Table of Contents
- What is Cloud Computing in 2022?
- What are the characteristics of Cloud Computing in 2022?
- What are the most common forms of the Cloud Deployment model?
- Different types of cloud computing deployment models include:
- Public Cloud Deployment Model
- The benefit of Public Cloud include:
- Cloud Architecture
- Cloud Architecture Model includes:
- Cloud Architecture Model: SaaS- Software as a Service
- Characteristics of SaaS
- Cloud Architecture Model: PaaS- Platform as a Service
- Characteristics of PaaS
- Cloud Architecture Model: IaaS- Infrastructure as a Service
- Characteristics of IaaS
- Cloud Architecture Model: XaaS- Everything as a Service
- Characteristics of XaaS
- Points to be taken into consideration while selecting a CSP
- Popular Cloud Computing Trends to watch out for in 2022
- Below we are listing some popular Cloud Computing Trends in 2022:
- Conclusion
Cloud Computing is one of the fastest-growing segments not just in India but in many countries around the globe. In 2021, it is estimated that cloud computing has generated nearly 400 billion dollars in revenue, and there are few signs that it will slow down. The adoption of cloud services is at an early stage in most countries, but the demand of working from home and business continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the growth. It has led more and more companies to adopt Cloud Computing Technology.
In this article, we will explain all aspects of Cloud Computing- Cloud Computing Model, Cloud Computing trends in 2022, and how it is beneficial for your business.
What is Cloud Computing in 2022?
By utilizing cloud computing, you can rent IT rather than buy it outright. It allows companies to access their compute power using the internet, or the cloud, and save them from investing heavily in databases, software, and hardware.
Cloud computing provides business organizations with the speed, scalability, and flexibility they require to develop, innovate, and operate their business IT solutions. The services include but are not limited to, servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and business intelligence.
With a cloud computing model, global service providers can rapidly provision and release resources that can be shared and configured with little effort. These resources can be accessed on-demand, anywhere, and anytime. The Cloud Computing model is a lot cheaper to acquire and operate.
What are the characteristics of Cloud Computing in 2022?
Ubiquitous
Cloud Computing allows users to access and upload data as and when required and from anywhere using the internet. So no matter which part of the world you are in, you can always access your data with just a few clicks.
Cloud Computing characteristics: Convenient
With Cloud computing, companies do not have to build large data centers or invest in hardware, server room, facilities, utilities, or other infrastructure to accommodate their growing businesses. Additionally, companies do not need large IT teams to operate cloud data centers since they can depend on the expertise of their cloud provider.
Scalability is also count as Cloud Computing characteristic
It gives you the flexibility of adaptive scaling. Cloud Computing enables companies to scale up and down as demand increases and decreases to eliminate the need to invest heavily in local infrastructure, which may or may not remain in use.
Cost-effectiveness
By utilizing cloud infrastructure, companies do not have to worry about investing in hardware, facilities, utilities, or building any large data centers. Since cloud providers have experts to handle cloud data center operations, companies don’t need to hire large teams of IT professionals. Cloud computing also reduces downtime costs as downtime rarely occurs.
Important Cloud Computing characteristic: On-Demand Self-service
The provision of computing services, such as server time and network storage, can be done unilaterally by consumers, with no interaction between them and their service providers. The services will be available for your use within minutes.
By choosing multi-tenancy, numerous customers can share the same physical infrastructure or the same applications while still maintaining the privacy and security of their data. By using resource pooling, cloud providers can serve multiple customers from the same physical resources.
Computing Resources
The cloud offers the newest and most powerful computational resources. Users have access to multiple-core CPUs with extreme processing power, allowing for heavy parallel processing.
Rapidly Provisioned
An advantage of the cloud computing model is that it allows users to easily access a shared set of configurable resources on-demand with minimal management effort and without needing to interact with their service providers.
Minimal Management
By implementing a robust security patch management process and a related implementation process, Cloud Computing can reduce the chance of vulnerabilities and ensure optimum cloud security. Moreover, it requires minimal human interaction as every aspect of cloud infrastructure is pretty much automated, from configuration to monitoring and maintenance.
Measured Services
It is one of the major benefits of using Cloud services. You pay as you use. It means the cloud provider will measure all the cloud services and computing resources like bandwidth, storage space, development tools, software, etc. You will be charged only for the services you will use in the billing cycle.
What are the most common forms of the Cloud Deployment model?
In determining the type of cloud environment to operate in, a cloud deployment model considers factors such as ownership, scale, and access, as well as the nature and purpose of the cloud. This model includes information such as where and who controls the servers.
Deployment types determine how your cloud infrastructure will appear, what changes you can make, and if you will be provided with services or will need to construct everything yourself. They also determine the relationship between your user environment and the infrastructure.
Different types of cloud computing deployment models include:
Public cloud
Private cloud
Hybrid cloud
Community cloud
Multi-cloud
Public Cloud Deployment Model
This sort of cloud deployment architecture, as the name implies, supports all customers who want to subscribe to a computer resource, such as hardware (OS, CPU, memory, storage) or software (application server, database). In a cloud model like this, the infrastructure is owned by the entity delivering the cloud service, instead of by consumers. Customers & users can gain access to system and service resources via the cloud.
Using the Public Cloud model, service providers supply arrays of services to a variety of customers. Data backup and retrieval services are provided free of charge, as subscriptions, or as a per-use service.
Some examples of public cloud are Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Cyfuture Cloud.
The benefit of Public Cloud include:
Public Cloud comes with minimal investment and you pay only for the services you are using. It is great for organizations that need immediate access to resources.
Because the cloud service providers are fully responsible for the infrastructure, no hardware needs to be set up.
No infrastructure management and maintenance are required.
It offers dynamic scalability. On-demand resources are available to serve your company’s requirements.
Private Cloud Deployment Model
A private cloud is one of the cloud deployment models that is meant exclusively for a single organization. These types of deployment models are managed and hosted by a third-party vendor or service provider. These deployment models can be physically situated at the company’s on-site data center or are managed and hosted by a third-party vendor or service provider.
Private clouds give organizations greater flexibility and control over cloud resources since they are installed in a secure cloud environment protected by powerful firewalls. Also known as the “internal cloud”, it refers to a system or service available within the borders of an organization or department.
Due to the capital expenditures involved with acquiring and maintaining private clouds, they are more expensive than public clouds. However private clouds can be more secure and provide more privacy for organizations today.
Private clouds offer more customization options that help meet organizations’ needs. Additionally, it’s an ideal solution for mission-critical processes that undergo frequent changes in requirements.
Some examples of Private clouds are OpenStack and Cloudify.
The benefits of Private Cloud include:
As the sole owner of the property, you gain complete control over services integration, IT operations, policy creation, and user behavior.
It is ideal for storing information on a corporate network that only authorized staff can access. By segmenting the infrastructure, it provides improved access and security.
In contrast to public cloud deployments, a private cloud lets a company customize the solution to meet its unique needs.
Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model

A hybrid cloud is a system that integrates a private cloud with public cloud services, allowing each service to communicate with the other. These are scalable models. Hybrid cloud deployment models provide businesses with more pliability and resilience by allowing them to move workloads between cloud platforms as their needs and costs change.
When an organization needs to quickly expand its IT infrastructure, such as to supplement capabilities in a private cloud, this model makes for an ideal choice frequently. Public clouds could be used, for instance, by an online retailer that needs more computing power to run their web applications during the holidays.
Cloud bursting is frequently used for hybrid clouds, which store less sensitive data on a public cloud. Mainly, companies with sensitive data will prefer a private cloud, while companies with less sensitive data will prefer a public cloud.
Some examples of Hybrid Cloud are Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
The benefits of Hybrid Cloud include:
Hybrid Cloud provides you with complete flexibility and control. With more flexibility, businesses can design solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
This cloud model is highly cost-effective. Cloud computing is scalable. So only if you need additional capacity will you have to pay.
By properly segregating data, attackers have a much smaller chance of stealing it.
Adding public cloud infrastructure to on-premises infrastructure can help enterprises unlock the power of their big data.
Community Cloud Deployment Model

Multiple groups sharing the same computing resources within a community are known as the community cloud deployment model. Most common examples include police departments within a country or state sharing the same computing resources.
It is typically managed by a third party or several organizations in the community which has shared concerns and responsibilities. A third party or a combination of organizations could manage the community infrastructure.
Some examples of Community Cloud are Government Organizations.
The benefits of Community cloud include:
Adaptable to the needs and requirements of every user, the community cloud is flexible and scalable. Documents can be customized based on a user’s needs and requirements.
Using a community cloud, various organizations can share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other capabilities.
You can easily share cloud resources with other organizations using Community Cloud.
Even though it offers less security than the Private Cloud but a lot safer to use the Public Cloud.
Multi-Cloud Deployment Model

Multi-Cloud is a cloud computing model in which an organization uses a mix of clouds, such as two or more public clouds, two or more private clouds, or a combination of both public and private clouds. Those organizations that do not wish to rely on one cloud provider may choose to use multiple cloud services to maximize the benefits.
While public cloud providers provide numerous tools for improving their services’ reliability, occasional problems occur. It rarely happens when two distinct clouds experience problems at the same time.
The benefits of Multi-Cloud include:
In the face of exponentially increasing data volumes, multi-cloud architecture offers businesses solutions for storing and processing their data. It allows organizations to scale up and down their storage requirements according to their needs.
A multi-cloud strategy improves security for businesses, provides better failover options, and enhances disaster recovery. The cloud infrastructure is always readily available, ensuring long-term continuity for the organization.
In the face of exponentially increasing data volumes, multi-cloud architecture offers businesses solutions for storing and processing their data. It allows organizations to scale up and down their storage requirements according to their needs.
Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture is the style in which all technology components come together to form a cloud. Using virtualization technology, resources get pooled together and shared over the network. The main components of a cloud architecture include a network, a front-end platform, a back-end platform, and any cloud-based delivery model.
When all these components come together, they build an architecture over, which you can run your applications. This setting allows end-users to incorporate the power of Cloud technology into their business.
Cloud Architecture Model includes:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Everything as a Service (XaaS)
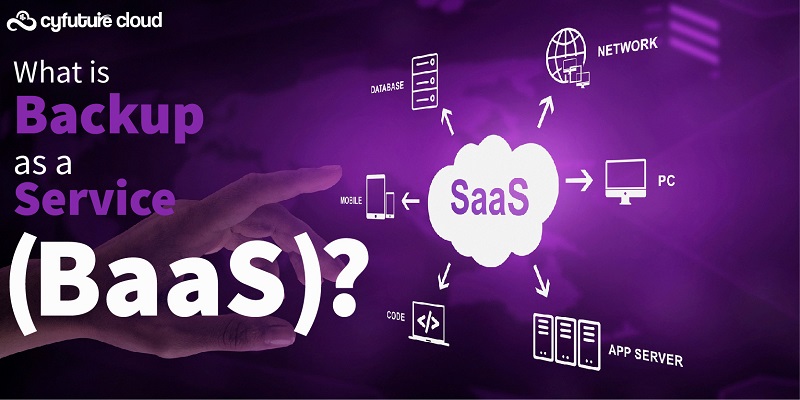
Cloud Architecture Model: SaaS- Software as a Service
SaaS, also known as Software as a service is a model through which applications get delivered over the internet. The main advantage of using this model is that it frees you from the hassle of downloadable software and hardware management.
This model uses the cloud delivery model where a software provider utilizes its databases, servers, computing resources, and networking to host the application and related data. Unlike other Cloud computing models, SaaS products are used by both B2B and B2C users. Moreover, SaaS has become the most preferred platform for all mission-critical data.
As per the McKinsey & Company report, the software as a service market will experience rapid growth and a market of $200 billion by 2024.
This model is also widely popular among businesses as web-based software, hosted software, or on-demand software. In short, for this model, all you need is an internet connection to access the applications. Businesses can also integrate SaaS applications with other software with the help of Application Programming Interfaces (API).
SaaS is widely popular among IT professionals for both personal and business use. Some examples of SaaS include Netflix, Adobe Cloud, salesforce automation, inventory management, and Microsoft Office 365.
Characteristics of SaaS
Multi-tenant architecture
Easily Customizable
Improved & easy access
Automatic updates
Highly Scalable
Cloud Architecture Model: PaaS- Platform as a Service
Offering a run-time environment to the developers, PaaS stands for Product as a service and is a cloud computing model where a service provider delivers hardware and software tools using the internet. These tools are majorly required for application development.
By leveraging PaaS, developers can develop or run a new application without installing any hardware or software in-house. PaaS tools are typically touted as easy-to-use and convenient. Users are typically pay-per-use. Considering potential cost savings over on-premises alternatives, organizations may find it compelling to switch to PaaS.
The cloud service provider hosts the infrastructure for PaaS that allows for access using a web browser. PaaS does not automatically replace an organization’s entire IT infrastructure. PaaS can deliver Java development and application hosting services on public, private, and hybrid clouds. Some examples of PaaS products and vendors include AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, etc.
Characteristics of PaaS
Built-in security
Customizable User Interface
Easy data customization
Services-enabled flexible integration model
Future-proof
Cloud Architecture Model: IaaS- Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a service is a highly efficient cloud computing model and is ideal for organizations that own and manage the infrastructure.
With Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), you can eliminate on-premises servers and data storage by shifting them into the cloud. IaaS solutions reduce your equipment and staffing needs because they eliminate the need for physical hardware.
Your IaaS provider will manage the service, but you’ll retain full control. You can add new features and services as your business grows, or decrease the size of your infrastructure without losing money on expensive investments. While the provider will manage and upgrade your infrastructure, you may select and configure your software, virtual machines, middleware, and applications to meet your specific business needs.
As a result of better preventative measures and higher SSD performance in newer networks, this issue is rarer than it used to be. Several customers prefer multi-tenancy at the expense of completely separate servers, as the noisy neighbor’s problem is becoming less common.
Moreover, IaaS allows you to access all your vital communication tools and files in a hassle-free manner. In this model, you only pay for the services you use. Examples of IaaS include Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
Characteristics of IaaS
Dynamic Scaling
API and GUI-based access
Self-service provisioning
High reliability and improved security
Offers interoperability
Cloud Architecture Model: XaaS- Everything as a Service
If you haven’t figured it out already, XaaS is an acronym that stands for everything. Therefore, the whole idea of XaaS is ‘all as a service. Any tool, application, service, game, etc., delivered to your laptop or other devices over the internet rather than acquired locally or in a physical format, can be called a cloud-based product.
In this cloud computing model, various tools and technologies are made available to clients as a service. Before XaaS and cloud services, companies purchased software products, installed them, installed all security regulations, and provided infrastructure for business purposes. This Everything as a Service is also widely known as “Anything as a Service” among organizations.
In addition to XaaS’s benefits, organizations often lack the resources and expertise necessary to manage their IT and keep up with new technologies, so they need someone to do it professionally. It is when the XaaS provider steps in to fill the gap.
Some examples of XaaS include healthcare as a service, disaster recovery as a service, security as a service, etc.
Characteristics of XaaS
Little to very low cost
Bring agility to business
Ease to access
Highly scalable
Multi-tenant architecture
Points to be taken into consideration while selecting a CSP
When selecting the right cloud service provider, we jump straight to the features and services they offer. But the first thing that needs to be taken into consideration is the requirements of your business. When organizations have this understanding, they can gather accurate computing metrics that can assist in finding the best cloud service for their needs. It ultimately leads to their selection of the best provider for the – one that ensures their long-term success.
In the figure given below, we have outlined some of the essential features you must consider while picking the Cloud Service Provider.
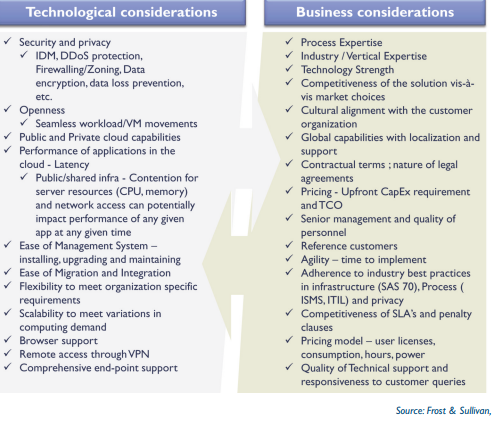
Capacity
It is one of the most vital factors you must look for while choosing the Cloud Service Provider. Check if the services you are choosing are offering the desired storage space, processing speed, IOPS, networking, processing power, and workload capability of the system.
Elasticity
While selecting the cloud service provider, check if they are offering you the flexibility to expand and contract as required. As to help your business grow, the Cloud services you are opting for must provide you with the scalability you need to expand your business if required. Be it CPU resources, storage space, or other computing resources, you must be in a position to add or remove them as per the requirement.
Service Model Maintenance
Check if your cloud service provider is using the metrics that measure your cloud resource consumption. The service they are provisioning must meet your current business needs. It should be a demand-driven service.
Technologies
You must ensure that the provider you are choosing is offering you the best platform and is using the latest technologies to equip your business needs. Various cloud service providers offer comprehensive migration services, and some of these providers also provide help in the assessment and planning phases. Ensure that you understand the support provided and map it against the project tasks so you can decide who will do what.
SLAs
Service-level agreements or SLAs is an agreement that is used to form the relationship between the client and the cloud service provider. You must not wait to establish such contractual relationships with your cloud provider if the provider is clear on establishing whatever SLAs you require based on your business standards.
Information Security
The security operations and governance processes of the cloud provider should be demonstrated risk-based and must directly support your security policies. Assess the provider’s security levels and assurance of data and system security. You can ask for reports on security audits and incident investigations, along with evidence of any corrective action. See if the provider can match your business requirements.
Service Delivery
You should search for clarity on the definition of the service and deliverables. Find out what each player’s role and responsibility is regarding the service (delivery, provisioning, service management, monitoring, support, escalation, etc.) and how it is shared between the provider and customer.
Resource Balancing
Resource balancing or load balancing is one of the vital issues in cloud computing. Your CSP must achieve load balancing using proper techniques, as it is directly related to higher resource utilization ratio and user satisfaction. By evenly distributing the dynamic local workload across all the nodes in the whole cloud, load balancing makes sure that no single node is overwhelmed, and some other nodes are kept idle. By keeping resource consumption at a minimum, the load balancing techniques help to reduce costs.
Several techniques can be used for resource balancing:
On-demand provisioning
Auto-scaling
Hybrid clouds
Serverless processing
Check if your cloud service provider uses these practices to ensure resource balancing.
But to make the most out of cloud computing technology, you must upgrade the technology as it evolves. To help you out, we will explain the promising Cloud computing trends that can help your business grow at a rapid speed.
Popular Cloud Computing Trends to watch out for in 2022
As most businesses become remote during a pandemic, the market shifts towards Cloud Computing technology. Be it social media or our popular streaming entertainment, cloud computing infrastructure plays a pivotal role in the delivery pipeline. It is not just limited to the entertainment industry but every digital business that includes IoT infrastructure etc. Cloud computing technology is growing rapidly, and it will continue to do so in years to come.
The rise in cloud computing technology is leading to many popular trends entering the market. So if you have not checked the Cloud Computing Trends in 2022 yet, you must check them out now to give your business a competitive edge.
Below we are listing some popular Cloud Computing Trends in 2022:
AI in Cloud Computing
Hybrid Cloud Deployment
Application & Database Modernization
Serverless Cloud
SaaS-ification
AI in Cloud Computing
The advantages of AI clouds are their ability to address complex challenges. It democratizes AI and makes it more accessible. It lowers adoption costs and facilitates co-creation, resulting in AI-powered transformation.
AI-driven insights are now accessible to all via the cloud, as cloud computing has already become widely implemented. Besides, AI is going to make cloud computing significantly more efficient, so we should expect it will be a major force multiplier in the future.
By leveraging the cloud’s flexibility, agility, and scale, artificial intelligence provides strategic inputs for the enterprise’s decision-making. The cloud will increase AI’s reach and sphere of influence significantly from the user enterprise itself. The cloud and AI are in fact mutually beneficial, helping AI bloom through the cloud.
Cloud Computing Trend 2022: Hybrid Cloud Deployment
The hybrid model offers you the best of both worlds- Public Cloud & Private Cloud. Hybrid cloud is becoming more popular because many companies are moving beyond their initial forays into cloud computing, and after securing the benefits, they are looking for more applications.
Thus, many companies are now exposed to a “multi-cloud” environment, using several different types of services provided by several different providers. With hybrid cloud provisioning, the user experience is streamlined and the backend stack is not visible when it is not required to be visible.
Cloud Computing Trend 2022: Application & Database Modernization
Your business needs to modernize to be able to scale, automate, and grow. The cloud offers you the opportunity to do this. As a result, monolithic applications are being migrated into multi-tenant architectures, API first approach is being used to refactor applications, and Databases are being containerized to support auto-scaling.
Businesses have invested way too much time and money over the years to build the application landscapes they have and simply replacing them with new ones is not easy commercially or technically. Additionally, Modernization will include the building of integration layers to enable all distributed applications to be accessed from a single pane and interoperability between services through iPaaS offerings within the Cloud environment.
Cloud Computing Trend 2022: Serverless Cloud
An organization’s resources are supported by serverless computing, where the cloud provider controls and manages the underlying infrastructure. Developers are unable to see server utilization with this platform because it executes code on-demand and scales and bills only when it is running. With the serverless cloud, your enterprise can become more dynamic, flexible, and service-oriented by incorporating it into the working model of the future.
Cloud computing with serverless architecture enables your enterprise to expand into the cloud and take advantage of public and private cloud resources. Bringing the IT environment to the cloud is an efficient way to ensure that a wide array of resources is available at scale. The serverless cloud platform eliminates the manual process of developing and maintaining servers and other hardware infrastructures for cloud-based applications.
Cloud Computing Trend 2022: SaaS-ification
Increasingly, businesses are becoming SaaS-based, and smart organizations are taking advantage of this by putting dynamic services on a platform, which are consumable by many users at any time. Within two years, 34 percent of enterprises will have 60 percent or more of their applications running on cloud platforms, according to a recent industry analyst estimate.
The SaaSification process is characterized by changing economic models in which on-demand services instead of hardware and software procurement provide companies with the flexibility they need. In this value-based, outcome-driven model, companies pay for what they use, upending the entire technology industry. In their model, they buy an outcome and look beyond hardware and software to achieve it.
Conclusion
There is no better way to sum up what cloud computing technology can do for your business is that it revolutionizes your business in every possible way. To migrate your business to Cloud and reap the benefits yourself, you must find a reliable Cloud Service Provider. For any inquiries and doubts related to Cloud.
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server Colocation
Server Colocation CDN Network
CDN Network Linux Cloud Hosting
Linux Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing Calculator
Pricing Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware Private Cloud
VMware Private Cloud VMware on AWS
VMware on AWS VMware on Azure
VMware on Azure Service Level Agreement
Service Level Agreement