of network functionality quickly and easily using a single interface.
Benefits of Network Function Virtualization
NFV offers several benefits to organizations that adopt it, including:
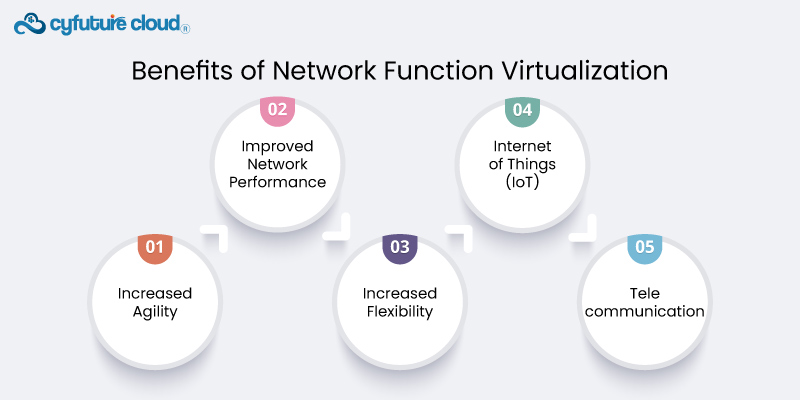
Increased Agility
NFV enables organizations to quickly deploy new network services and functions, without the need for specialized hardware. It empowers organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
Reduced Costs
By eliminating the need for specialized hardware, NFV can reduce the cost of deploying network services.Moreover, NFV can decrease operational expenses by automating numerous tasks related to network service management.
Improved Scalability
NFV enables organizations to quickly and easily scale network services to meet changing demand. This is particularly advantageous for organizations that experience spikes in the demand for network services.
Increased Flexibility
NFV enables organizations to deploy network services in a variety of environments, including on-premises, in the cloud, and at the edge of the network.
Improved Network Performance
NFV can improve network performance by allowing organizations to optimize network functions for specific workloads.
Use of Network Function Virtualization
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is used in a variety of networking environments where virtualization can provide benefits such as increased agility, flexibility, and cost savings. Some common use cases for NFV include:
Telecommunications
NFV is often used in telecommunications networks to provide services such as voice over IP (VoIP), virtual private networks (VPNs), and session border controllers (SBCs). NFV enables telecommunications providers to reduce costs and increase flexibility by replacing dedicated hardware with virtualized software components.
Cloud computing
NFV is used in cloud computing environments to provide networking services, such as load balancing, security, and content delivery. By using virtualized network functions, cloud service providers can scale their services quickly and efficiently to meet changing demand.
Enterprise networking
NFV can be used in enterprise networking environments to provide network services such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and wide area network (WAN) optimization. By using virtualized network functions, enterprises can reduce costs and increase agility by dynamically allocating resources to meet changing business needs.
Internet of Things (IoT)
NFV in IoT networks provides services such as network slicing, edge computing, and security. By using Network Function Virtualization in IoT, service providers can optimize network performance, reduce latency, and enhance security.
NFV in IoT networks provides services such as network slicing, edge computing, and security. By using Network Function Virtualization in IoT, service providers can optimize network performance, reduce latency, and enhance security.
What is NFV in IoT?
Internet of Things (IoT) Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is similar to possessing a virtual toolbox that helps you create, control, and manage all kinds of IoT devices you use in your home or workplace.
Picture the situation where you have a smart thermostat, security cameras, and lights that are sort of a family because they are in your Internet of Things. Specifically, each one of these machines works as an autonomous actor, for example, regulating the temperature, observing events, and controlling the lights.
And thus, when the need arises for each device to have its own suite of specialized hardware to have it work independently, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) comes in handy, to drive the needed computations into standard computers or the cloud server. It’s indeed as if you get virtual and practical versions of these tools, all possible within the scope of the same virtual system.
All right, why would this make industries happy? In sum, it is a combination of adaptability and effectiveness. Operators can add or change IoT devices faster than hardware replacements, which means that operators can benefit from NFV by adding or changing IoT devices based on changes in requirements and capacities.
They can consolidate everything in a single place for managing all devices, which means it becomes less cumbersome when things are in perfect working condition. Moreover, NFV is based on general infrastructure, which results in lower power consumption, lower costs, and, therefore, sustainability over time.
NFV in IoT can be considered an innovative way for businesses to connect and manage their smart devices quickly, resulting in savings of time and money and improved performance.
Challenges of Network Function Virtualization
Despite its benefits, NFV can present several challenges to organizations that adopt it, including:
|
Challenges |
Potential Solutions |
|
|
Performance Issues |
Virtualized network functions may not perform as well as dedicated hardware devices, especially for high-performance workloads. |
Use hardware acceleration techniques such as DPDK, SR-IOV, and Virtio to enhance performance. |
|
Security Concerns |
Virtualized network functions can create new security risks, such as the potential for a compromised virtual network function to affect other virtual functions on the same server. |
Incorporate security measures such as encryption, virtual firewalls, and intrusion detection and prevention systems to secure the virtualized network functions. |
|
Compatibility Issues |
The management complexity issue in Network Function Virtualization (NFV) refers to the difficulty of deploying, scaling, and managing virtual network functions (VNFs) in a complex and dynamic network environment. |
Implement standard interfaces and application programming interfaces (APIs) to ensure compatibility between different virtual network functions (VNFs) and software platforms. |
|
Management Complexity |
Deploying and managing virtual network functions can be more complex than managing dedicated hardware devices. |
Employ orchestration tools to automate and streamline the deployment, scaling, and management of VNFs. |
|
Scalability Limitations |
Scalability limitations in NFV refer to the challenge of efficiently and cost-effectively allocating and deallocating resources to VNFs as demand for network services fluctuates. |
Use elastic scaling techniques to dynamically allocate and deallocate resources based on the current demand for network services. |
|
Interoperability Challenges |
Incorporating virtual network functions from various vendors can pose a challenge due to the use of different protocols and interfaces by different vendors.. |
Foster open standards and interoperability testing to facilitate the interoperability between different NFV components and vendors. |
Future of Network Function Virtualization
The future of Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is likely to involve increasing adoption and innovation in areas such as cloud-native architectures, edge computing, and 5G networks. NFV technology is expected to become more mature and stable, with enhanced automation, orchestration, and security features.
NFV is anticipated to have a growing significance in the network infrastructure’s future. Some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of NFV include:
- Edge Computing: NFV is well-suited to support edge computing, which involves deploying network functions at the edge of the network. This can help organizations reduce latency and improve network performance.
- 5G Networks: NFV is expected to play a critical role in the deployment of 5G networks, which require a flexible and scalable network infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can be used to optimize network functions, such as load balancing and traffic management. NFV can provide a flexible and scalable platform for deploying AI-based network functions.
- Automation: NFV can be used to automate many of the tasks associated with managing network functions, including provisioning, scaling, and monitoring. This can help organizations reduce operational costs and improve network performance.
NFV is also likely to play a significant role in the ongoing transformation of telecommunications networks, as network operators seek to deliver more flexible and cost-effective services to their customers. Additionally, NFV is expected to facilitate the creation of new business models and revenue streams, particularly in industries such as healthcare, finance, and transportation, where the deployment of edge computing and IoT devices can significantly improve operations and customer experience.
These future trends in NFV are anticipated to shape the evolution of networking, ensuring greater flexibility, agility, and efficiency in network infrastructures.
| Future Trends in NFV | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Automation | Utilizing AI/ML for self-healing networks, predictive maintenance, and automatic scaling of functions. |
| Integration with 5G and Edge Computing | NFV enabling virtualized functions at the edge for low-latency, high-bandwidth applications in 5G. |
| Adoption of Cloud-Native Architectures | Embracing containers, microservices, and serverless computing for agility, scalability, and resilience. |
| Network Slicing for Diverse Services | Partitioning single physical networks into virtual networks, catering to various service requirements. |
| Emphasis on Security and Trust | Ensuring robust security measures for virtualized network functions and multi-tenancy environments. |
| Standardization and Interoperability | Efforts to standardize NFV interfaces for seamless integration and interoperability across vendors. |
| Bridging the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum | NFV enabling seamless service delivery across centralized cloud infrastructure and distributed edge. |
| Fostering Service Innovation | Facilitating rapid rollout of new services and applications to meet evolving consumer and enterprise needs. |
| Focus on Energy Efficiency | Optimizing energy consumption in virtualized network functions and data centers for cost savings. |
| Contributions in Open Source Communities | Collaborative development in open-source communities (OpenStack, OPNFV, ONAP) for shared resources. |
NFV in Cloud and Networking:
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) in networking refers to the concept of virtualizing and abstracting network functions, traditionally performed by dedicated hardware appliances, into software-based instances that run on standard hardware. By decoupling network functions from specialized hardware, NFV Cloud enables increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in deploying and managing network services. It leverages virtualization technologies to create nfv networking that can be dynamically orchestrated and scaled, leading to quicker service deployment, improved resource utilization, and easier network management for operators and service providers.
| Aspect | NFV in Cloud Computing | NFV in Networking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizes virtualization for network | Virtualizes network functions to |
| functions in cloud environments | decouple them from hardware | |
| Key Objective | Enhance flexibility & scalability | Improve agility & resource |
| of network services | utilization in network operations | |
| Infrastructure | Relies on cloud-based resources, | Implemented in traditional networks, |
| virtual machines, and containers | transforming physical devices into | |
| for delivering network services | software-based virtual instances | |
| Deployment Model | Utilizes cloud infrastructure | Implemented in various networking |
| models (public, private, hybrid) | environments (data centers, edge, | |
| service provider networks) | ||
| Benefits | – Rapid service deployment | – Increased scalability & flexibility |
| – Cost efficiency through | – Cost savings through resource | |
| resource optimization | optimization | |
| – Dynamic scaling of resources | – Greater agility in service | |
| provisioning | ||
| Challenges | – Security concerns due to | – Integration complexities with |
| multi-tenancy | legacy systems | |
| – Performance & latency issues | – Ensuring interoperability | |
| in virtualized environments | among diverse vendors’ solutions | |
| Use Cases | – Virtualized network functions | – Virtual CPE (Customer Premises |
| (VNFs) for routing, firewall, | Equipment) | |
| load balancing, etc. | – Network Slicing for 5G networks | |
| – Network automation & | – Virtualized WAN solutions | |
| orchestration | – SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide | |
| Area Network) |
Conclusion
NFV is an important technology for cloud networking, providing a flexible and cost-effective solution for deploying network functions in a cloud environment. It is expected to play a growing role in the ongoing transformation of telecommunications networks and in the creation of new business models and revenue streams in industries such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
How Cyfuture Cloud can help you?

Well, our subject matter experts are available 24/7 to guide you down the best path. Our Network Function Virtualization solution is open-source and standards-based. Thus giving you a stable, interoperable foundation to build on. So, why wait? Get in touch with Cyfuture Cloud and start your cloud journey today!
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server Colocation
Server Colocation CDN Network
CDN Network Linux Cloud Hosting
Linux Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing Calculator
Pricing Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware Private Cloud
VMware Private Cloud VMware on AWS
VMware on AWS VMware on Azure
VMware on Azure Service Level Agreement
Service Level Agreement