Table of Contents
Large and small businesses alike are moving more and more toward cloud-based services. The ability of both public and private clouds to reduce operating costs while enhancing operational flexibility is what has led to their rapid growth in recent years. Unlike traditional on-premises architecture, components of cloud infrastructure use remote servers to store, manage, and access data over the Internet.
Transparency, scalability, security, and intelligent monitoring are some of the key limitations facing cloud infrastructure. Current research into other important limitations is helping cloud computing systems develop new capabilities and strategies with greater capabilities to deliver more advanced cloud solutions.
As per its capacity to furnish virtualized resources as needed, cloud computing, which is among the most significant technologies of our era, is revolutionizing businesses. Businesses of all sizes utilize cloud services for storing and accessing data easily from any location on the globe.
This blog explains the function of Content Delivery Networks (CDN) in this constantly changing environment by looking at the fundamental foundational mechanisms of cloud components, and also essential components of cloud infrastructure as a service.
Let’s get started!
Visit Cyfuture Cloud to know more
Why Cloud Computing?
Components of cloud infrastructure enable you to stream audio and video content with ease, host dynamic blogs and websites for data analysis, protect and store your data, and develop cutting-edge apps and services. All of this happens on remote servers, which are also called cloud servers. This means that large and complex components of cloud infrastructure are not needed.
The software platform and database are hosted remotely, offloading storage and computing tasks from each computer. Cloud computing offers many benefits such as high efficiency, cost savings, data security, scalability, mobility, disaster recovery, and complete control over your data.
What are the Components of Cloud
The architecture of cloud components consists of two main parts: the front end that customers use and the back end that the host manages. The Internet allows for the seamless connection of these parts.
The front end consists of attractive applications and user interfaces that make cloud services accessible. Companies that provide essential components of cloud infrastructure as a service are in charge of carefully maintaining the backend in the meantime. It includes essential cloud components, including servers, virtual machines, strong security mechanisms, and data storage facilities.
Visit Cyfuture Cloud to know more
Below is a list of cloud computing architecture components.
1. Client Infrastructure
The client infrastructure component is part of the front end that provides a graphical user interface through which the user can interact with the cloud. Check out UpGrad’s Advanced Certification in DevOps
2. Application
An application is a platform for a client to access the cloud, such as an app or software provided by an enterprise.
3. Service
Cloud services manage the types of services that clients should use as needed. There are three types of cloud computing services. -Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS-based services are called cloud application services. They run directly from your web browser, so you don’t need to download or install any applications. B. Slack, Hubspot and Google apps.
–Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS services are similar to SaaS. However, PaaS services provide a platform for users to create, edit, and launch software. For example, Magneto Commerce Cloud and Windows Azure. – Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS manages the runtime environment for application data and middleware. Provides virtual services that eliminate the need for physical computing resources such as RAM, CPU, and data centers. With IaaS, companies pay to operate virtual servers, networks, and storage in the cloud. For example, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud, Amazon Web Services.
4. Storage
The storage component of cloud computing provides storage capacity in the cloud for storing and managing data. Cloud storage allows multiple clients to access data simultaneously. In general, cloud storage has three basic configurations: public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud.
5. Infrastructure
Infrastructure provides host-level, application-level, and network-level services. This includes software and hardware components such as storage network devices, servers, and all other storage resources required to support the cloud computing model.
6. Management
Management is used to manage and coordinate components such as storage services, applications, runtime cloud infrastructure, and backend security concerns.
7. Security
Security is the backend component of cloud computing that ensures the security of data in the cloud. Cloud security systems include a wide range of policies, technologies, and applications.
8. Web
The Internet is the medium through which front-end and back-end components communicate and interact with each other.
Visit Cyfuture Cloud to know more
Transparency, scalability, security, and intelligent monitoring are some of the essential components of cloud infrastructure as a service. Current research into other important limitations is helping cloud component systems develop new capabilities and strategies with greater capabilities to deliver more advanced cloud solutions.
Components of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure comprises several key components that form the backbone of cloud components. This includes physical data centers housing servers, storage, networking equipment, and other hardware that provide the foundational resources for cloud computing. Virtualization technology enables the creation of virtual instances, optimizing resource utilization. Networking components, such as routers, switches, and load balancers, facilitate data transmission within and between data centers.
Storage infrastructure encompasses various types, such as object storage, block storage, and file storage, catering to diverse data needs. Security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and identity management tools, safeguard data and applications across the infrastructure.
Automation and orchestration tools streamline resource management, ensuring efficient deployment, scaling, and maintenance of cloud components services. Overall, these integrated cloud components form a robust and scalable cloud infrastructure to deliver reliable and scalable computing services.
Below table outlines the key components of cloud computing, encompassing various service models
| Cloud Computing Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Offers fundamental computing resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking on-demand. |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Provides a platform for application development, offering tools and frameworks for deployment. |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis, eliminating local installation. |
| Public Cloud | Services provided by third-party vendors over the Internet to multiple users or businesses. |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated cloud environment for a single organization, hosted on-premises or by a third-party. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combination of public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. |
| Community Cloud | Shared infrastructure among several organizations with similar computing concerns. |
| Virtualization Technology | Enables multiple virtual instances on a single physical machine, optimizing resource utilization. |
Cloud Computing FAQs
How is cloud computing different from traditional IT infrastructure?
There is a difference between how cloud computing and traditional IT infrastructure are managed. Cloud hosting is managed by a storage provider who is responsible for all necessary hardware, takes security measures and maintains smooth operations. In contrast, traditional data centers require extensive internal controls that can be costly and time-consuming for organizations. Staff should ensure regular monitoring and maintenance of servers. B. Upgrades, threat protection, installation, etc. Cloud-based applications are autonomous. Traditional applications, on the other hand, consistently rely on a particular operating system to function.
Visit Cyfuture Cloud to know more
What is Cloud Computing, and how does it work?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. Instead of owning physical hardware, users access resources via the cloud provider’s infrastructure. This eliminates hardware maintenance costs, offers scalability, and allows on-demand access to resources. Data and applications are stored on remote servers, which can be accessed from any device with internet connectivity.
What are the flaws in cloud computing architectures?
Cloud computing systems are internet-based, and service failure is always an unfortunate possibility, and can happen for any number of reasons. Security and privacy is another structural risk that is always at risk when storing data and critical files with external service providers. Online components introduce potential vulnerabilities. Another drawback is that the cloud infrastructure is fully owned, managed, and monitored by the service provider, so the customer has limited and minimal control. Data movement, technical issues, weak connectivity, and data confidentiality risks are other specific drawbacks of cloud computing architectures.
Can you provide real-world examples of these cloud computing components in action?
The call for concrete examples of cloud computing components in use looks for situations in which important cloud technology components are used in real-world settings. The following examples highlight how companies and institutions use cloud-based technologies to streamline processes, improve security, and offer smooth services. For example, businesses might rely on a strong networking infrastructure to provide secure communications or use virtualization to reduce server resources. These illustrations give an idea of how cloud computing is revolutionizing a number of different fields and industries.
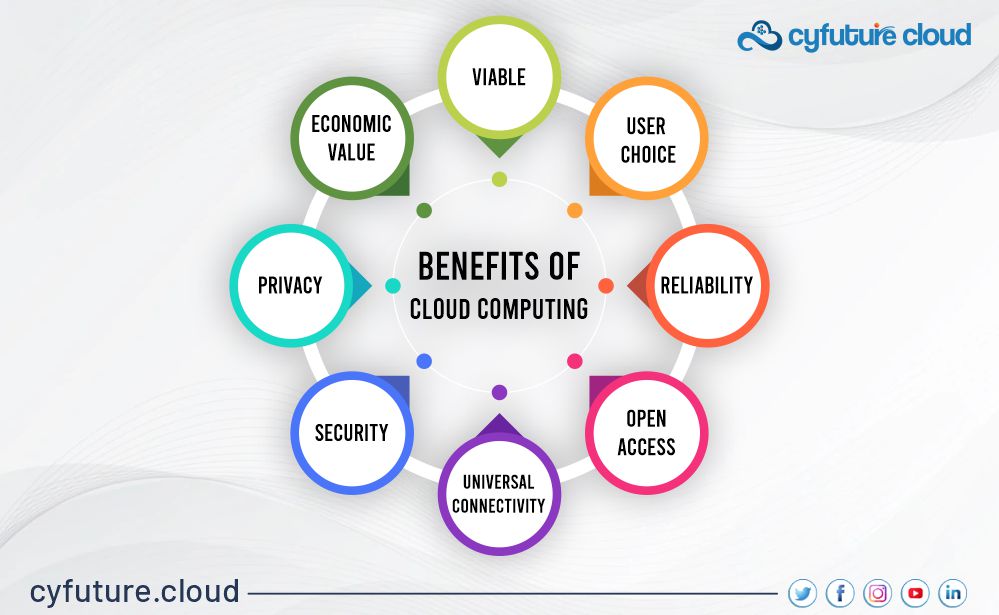
What are the benefits of using Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing provides several advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the need for buying and maintaining physical servers.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on business needs.
- Accessibility: Enables access to data and applications from anywhere.
- Data Security: Advanced security measures are implemented by the providers.
- Disaster Recovery: Offers reliable backup and recovery solutions.
These features make cloud computing ideal for businesses of all sizes.
Visit Cyfuture Cloud to know more
Recent Post
Send this to a friend

 Server
Colocation
Server
Colocation CDN
Network
CDN
Network Linux
Cloud Hosting
Linux
Cloud Hosting Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pricing
Calculator
Pricing
Calculator
 Power
Power
 Utilities
Utilities VMware
Private Cloud
VMware
Private Cloud VMware
on AWS
VMware
on AWS VMware
on Azure
VMware
on Azure Service
Level Agreement
Service
Level Agreement 



















