Get 69% Off on Cloud Hosting : Claim Your Offer Now!
- Products
-
Compute
Compute
- Predefined TemplatesChoose from a library of predefined templates to deploy virtual machines!
- Custom TemplatesUse Cyfuture Cloud custom templates to create new VMs in a cloud computing environment
- Spot Machines/ Machines on Flex ModelAffordable compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads.
- Shielded ComputingProtect enterprise workloads from threats like remote attacks, privilege escalation, and malicious insiders with Shielded Computing
- GPU CloudGet access to graphics processing units (GPUs) through a Cyfuture cloud infrastructure
- vAppsHost applications and services, or create a test or development environment with Cyfuture Cloud vApps, powered by VMware
- Serverless ComputingNo need to worry about provisioning or managing servers, switch to Serverless Computing with Cyfuture Cloud
- HPCHigh-Performance Computing
- BaremetalBare metal refers to a type of cloud computing service that provides access to dedicated physical servers, rather than virtualized servers.
-
Storage
Storage
- Standard StorageGet access to low-latency access to data and a high level of reliability with Cyfuture Cloud standard storage service
- Nearline StorageStore data at a lower cost without compromising on the level of availability with Nearline
- Coldline StorageStore infrequently used data at low cost with Cyfuture Cloud coldline storage
- Archival StorageStore data in a long-term, durable manner with Cyfuture Cloud archival storage service
-
Database
Database
- MS SQLStore and manage a wide range of applications with Cyfuture Cloud MS SQL
- MariaDBStore and manage data with the cloud with enhanced speed and reliability
- MongoDBNow, store and manage large amounts of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud MongoDB
- Redis CacheStore and retrieve large amounts of data quickly with Cyfuture Cloud Redis Cache
-
Automation
Automation
-
Containers
Containers
- KubernetesNow deploy and manage your applications more efficiently and effectively with the Cyfuture Cloud Kubernetes service
- MicroservicesDesign a cloud application that is multilingual, easily scalable, easy to maintain and deploy, highly available, and minimizes failures using Cyfuture Cloud microservices
-
Operations
Operations
- Real-time Monitoring & Logging ServicesMonitor & track the performance of your applications with real-time monitoring & logging services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Infra-maintenance & OptimizationEnsure that your organization is functioning properly with Cyfuture Cloud
- Application Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of your applications over cloud with us
- Database Performance ServiceOptimize the performance of databases over the cloud with us
- Security Managed ServiceProtect your systems and data from security threats with us!
- Back-up As a ServiceStore and manage backups of data in the cloud with Cyfuture Cloud Backup as a Service
- Data Back-up & RestoreStore and manage backups of your data in the cloud with us
- Remote Back-upStore and manage backups in the cloud with remote backup service with Cyfuture Cloud
- Disaster RecoveryStore copies of your data and applications in the cloud and use them to recover in the event of a disaster with the disaster recovery service offered by us
-
Networking
Networking
- Load BalancerEnsure that applications deployed across cloud environments are available, secure, and responsive with an easy, modern approach to load balancing
- Virtual Data CenterNo need to build and maintain a physical data center. It’s time for the virtual data center
- Private LinkPrivate Link is a service offered by Cyfuture Cloud that enables businesses to securely connect their on-premises network to Cyfuture Cloud's network over a private network connection
- Private CircuitGain a high level of security and privacy with private circuits
- VPN GatewaySecurely connect your on-premises network to our network over the internet with VPN Gateway
- CDNGet high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users with CDN
-
Media
-
Analytics
Analytics
-
Security
Security
-
Network Firewall
- DNATTranslate destination IP address when connecting from public IP address to a private IP address with DNAT
- SNATWith SNAT, allow traffic from a private network to go to the internet
- WAFProtect your applications from any malicious activity with Cyfuture Cloud WAF service
- DDoSSave your organization from DoSS attacks with Cyfuture Cloud
- IPS/ IDSMonitor and prevent your cloud-based network & infrastructure with IPS/ IDS service by Cyfuture Cloud
- Anti-Virus & Anti-MalwareProtect your cloud-based network & infrastructure with antivirus and antimalware services by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat EmulationTest the effectiveness of cloud security system with Cyfuture Cloud threat emulation service
- SIEM & SOARMonitor and respond to security threats with SIEM & SOAR services offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Multi-Factor AuthenticationNow provide an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cloud account, even when the password has been stolen!
- SSLSecure data transmission over web browsers with SSL service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Threat Detection/ Zero DayThreat detection and zero-day protection are security features that are offered by Cyfuture Cloud as a part of its security offerings
- Vulnerability AssesmentIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Vulnerability Assessment service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Penetration TestingIdentify and analyze vulnerabilities and weaknesses with the Penetration Testing service offered by Cyfuture Cloud
- Cloud Key ManagementSecure storage, management, and use of cryptographic keys within a cloud environment with Cloud Key Management
- Cloud Security Posture Management serviceWith Cyfuture Cloud, you get continuous cloud security improvements and adaptations to reduce the chances of successful attacks
- Managed HSMProtect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements for secure data storage and processing.
- Zero TrustEnsure complete security of network connections and devices over the cloud with Zero Trust Service
- IdentityManage and control access to their network resources and applications for your business with Identity service by Cyfuture Cloud
-
-
Compute
- Solutions
-
Solutions
Solutions
-
 Cloud
Hosting
Cloud
Hosting
-
 VPS
Hosting
VPS
Hosting
-
GPU Cloud
-
 Dedicated
Server
Dedicated
Server
-
 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation
-
 Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service
-
 CDN
Network
CDN
Network
-
 Window
Cloud Hosting
Window
Cloud Hosting
-
 Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting
-
Managed Cloud Service
-
Storage as a Service
-
 VMware
Public Cloud
VMware
Public Cloud
-
 Multi-Cloud
Hosting
Multi-Cloud
Hosting
-
 Cloud
Server Hosting
Cloud
Server Hosting
-
 Bare
Metal Server
Bare
Metal Server
-
 Virtual
Machine
Virtual
Machine
-
 Magento
Hosting
Magento
Hosting
-
Remote Backup
-
 DevOps
DevOps
-
 Kubernetes
Kubernetes
-
 Cloud
Storage
Cloud
Storage
-
NVMe Hosting
-
 DR
as s Service
DR
as s Service
-
-
Solutions
- Marketplace
- Pricing
- Resources
- Resources
-
By Product
Use Cases
-
By Industry
- Company
-
Company
Company
-
Company
Data Security in Cloud Computing – 2023 Edition
Table of Contents
- Why companies are utilising more and more of cloud computing
- What does data security in cloud computing entail of?
- What justifies the necessity of data security in cloud computing?
- What methods do cloud computing companies use to secure data?
- Key Aspects of Cloud Computing and Data Security:
- The cloud’s limits for data security
Data security used to be mostly a human-driven process, and data existed only on paper. However, since then, much has changed thanks to digitization. Organizations today are made up equally of concrete and clouds. 77% of businesses, according to Accenture, use the cloud for at least some of their operations.
This change necessitated a new security strategy that can completely safeguard the priceless assets now kept on the cloud. This blog post explores in-depth the importance of data security in cloud computing and what it will take to protect your data in 2023.
Why companies are utilising more and more of cloud computing
The use of cloud-based applications has increased significantly over the past few decades because of the enormous benefits they offer, even if they can be more difficult to secure than on-premises systems. These benefits include shorter development times, increased performance, and easier device-to-device access to data storage.
The acceptance of remote work is one of the sociological trends that has fueled the expansion of cloud computing. Although work-from-home (WFH) agreements had been expanding in the private sector for years, particularly for IT roles, the pandemic drastically sped up this development. The significance of security executives enhancing their cloud security profiles has grown in light of the most recent spike.
What does data security in cloud computing entail of?
Data security is the process of securing digital data against loss or destruction. It comprises defences against unauthorised access to electronic documents, falsified data change, and access disruption brought on by natural disasters. Business owners have always been concerned about data security, but the emergence of cloud computing has made it considerably more crucial – and difficult. As a result, any data kept on a remote server must be protected using many layers of access controls and encryption/decryption technology, just as if it were kept on a server inside a company’s network.
What justifies the necessity of data security in cloud computing?
The security of your company’s cloud data is crucial for a variety of reasons. Important corporate data could be lost, stolen, or destroyed without a strong approach to data security in cloud computing, and such accidents can be disastrous on a number of levels. Your cloud-managed data assets being compromised could cause serious financial losses, seriously sour client relations, and expose your company to harsh regulatory action.
What methods do cloud computing companies use to secure data?
After going over the fundamentals, let’s examine the key methods for obtaining and upholding secure cloud usage throughout your company.
Access to data
Identity and access management (IAM), which aids in the protection of data assets through authentication and authorisation procedures, allows security teams to govern data access. Users must provide unique credentials as part of the authentication process in order to access an application and its data, and using multifactor authentication has become a widely accepted best practise to increase security. Users must confirm their identity using various sources, such as a password and a text-based code, while employing multifactor authentication.
Firewall
Web application firewalls (WAF) monitor and stop malicious traffic to protect cloud applications against compromise. WAFs shield applications from a sizable number of attack types and vulnerabilities, despite not being fully complete. WAFs are one of the most crucial components of data security in cloud computing because without this security layer, attackers might simply exploit cloud apps and their data stores.
Data encryption, a basic security feature provided by cloud service providers, uses mathematical encoding to block unauthorised access to information. Even while data encryption is commonplace, not all service providers offer the same level of encryption. Despite the fact that this might not be feasible throughout your entire cloud infrastructure, make sure that the services that are of the utmost importance offer your team a high level of control and a variety of encryption alternatives.
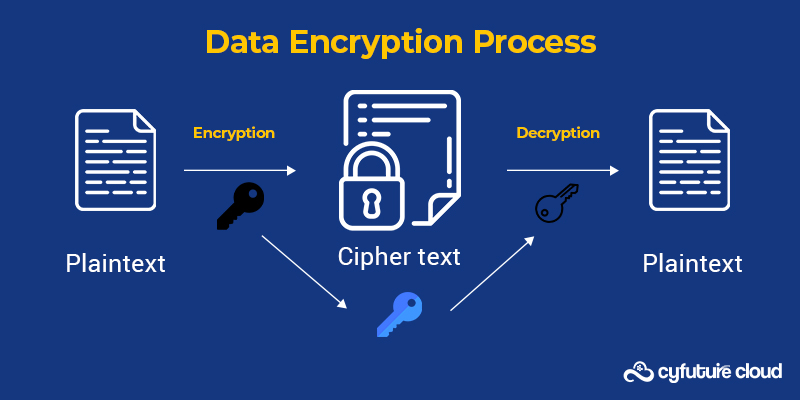
Data removal
Data security includes properly getting rid of sensitive information that is no longer needed. If such material is permitted to stay permanently within cloud data repositories, unnecessary liability may result, posing a serious organisational risk. Organizations must create and adhere to a data destruction plan to reduce this risk. This protocol should decide when data should expire depending on its usefulness, legal restrictions, and other factors. The protocol should also describe every facet of the disposal process, including frequency and approach. Even though it can be time-consuming, this practise is vital to lessening an organization’s risk.
Data restoration
Another pillar of cloud data security is reliable data recovery procedures. Every system that depends on cloud-based applications must be continually backed up because data loss might happen for a variety of unanticipated reasons. Data, software, and operating systems from each machine should all be included in the backup. Don’t stop there, though; it’s also a good idea to periodically test your backups in order to confirm them.
Key Aspects of Cloud Computing and Data Security:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Utilizes remote servers to store, manage, and process data over the internet, offering scalability and accessibility. |
| Data Encryption | Ensures data is encoded to prevent unauthorized access or interception, safeguarding confidentiality. |
| Access Control | Regulates user permissions, limiting access to data based on roles or authentication levels. |
| Compliance Measures | Adherence to industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) ensuring data protection and privacy regulations are met. |
| Regular Audits | Periodic evaluations of security protocols to identify vulnerabilities and maintain system integrity. |
| Data Backup & Recovery | Regularly backing up data and implementing strategies to restore information in case of data loss or system failure. |
The cloud’s limits for data security
Even with the finest firewalls, access restrictions, and encryption in place, most organisations lack the level of cloud data security required to safeguard their most priceless assets. Although each of the strategies we’ve examined delivers a crucial piece of the stack, they don’t provide comprehensive coverage of the full data store landscape.
Data store and object security is a new subset of data security that has emerged as a result of this huge gap (DSOS). The main goals of DSOS are to map out an organization’s data repositories, find vulnerabilities, and notify teams of potential problems.
Numerous conventional data security methods will still be required in the years to come, but innovative strategies, such as DSOS, will set apart security teams from those that are only ticking boxes from those that are actually defending their organisations.
In this field, Cyfuture Cloud is one of the top suppliers. Its offers a clear view into your whole data store landscape, warning you of potential vulnerabilities, spotting threats, and facilitating quick action.
To learn more about Cyfuture Cloud, get in touch. Our staff will promptly set you up with a demo.
Recent Post

Stay Ahead of the Curve.
Join the Cloud Movement, today!
© Cyfuture, All rights reserved.
Send this to a friend

 Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 


















